Tibial tubercle osteotomy guide
A guide, osteotomy technology, applied in the direction of bone drill guidance, surgery, skull, etc., can solve the problems of using complex multiple units, not suitable for anatomical structures, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
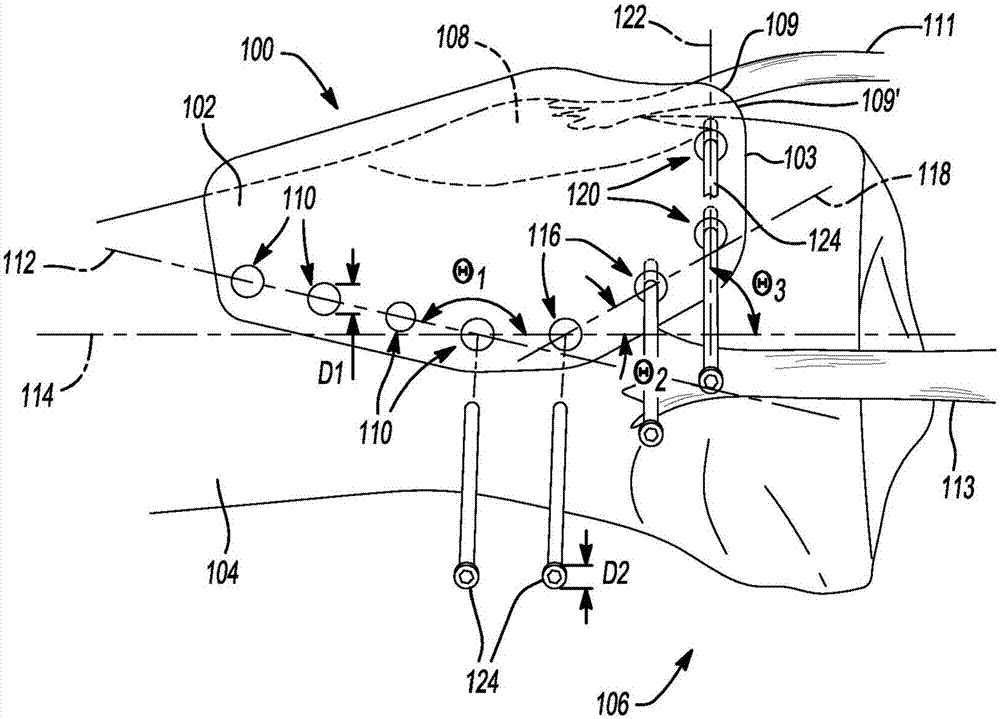
[0058] In Example 1, a patient-specific system for tibial osteotomy can include a patient-specific guide comprising: a guide body defining: a bone having a bone-engaging surface an articulation portion, the bone-engaging surface conforming as a negative surface to the corresponding surface of the patient-specific tibia; and a guide portion, which guides the surgical instrument to a specific location on the patient-specific tibia, wherein, during the pre-operative planning phase The bone-engaging surface and the guide portion are constructed during construction; a patient-specific implantable wedge having a predetermined shape, wherein the wedge can be constructed during a pre-operative planning stage; and a plurality of pins.
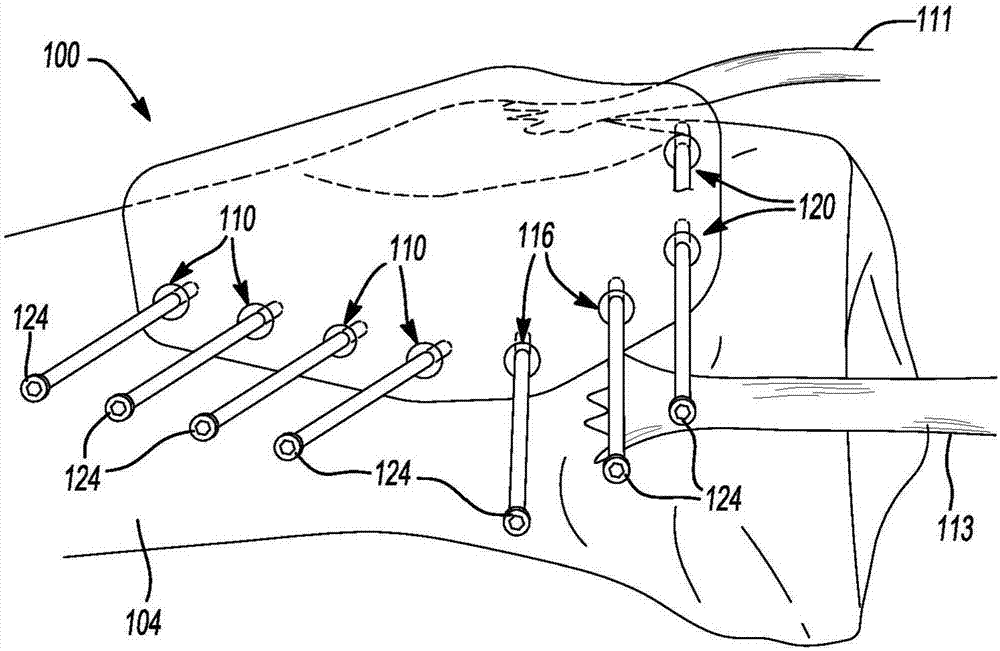
[0059] In Example 2, the patient-specific system according to Example 1 can optionally be configured such that the guide portion can include a plurality of apertures defined by the guide body, wherein the plurality of apertures can be configured to The ...
