LTE downlink resource scheduling method for minimizing compression loss
A technology of compression loss and resource scheduling, applied in electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve problems such as CQI drop, low CQI, and uneven resource allocation, and achieve the effects of reducing compression loss, improving compression efficiency, and high throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
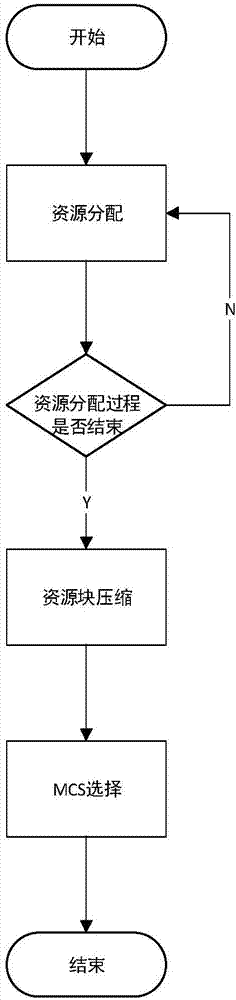
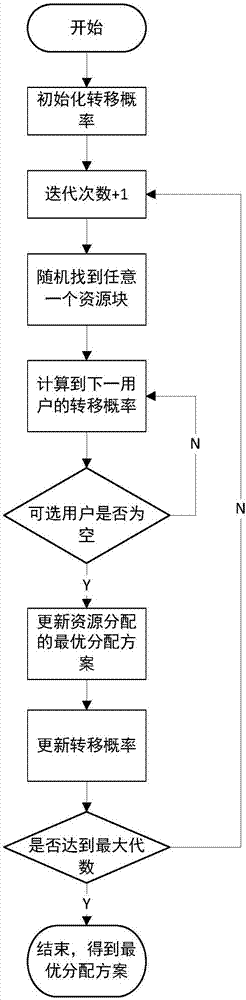
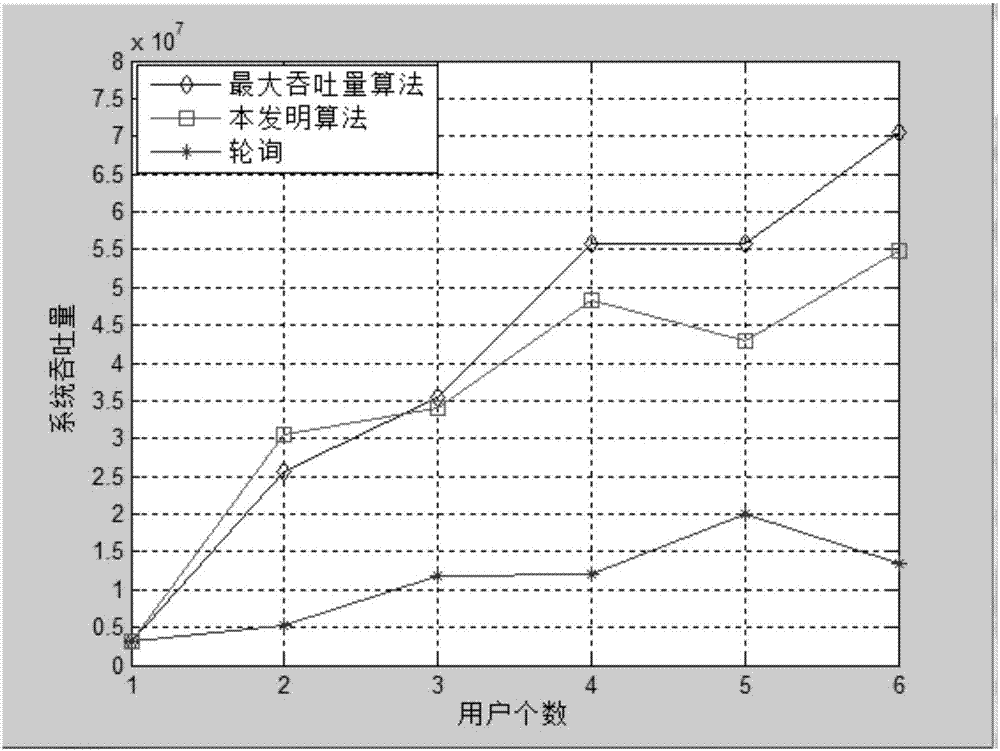
[0030] The embodiments and effects of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0031] Suppose the number of resource blocks in the system is N, the total number of users is M, and the rate obtained by each user in each scheduling cycle is R k k=1,2,...,M, assuming that the base station can obtain the channel state information CQI value of the user terminal through the feedback channel, and dynamically allocate resource blocks for each user according to the feedback value.
[0032] Define ρ k,n Indicates the occupancy of resource blocks, when ρ k,n =1, it means resource block n is occupied by user k, when ρ k,n =0 means that resource block n is not occupied by user k.
[0033] define c k,n Represents the number of bits allocated by user M on resource block n, defines T as the throughput of the system, and maximizes the total throughput T of the system through the dynamic allocation of resource blocks, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com