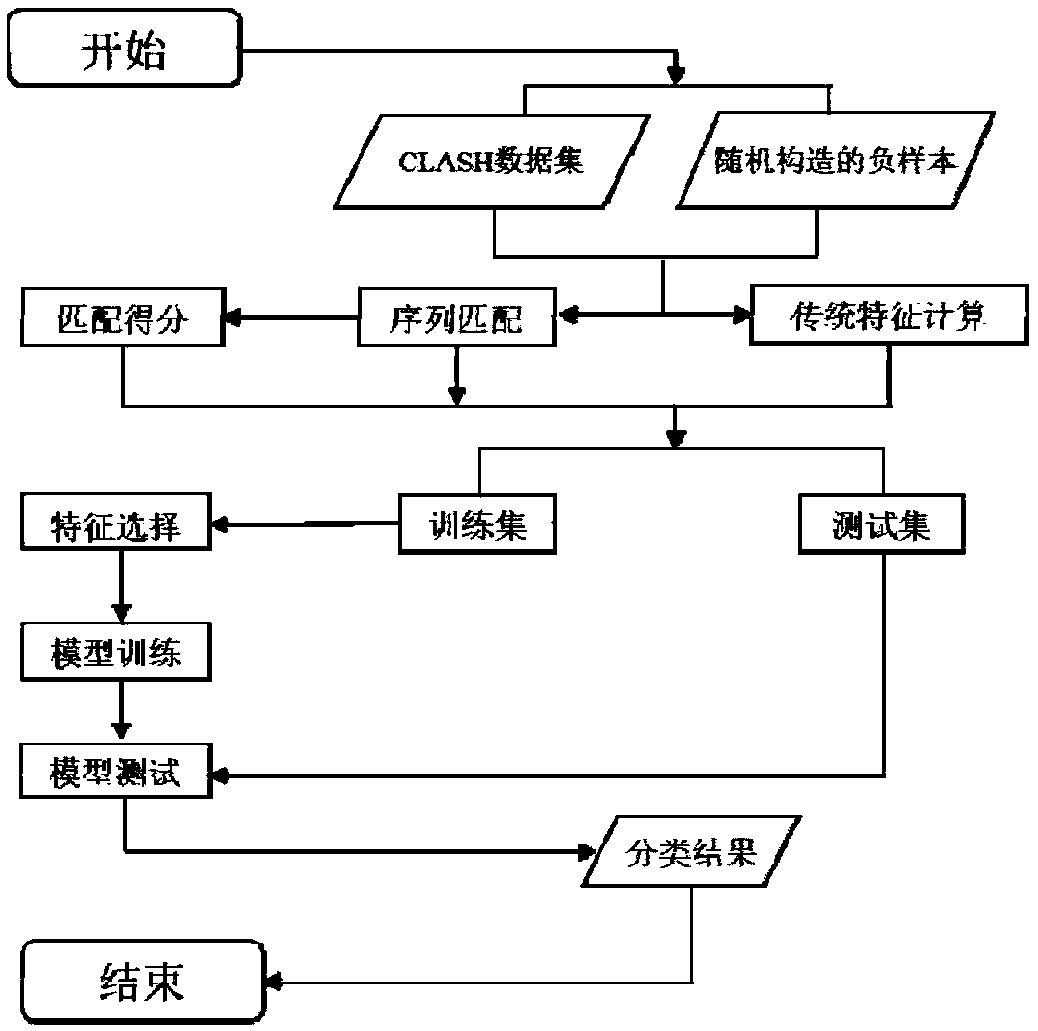
A Sequence Feature Analysis Method for Predicting miRNA Target Genes
A feature analysis, target gene technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and bioinformatics, can solve the problem of low specificity, achieve the effect of balancing differences, good prediction accuracy, and fast training and prediction speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1 Experimental method
[0062] 1. Experimental environment
[0063] Experimental instrument: ASUS N551JM computer
[0064] Programming software: Anaconda3 Spyder, Visual Studio 2013
[0065] Programming languages: Python 3.5, C++
[0066] 2. Positive and negative samples and their forms
[0067] The positive sample is selected from the CLASH experimental data set, with a total of 18514 pieces of data, each piece of data contains the following information: miRNA name, miRNA sequence, mRNA name to which the target site belongs (taken from the ENSEMBL database), and the target site is on the mRNA The start position of the target site, the end position of the target site on the mRNA, and the sequence of the target site.
