Low-complexity maximum likelihood approximate q-ary LDPC (Low-Density Parity-Check) code decoding method
A LDPC code, low-complexity technology, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve the problem of non-convergence of iterative decoding algorithm, and achieve the effect of low-complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings.
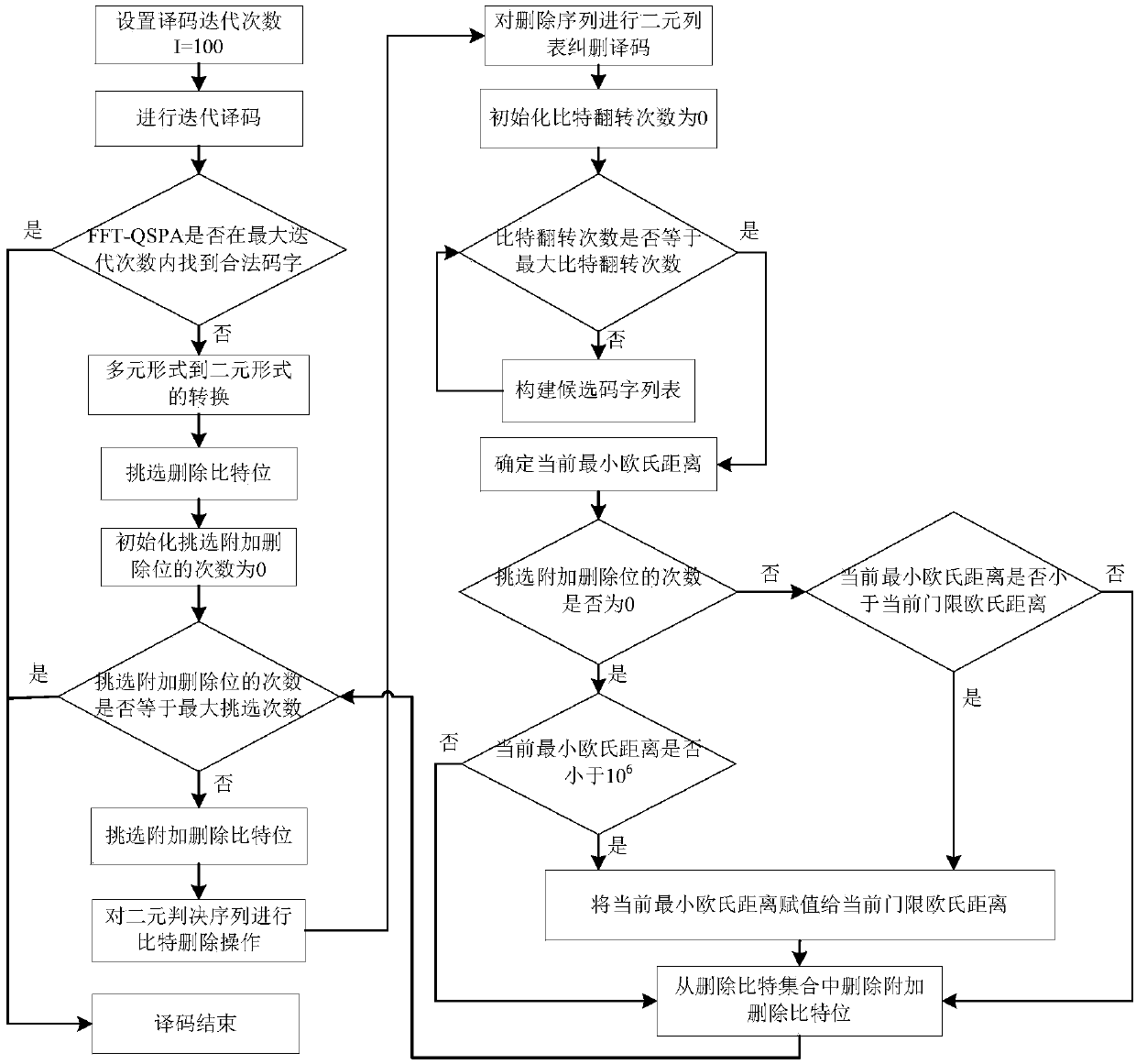
[0049] Reference attached figure 1 , The implementation method of the present invention will be further described.
