Starting method for cold-crucible vitrification treatment of radioactive liquid waste
A technology of radioactive waste liquid and glass solidification, which is used in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering and other directions to achieve the effect of simple start-up process, no radioactive leakage and improved safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
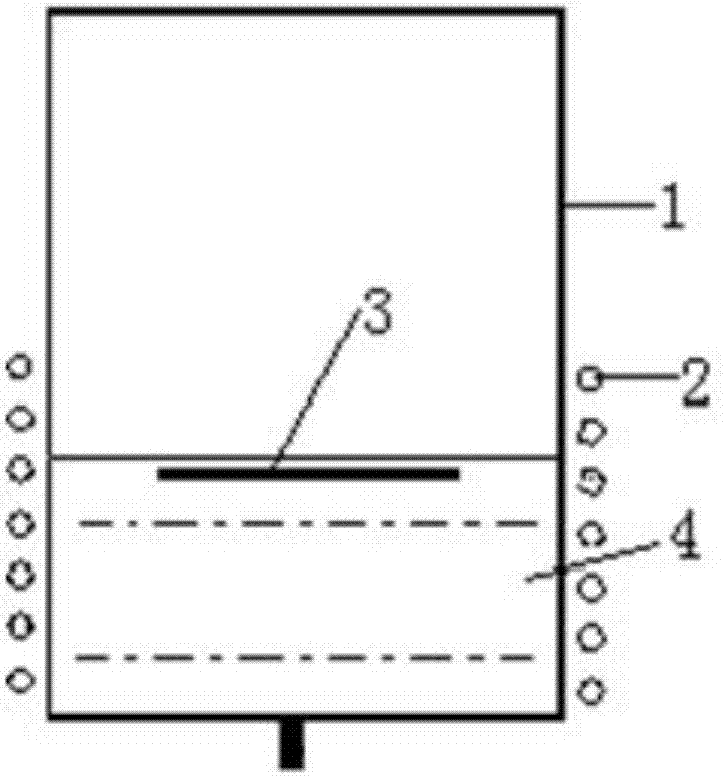
[0035] First, the starting glass 4 is put into the cold crucible 1 of Φ300mm, and the starting glass 4 added is the starting glass 4 whose resistivity should be 1-10Ωcm at 1100-1200°C. The height of adding start glass 4 is 1 / 3 position of induction coil 2. Then put into the graphite ring 3 of 40g, Φ150mm; then put into the starting glass 4 to cover the graphite ring 3, as figure 1 As shown, the starting glass 4 added to cover the graphite ring 3 has a thickness of 1 cm; the frequency of the high-frequency power supply of the cold crucible 1 is adjusted to the starting frequency of the graphite ring 3-start with a power of 30kW, and then increase by 5kW every ten minutes until 70kW; the graphite ring 3 is gradually heated until it burns, and after the graphite ring 3 starts to burn, the 6m 3 Oxygen is introduced into the cold crucible 1 at a rate of / h, and the graphite burns to release a large amount of heat to melt the surrounding glass. After about 30 minutes, the graphite...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, and the difference is that firstly, after putting the starting glass 4 into the Φ300mm cold crucible 1, the height of the starting glass 4 is 3 / 4 of the position of the induction coil 2, and the 40g, Φ225mm Graphite sheet, the whole process took about 2h.
Embodiment 3
[0039] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, and the difference is that firstly, after putting the starting glass 4 into the Φ300mm cold crucible 1, the height of adding the starting glass 4 is 3 / 5 of the position of the induction coil 2, and the whole process takes about 1h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com