example 7
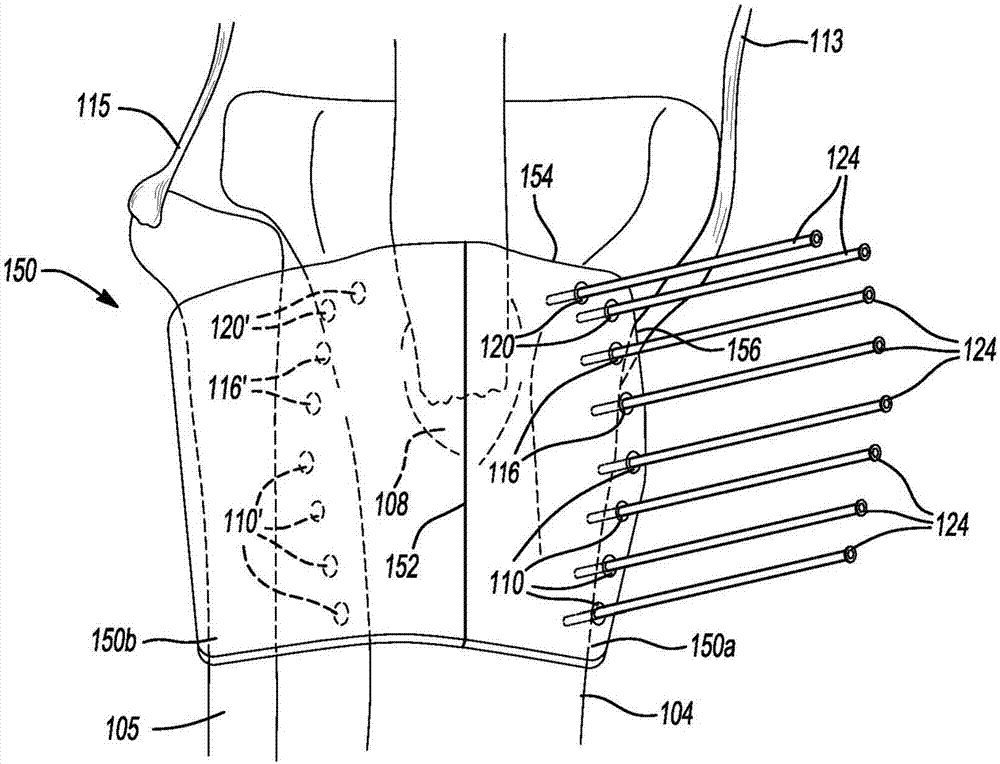
[0064] In Example 7, a patient-specific system for tibial osteotomy can include a patient-specific guide optionally including a guide body defining a bone engaging surface having a bone engaging surface Part, the bone engaging surface is configured during the preoperative planning stage of tibial osteotomy to be at the patient's tibial tubercle, around the tibial tubercle or near the tibial tubercle as the negative surface of the tibia of the specific patient and a plurality of first apertures positioned along a first straight line relative to the proximal-distal side of the tibia of the particular patient selected during the preoperative planning phase of the tibial osteotomy The axis defines a first predetermined angle.
[0065] In Example 8, the patient-specific system of Example 7 may optionally be configured such that the plurality of apertures are configured to guide insertion of the plurality of pins in the tibia.
[0066] In Example 9, the patient-specific system of a...
example 22
[0079] In Example 22, a method for performing a tibial tuberosity osteotomy on a patient's tibia can include positioning a patient-specific guide on the patient's tibia, wherein the guide includes a guide body, the The guide body defines a bone-engaging portion having a bone-engaging surface configured during a preoperative planning phase of a tibial osteotomy as a negative surface with a particular patient's tibia at the tubercle of the patient's tibia, around the The tubercle or the corresponding surface in the vicinity of the tubercle remains consistent, and the guide body defines a plurality of apertures; the tibia is resected in three intersecting planes using a saw to produce a tubercle flap, wherein the patient-specific guide is Resection provides visual markers; and repositioning the nodular flap in an anterior direction or in an anterior and medial-lateral direction to create a void between the nodular flap and the resected surface of the tibia.
[0080] In Example 23...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com