[0050] Step 1. Set the maximum number of decoding iterations I=100.
[0051] Step 2. Perform iterative decoding.
[0052] After binary phase shift keying BPSK modulation is performed on the multi-element low-density parity-check LDPC code, the modulated information is sent to the additive white Gaussian noise AWGN channel for noise processing to obtain the noise-added message.
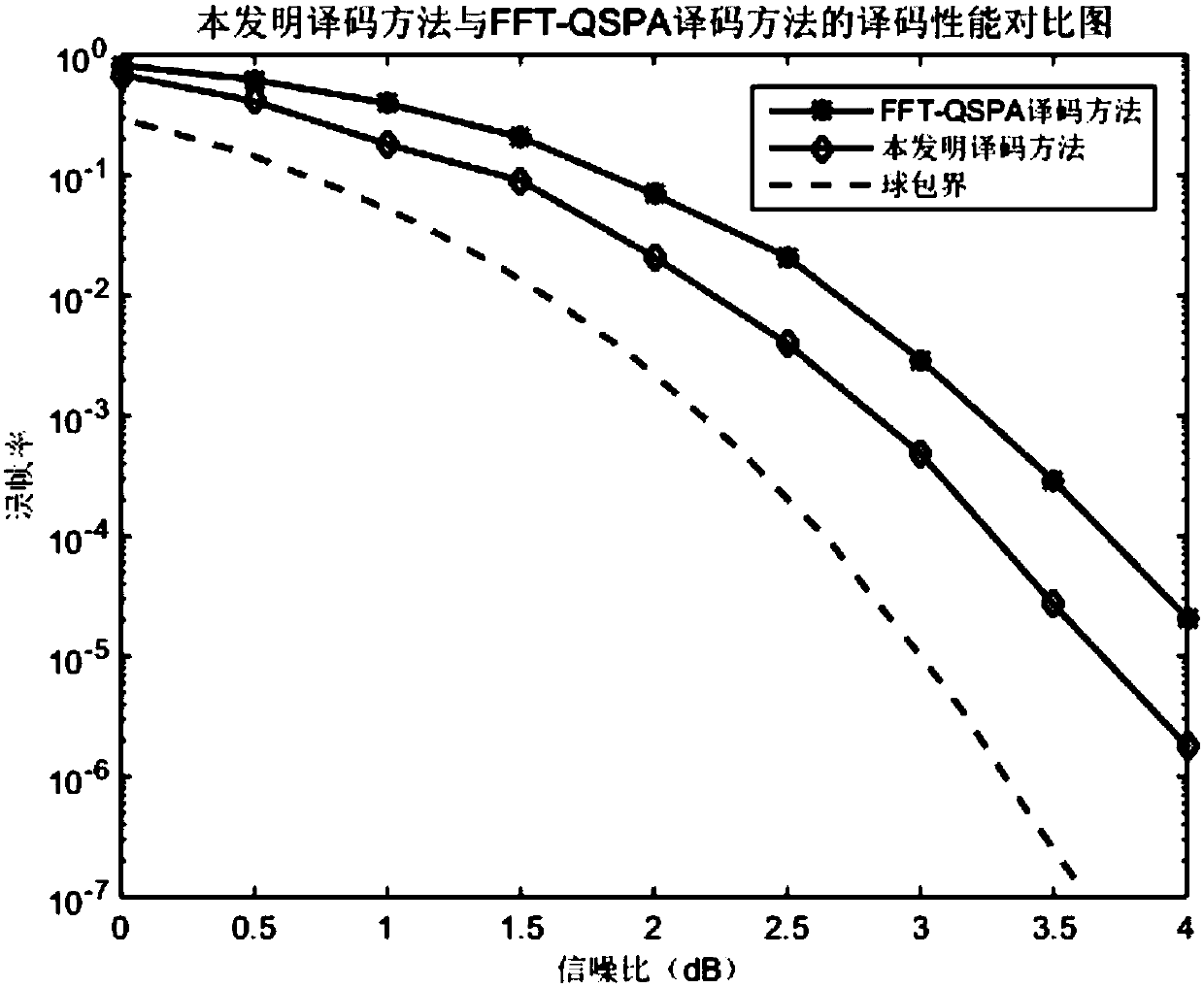
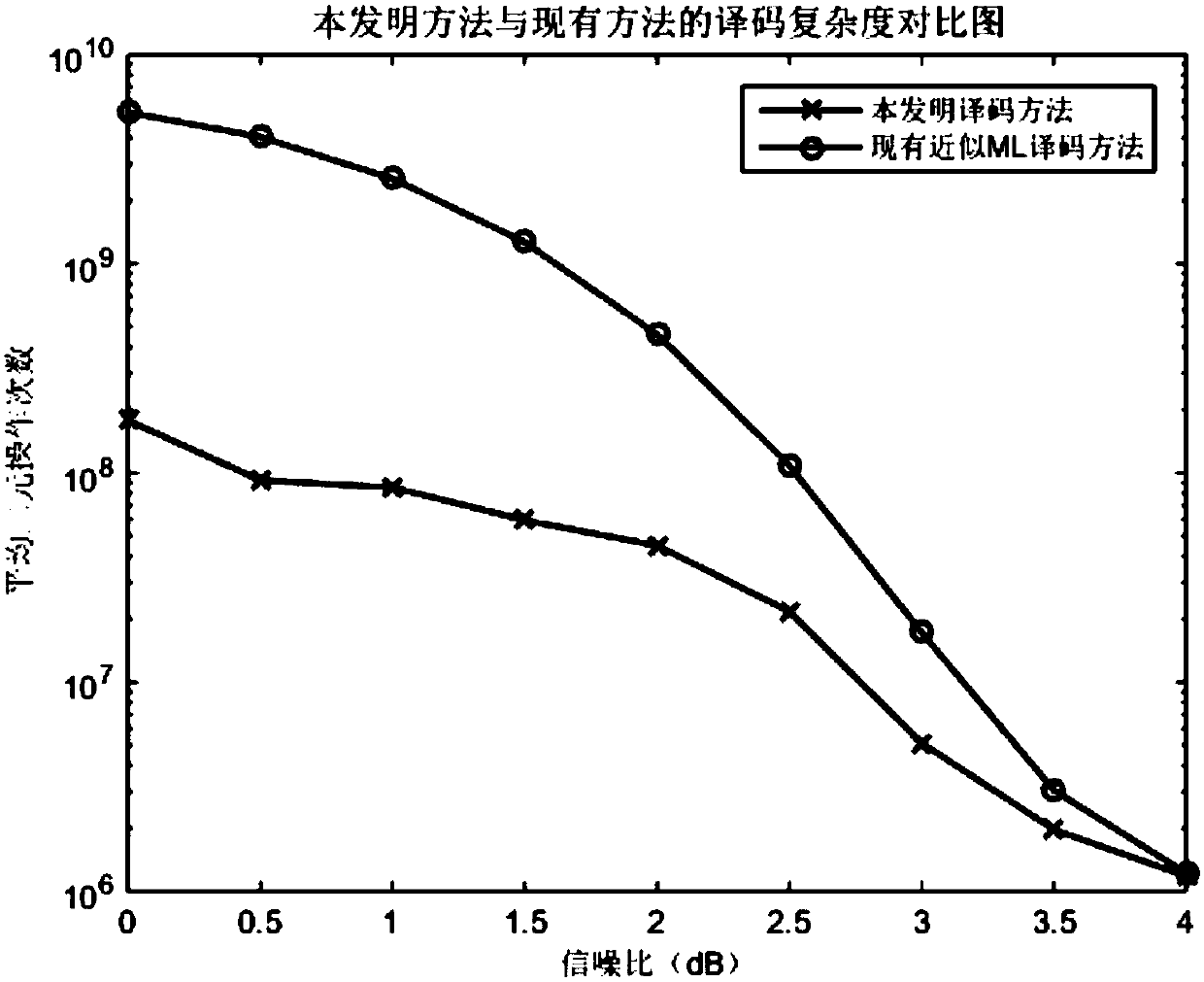
[0053] The sum-product algorithm FFT-QSPA based on fast Fourier transform is used to iteratively decode the noise-added message.
[0054] Step 3. Determine whether a legal codeword is found within the maximum iteration times of the sum-product algorithm FFT-QSPA based on the fast Fourier transform, if yes, perform step (19), otherwise, perform step (4).
[0055] The legal codeword refers to a sequence t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com