Corneal astigmatism analysis method for corneal topography diagnosis
An analysis method and technology of corneal topography, which are applied in the fields of diagnosis, eye testing equipment, medical science, etc., can solve the problems that are not suitable for quantitative evaluation of irregular astigmatism, and cannot provide axial information of corneal astigmatism distribution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Calculation and analysis of corneal astigmatism in ordinary people:
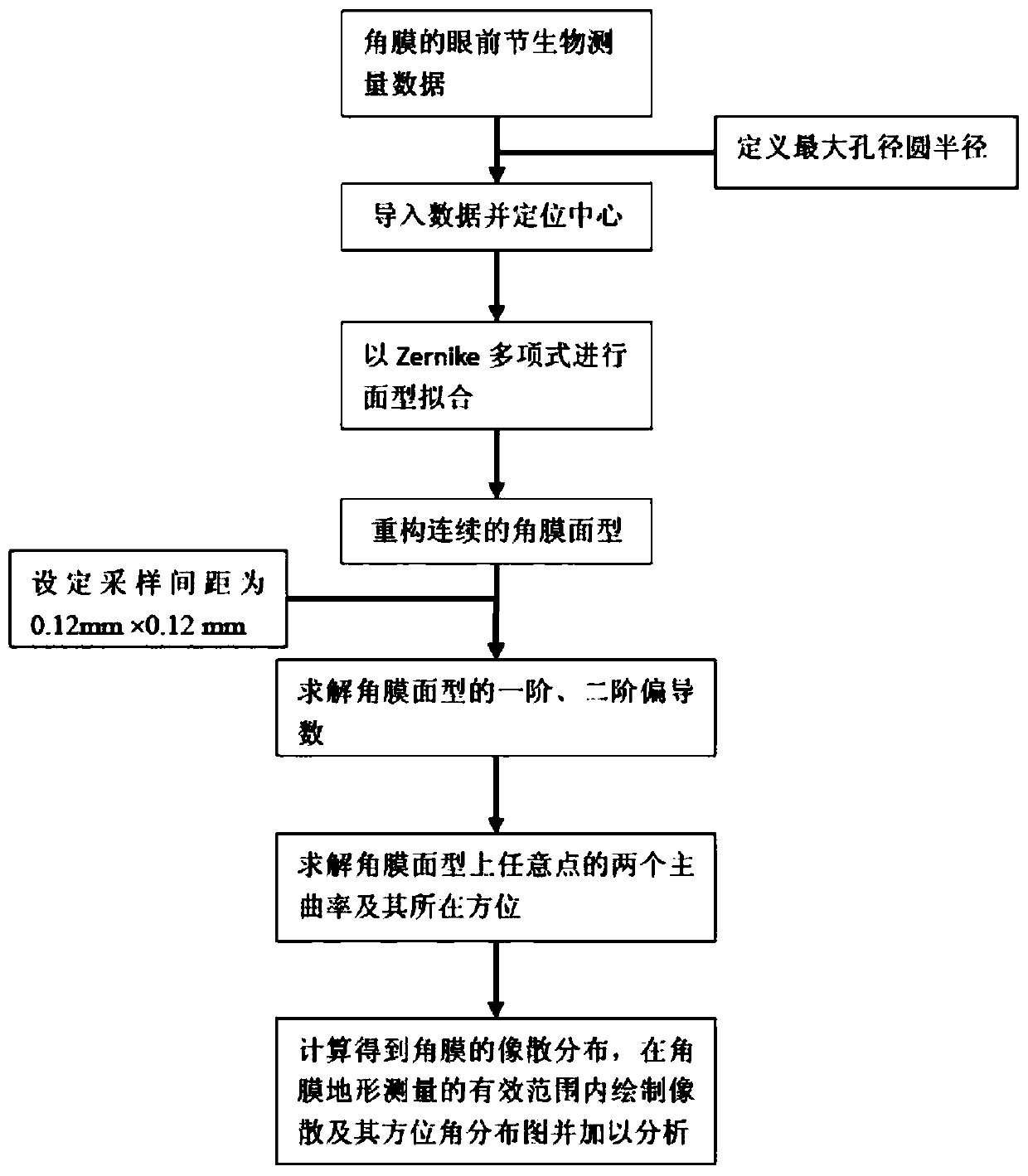
[0033] (1) Collect the anterior segment biometric data of ordinary human eyes to obtain the full corneal height distribution, and obtain the pupil eccentricity from the coordinates of the corneal topographic positioning measurement center and the pupil measurement center;
[0034] (2) Define the maximum aperture circle radius including all effective measurement points of the cornea;
[0035] (3) Using the least squares method, Zernike polynomials were used to fit the height data of all corneal measurement points within the radius of the aperture circle, and the Zernike radial order was 20;
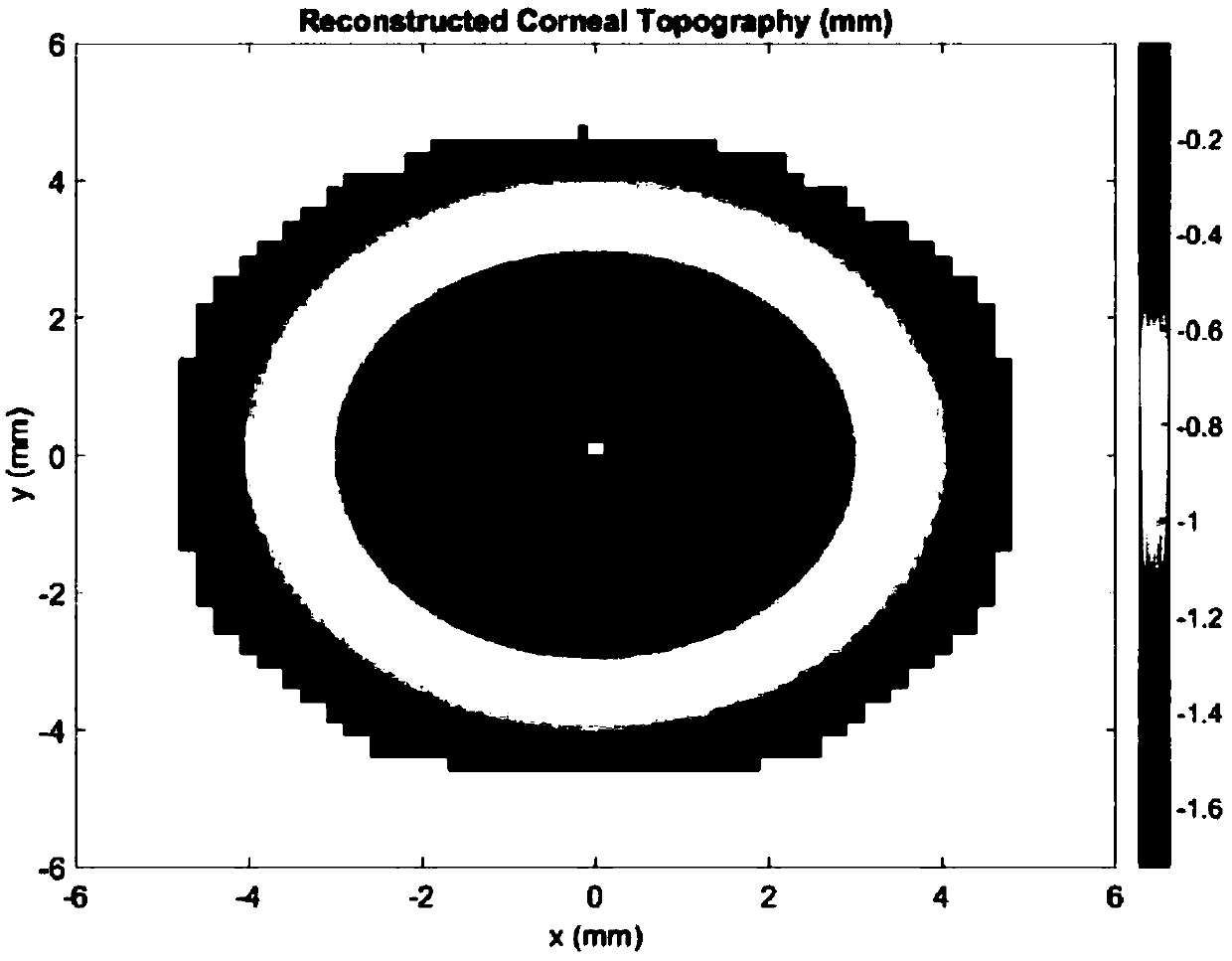