[0068] Because the number of target sites that can be combined with miRNA is definitely much smaller than the number of target sites that cannot be combined with it, the positive samples are removed by randomly matching the miRNA and target ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2 Sequence feature analysis of predicted miRNA target genes
[0098] 1. Based on miRNA-target site pairing
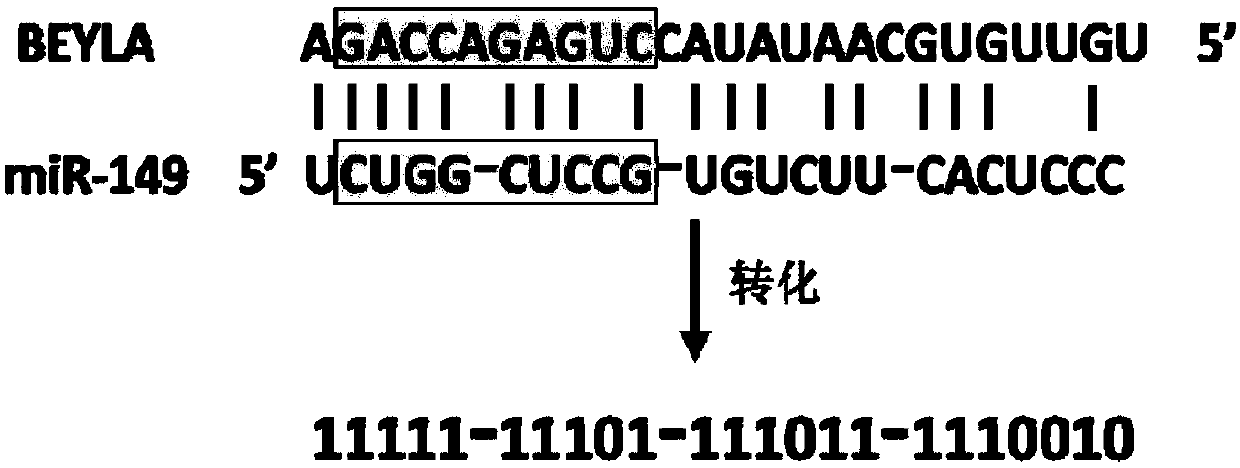
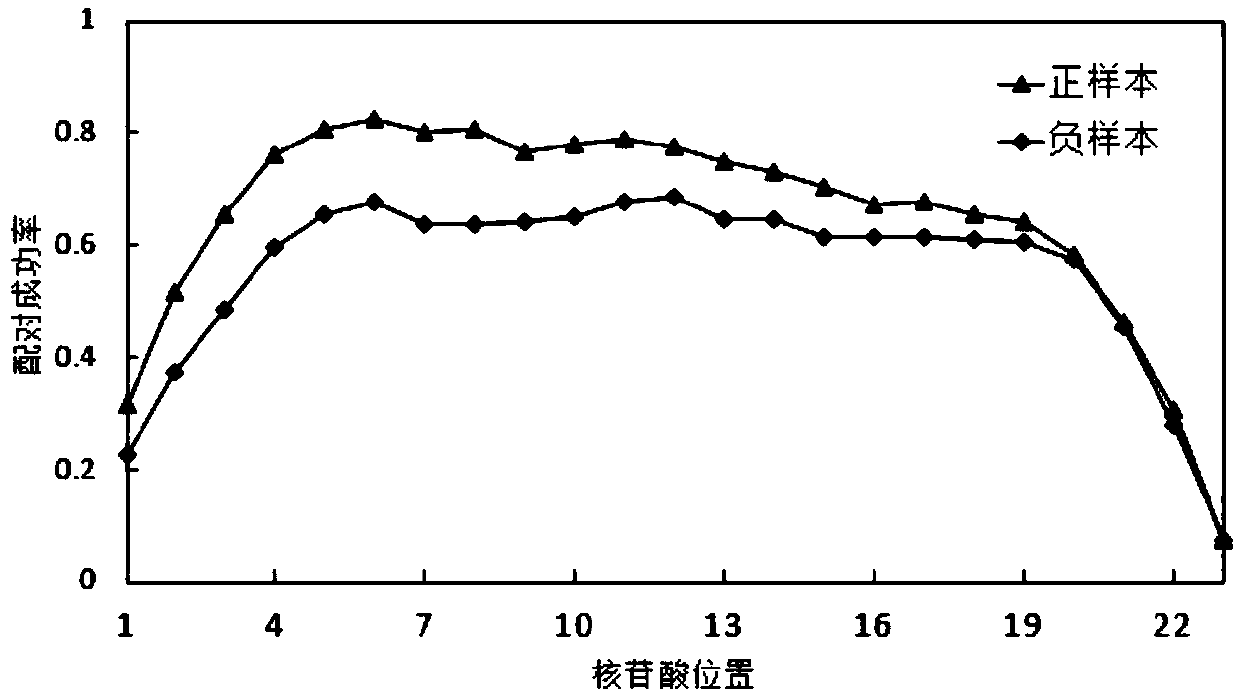
[0099] miRNAs are not perfectly matched to their target sites, and matches vary widely. According to the pairing situation of miRNA and its target site in the sample set, this method expresses the double strand of each miRNA combined with the target site as a binary sequence composed of "0" and "1", and analyzes the binary sequence formed , the specific process is as figure 2 As shown, the shaded part is the "seed area".
[0100] exist figure 2 Among them, the BEYLA sequence is the target site sequence corresponding to miR-149. First, the improved Smith-Waterman method was used to perform sequence matching according to the principle of base A:U and G:C complementary pairing, allowing G:U mismatches. Starting from the first nucleotide at the 5' end of the miR-149 sequence, it is compared with each nucleotide of the BEYLA sequence. If it matches, it ...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Example 3 Model construction and method for predicting miRNA target genes
[0134] Based on the above research and analysis, the method and model for predicting miRNA target genes were constructed, as follows:
[0135] 1. Collect data sets (collect miRNAs with high reliability and target site data that can be combined with them), and construct positive and negative samples
[0136] Select the CLASH data set as a positive sample, and construct a negative sample based on the data set, randomly pair the miRNAs in the CLASH data set with the target site sequence, delete the positive samples, and then randomly select 18514 entries from the remaining data set as negative samples ;
[0137](1) Select the positive sample data from the CLASH data set, the positive sample data includes miRNA name, miRNA sequence, mRNA name to which the target site belongs, the starting position of the target site on the mRNA, and the position of the target site on the mRNA. Termination position...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com