Distant-relative pointer genetic algorithm-based cross section size optimization method of steel truss structure
A technology of genetic algorithm and cross-section size, which is applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as lack, low computing efficiency, and premature convergence of standard genetic algorithms, so as to prevent individual degradation, ensure complete effects, and ensure The effect of global convergence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, technical scheme of the present invention is described in further detail:
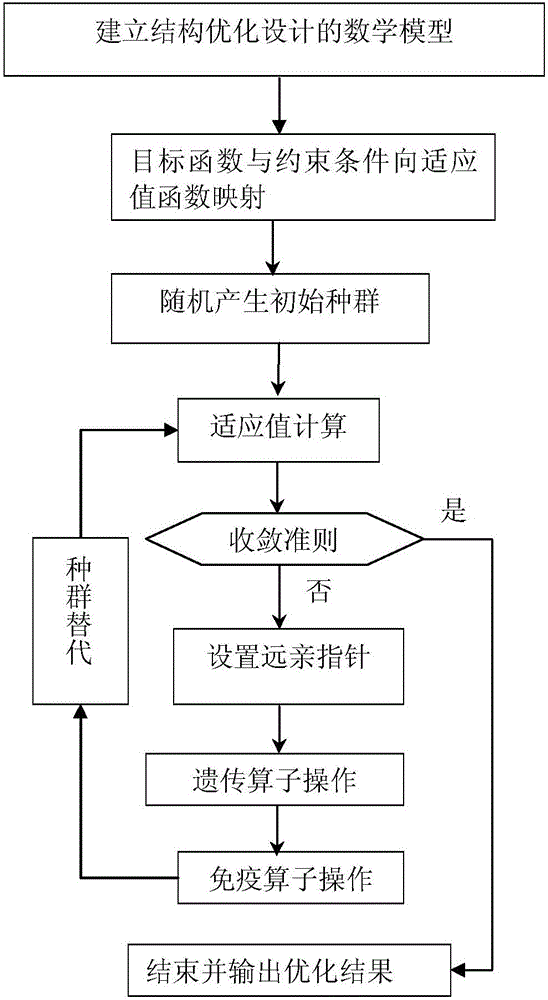
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for optimizing the cross-section size of steel truss structures based on the genetic algorithm of distant relative pointers, specifically includes the following steps,
[0030] Step 1, establish a mathematical model for structural optimization design; the model is as follows:
[0031]
[0032] Among them: W is the total mass of the steel truss structure system; A is the design variable, that is, the cross-sectional area of the member; L is the length of the member; ρ is the density of the member; β s is the constraint variable; β s a is the allowable constraint index; s.t. is the abbreviation of constraint condition; n is the total number of members of the structural system.
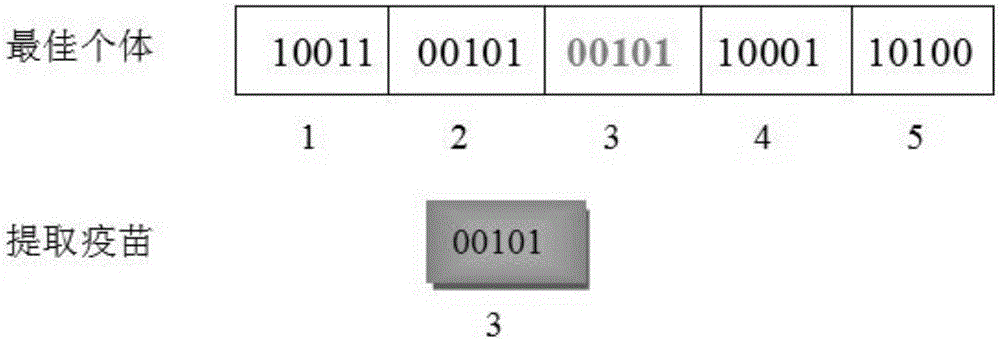
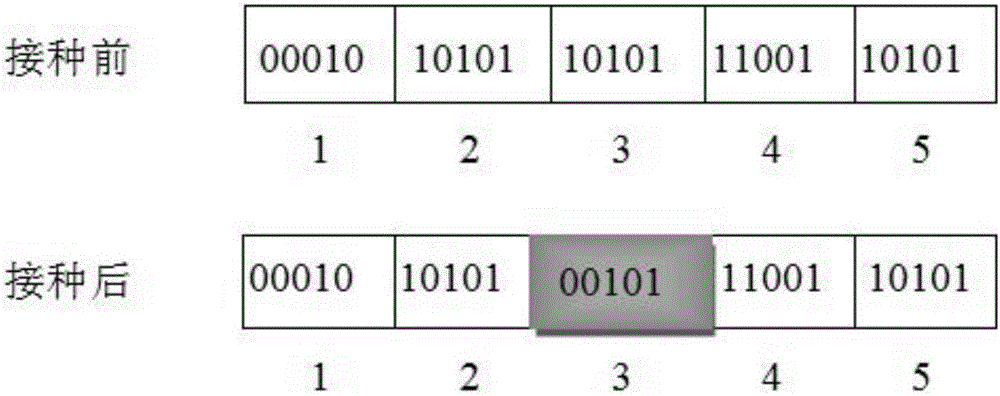
[0033] In step 2, the objective function and constraint conditions are mapped to the fitness value function, and then the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com