Regular overlapped sub-array-based adaptive beamforming method
An adaptive beam and sub-array technology, applied in the field of radar, can solve the problems of increasing beam sidelobe, reducing output signal-to-interference-noise ratio, shrinking, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing beam sidelobe and improving output signal-to-interference-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
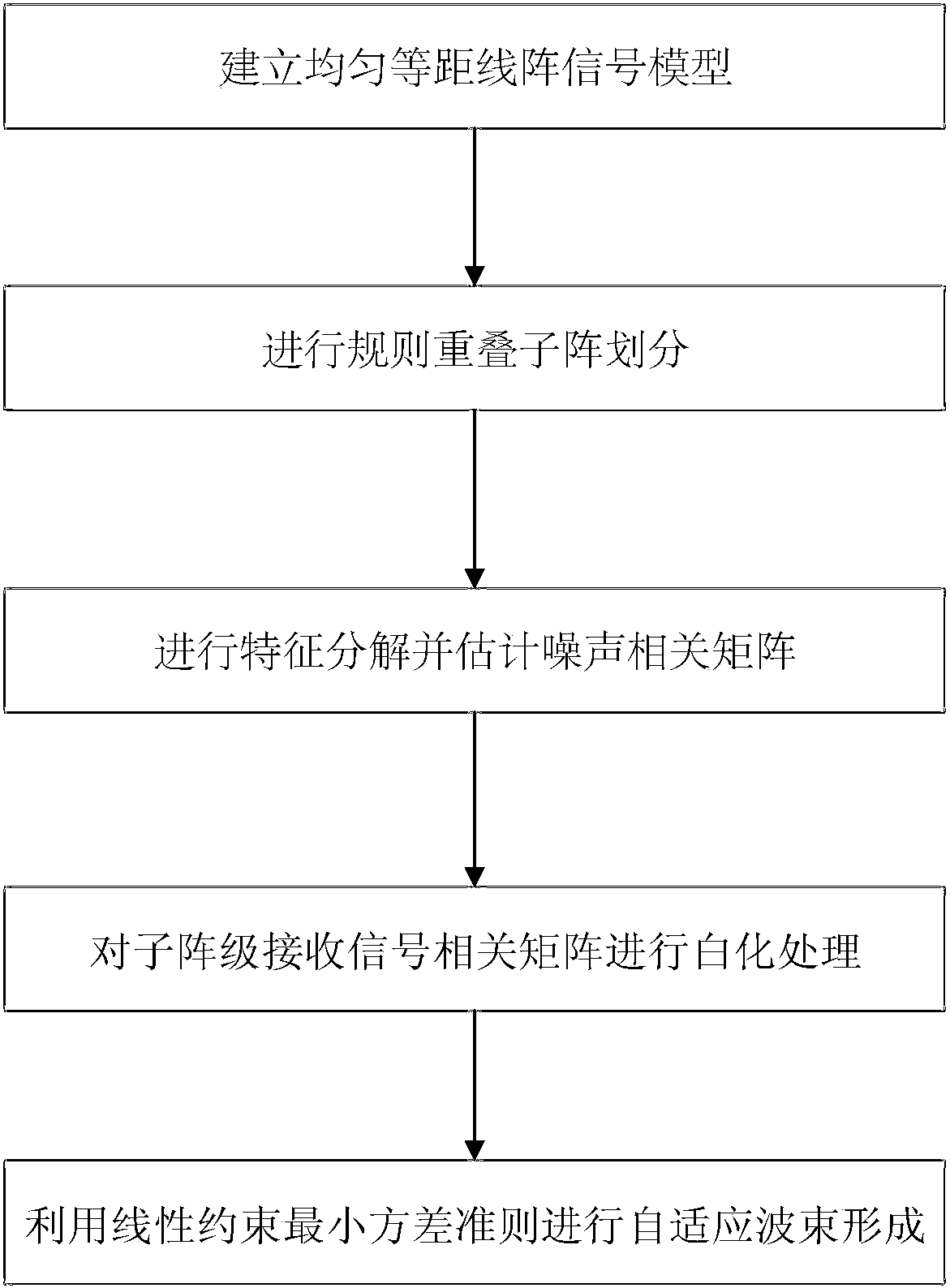
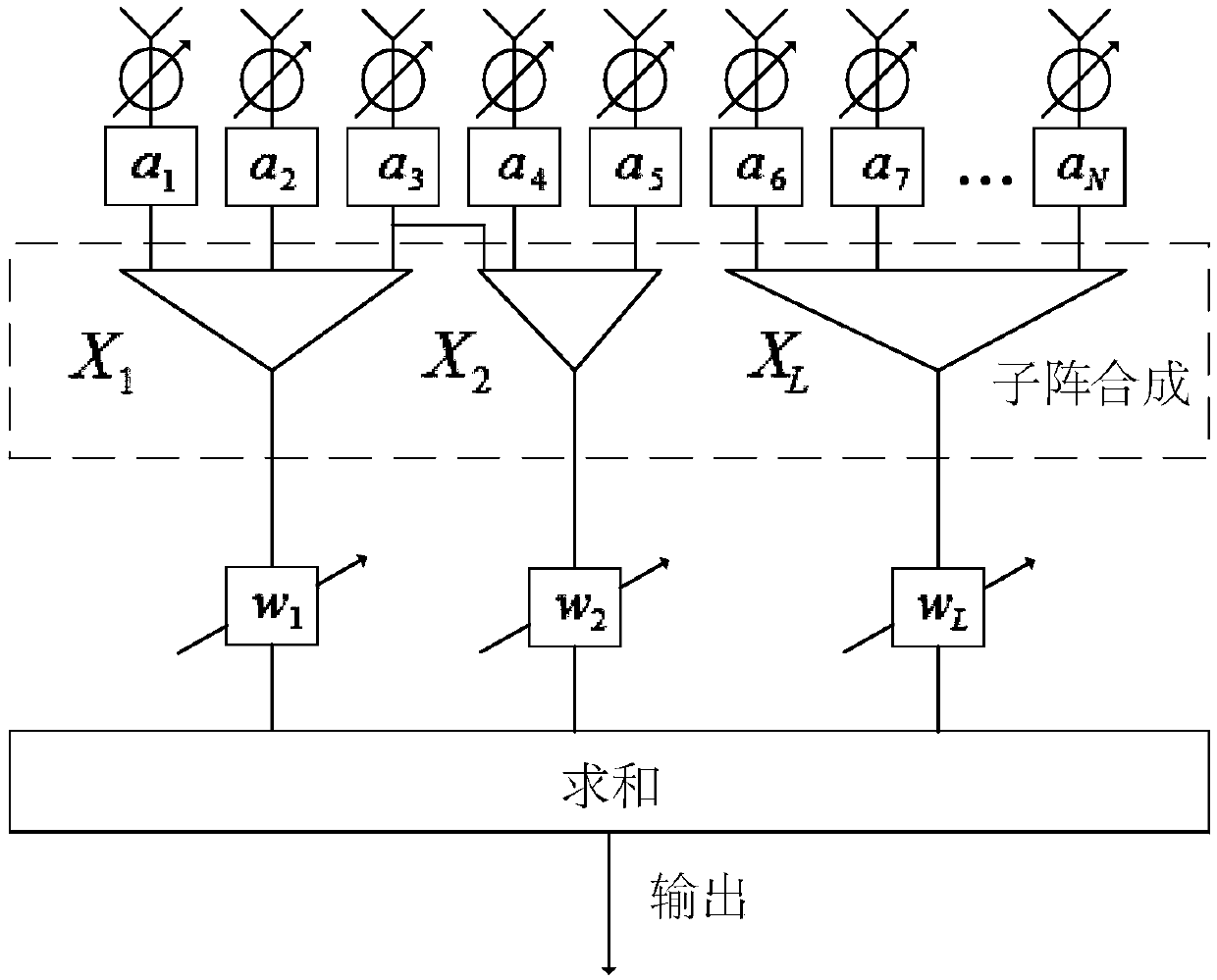
[0032] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention include as follows:
[0033] Step 1: Establish a received signal model X(t) at the element level of the uniform and equidistant linear array.
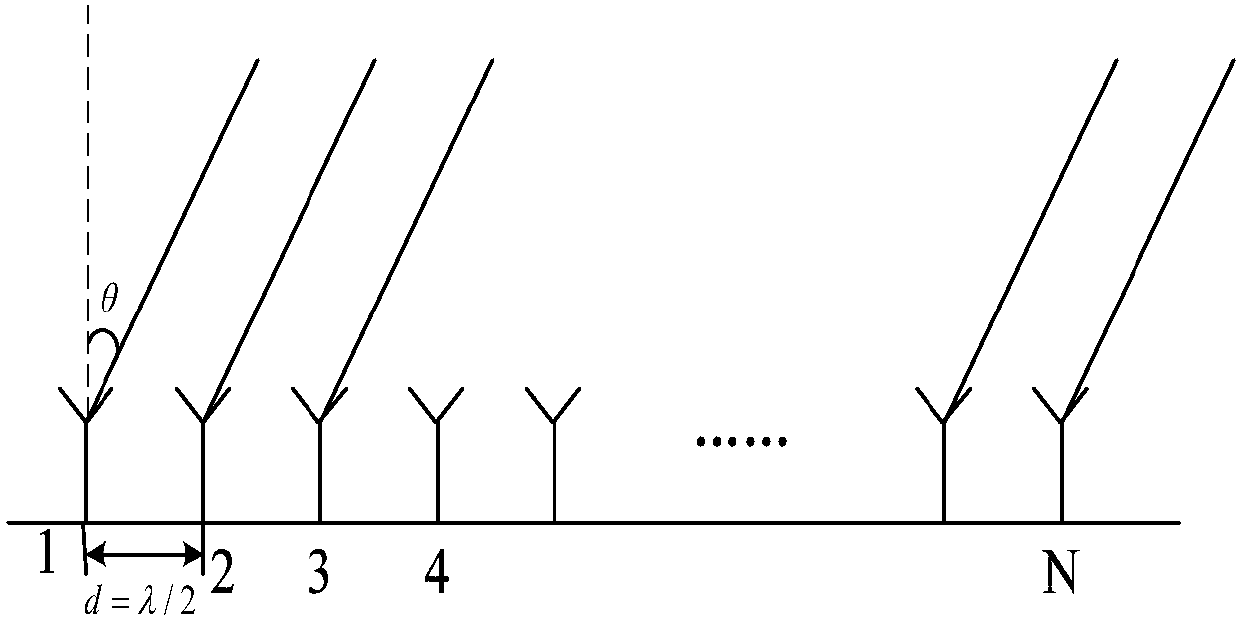
[0034] refer to figure 2 , the specific implementation of this step is as follows:
[0035] The receiving signal model is established by using an N-element uniform equidistant line array, the array element spacing d=λ / 2, and λ is the desired signal wavelength: 1a) Assume that the narrow-band far-field incident signal is s(t), and the incident direction is θ 0 , taking array element 1 as the reference point, the expected signal received by the array is expressed as:
[0036]
[0037] in, Indicates the signal received by the i-th array element, i∈{1,2,...i,...N}; Denotes the desired signal steering vector received by the array.
[0038] 1b) Assuming that the N×1-dimensional noise signal received by the selected uniform equidistant linear array is n(t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com