Monocular multi-target identification and positioning method based on artificial mark
A recognition method and multi-target technology, which is applied in the field of monocular multi-target recognition and positioning based on artificial signs, can solve the problems of loss of object depth information, difficulty in realizing computing power, and increased cost, and achieve high real-time performance and simple solutions Easy-to-do, low-time-complexity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
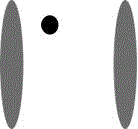
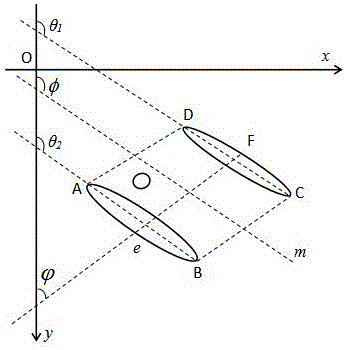
[0025] The artificial sign designed by the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, the logo is composed of 2 ellipses and 1 circle. The endpoints of the long axis of the ellipse form the feature points, and the circles in the logo are used to determine the order of the feature points.
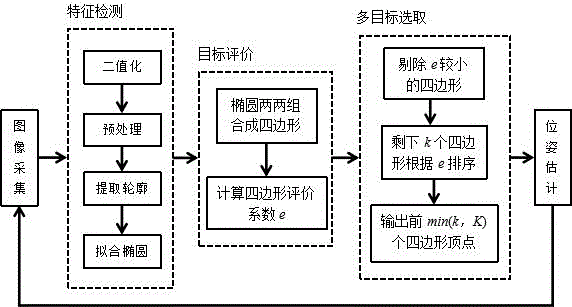
[0026] The present invention provides a single-eye multi-target recognition and positioning method, the process is as follows figure 2 shown, including:
[0027] S1. Binarize the original image according to the set color to obtain a binary image;
[0028] S2. Extract the contour after preprocessing the binary image;
[0029] S3. Perform ellipse fitting on each contour, and eliminate ellipses whose sha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com