Device for in-situ biological monitoring by using mussels, clams and snails
A bio-monitoring and mussel technology, applied in the field of in-situ bio-monitoring devices, can solve problems such as threats to people's life safety, difficulty in sampling, and chemical detection cannot fully meet environmental monitoring, and achieve the effect of avoiding proliferation problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
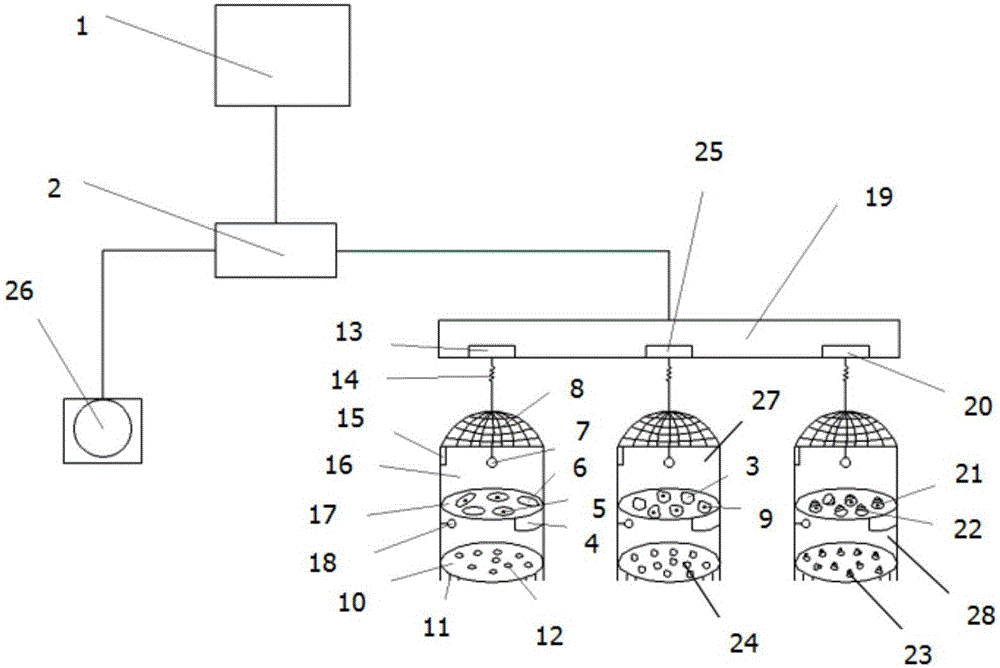
[0023] Below, combined with figure 1 And embodiment, the specific embodiment of the present invention is described in detail:
[0024] Such as figure 1 It shows a device for in-situ biological monitoring using mussels, clams and snails of the present invention, including the following components: computer monitor 1, signal receiving device 2, omnidirectional camera 26, floating plate 19, placement cage 16 , placing cage two 27, placing cage three 28; described floating plate 19 connects three placing cages by telescopic rope 14, and described placing cage one 16, placing cage two 27 and placing cage three 28 are three completely identical cages of structure , its structure is made up of wide net 4, camera one 7, cage top cover 8, bottom net 10, spikes 11, temperature controller 15, sieve 17, camera two 18, and places in described placement cage one 16 Mussels 6, and adopt random sampling to install sensor one 5 on mussels 6, described mussels 6 is sieved by sieve 17 and muss...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com