[0036] (4) Reconstruct the continuous and complete corneal surface shape according to the Zernike polynomial coefficients obtained by surface fitting (see figure 2 ), the sampling distance of the surface is 0.12mm*0.12mm;
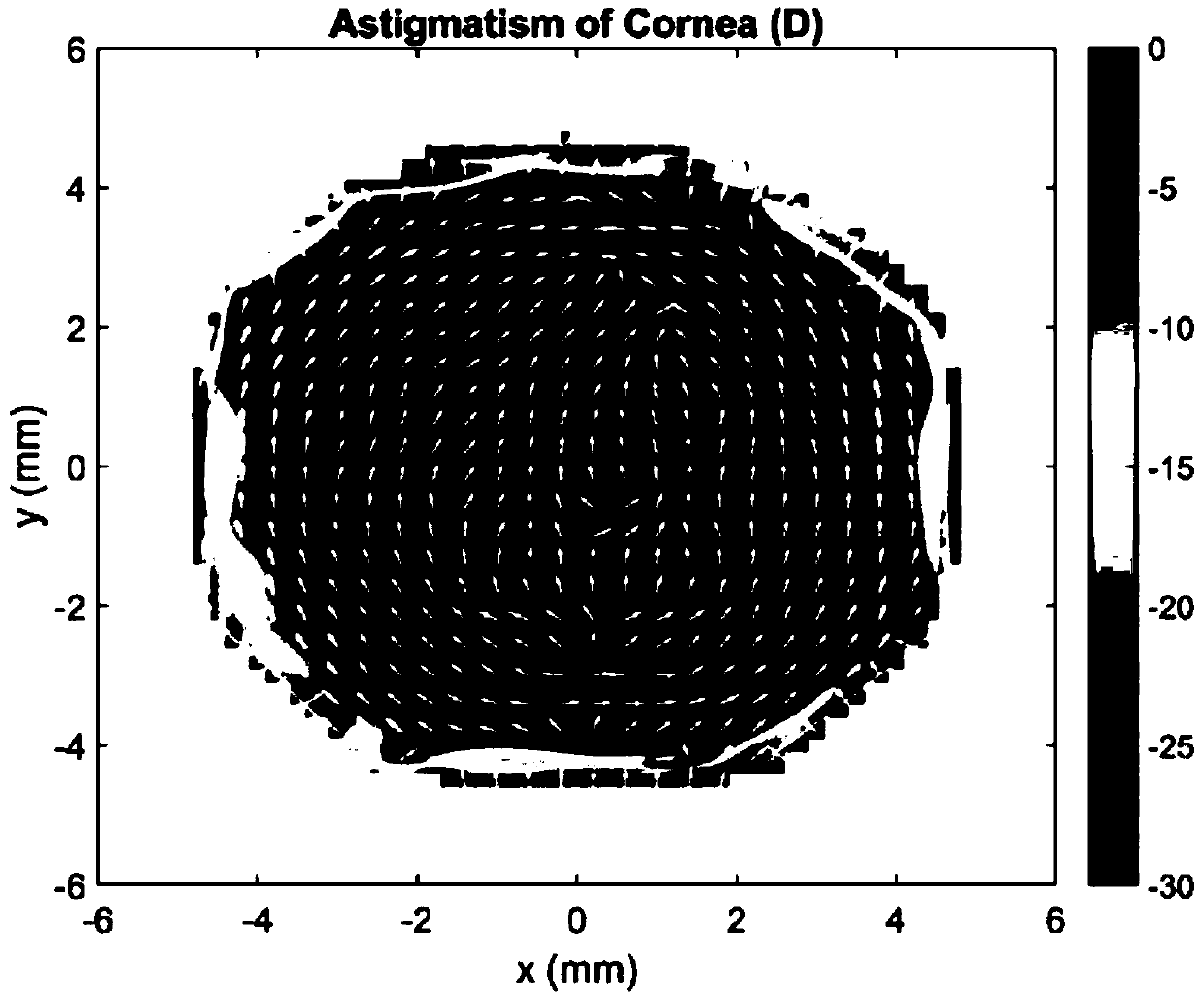
[0037] (5) Solve the first-order and second-order partial derivative expressions of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Calculation and analysis of corneal astigmatism after wearing orthokeratology lenses:
[0043] (1) Collect the biometric data of the anterior segment of the patient wearing orthokeratology lenses to obtain the full corneal height distribution, and obtain the pupil eccentricity from the coordinates of the corneal topographic positioning measurement center and the pupil measurement center;
[0044] (2) Define the maximum aperture circle radius including all effective measurement points of the cornea;
[0045] (3) Using the least squares method, Zernike polynomials were used to fit the height data of all corneal measurement points within the radius of the aperture circle, and the Zernike radial order was 20;
[0046] (4) According to the Zernike polynomial coefficients obtained by surface fitting, a continuous and complete corneal surface shape was reconstructed, and the sampling distance of the surface shape was 0.12mm*0.12mm;
[0047] (5) Solve the first-order and secon...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Calculation and analysis of astigmatism in untreated keratoconus:
[0054] (1) Select the keratoconus case, collect the anterior segment biometric data of the keratoconus case, obtain the whole corneal height distribution, and obtain the pupil eccentricity from the coordinates of the corneal topographic positioning measurement center and the pupil measurement center;
[0055] (2) Define the maximum aperture circle radius including all effective measurement points of the cornea;
[0056] (3) Using the least squares method, Zernike polynomials were used to fit the height data of all corneal measurement points within the radius of the aperture circle, and the Zernike radial order was 20;
[0057] (4) According to the Zernike polynomial coefficients obtained by surface fitting, a continuous and complete corneal surface shape was reconstructed, and the sampling distance of the surface shape was 0.12mm*0.12mm;
[0058] (5) Solve the first-order and second-order partial deriv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com