Human face recognition method and device for quickly processing human face shading
A face recognition and human processing technology, applied in the field of computer vision and pattern recognition, can solve problems such as not applicable to real-time scenes, SEC_MRF has high computational complexity, and cannot solve continuous occlusion well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
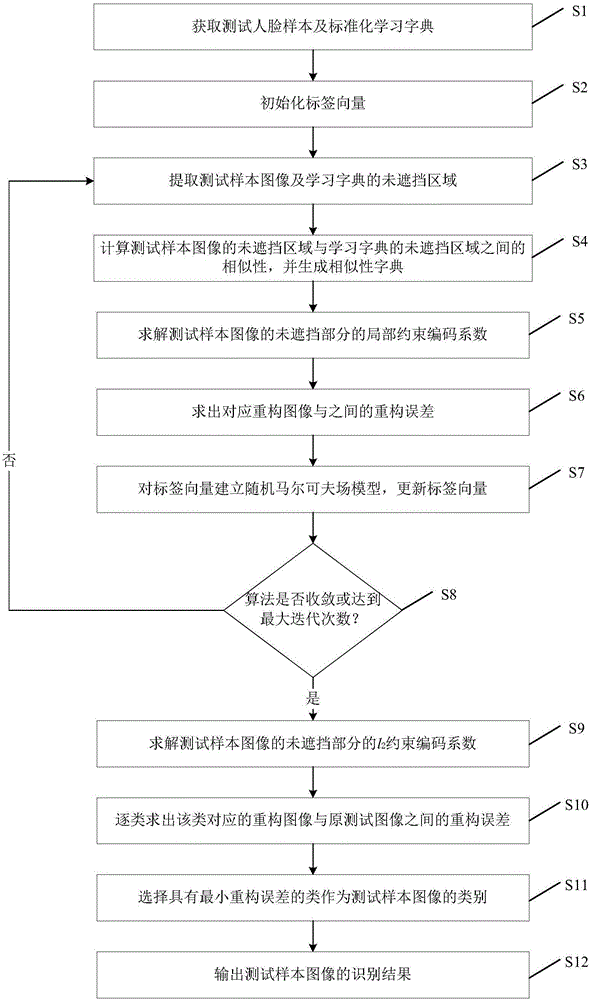
[0101] This embodiment discloses a face recognition method for quickly processing face occlusion, the purpose of which is to have a faster recognition speed under the premise of ensuring a high recognition success rate when recognizing faces with occlusion or noise pollution, so that Better face recognition. A schematic flow chart of a face recognition method for quickly processing face occlusion in this embodiment is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0102] S1. Obtain a test face sample and a standardized learning dictionary. Assuming that the sample image used for testing is y, the dimension is consistent with the training sample image, and it is also converted into an m×1 column vector, then Assuming that the sample images for training have class a, and each class has b sample images, then there are n=a×b sample images for training in total, and the length and width of each image are f and g respectively, then each image The d...
Embodiment 2
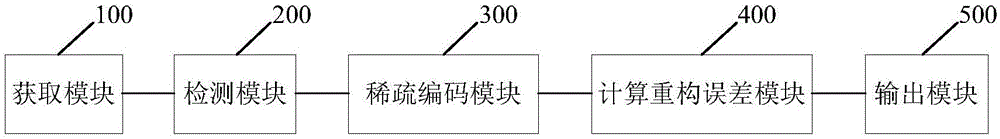
[0163]The present invention also provides a face recognition device for quickly processing face occlusion, a structural schematic diagram of a specific implementation is as follows image 3 As shown, the device includes:
[0164] Obtaining module 100, for obtaining test face sample and standardized learning dictionary;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com