Inter-component de-correlation for video coding
A video coding and component technology, which is applied in the field of de-correlation between components for video coding, can solve problems such as inefficient architecture and operation implementation mode, complexity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] Illustrative embodiments will now be described in detail with reference to the various figures. While this specification provides detailed examples of possible implementations, it should be noted that these details are for purposes of illustration, and are not intended to limit the scope of the application.
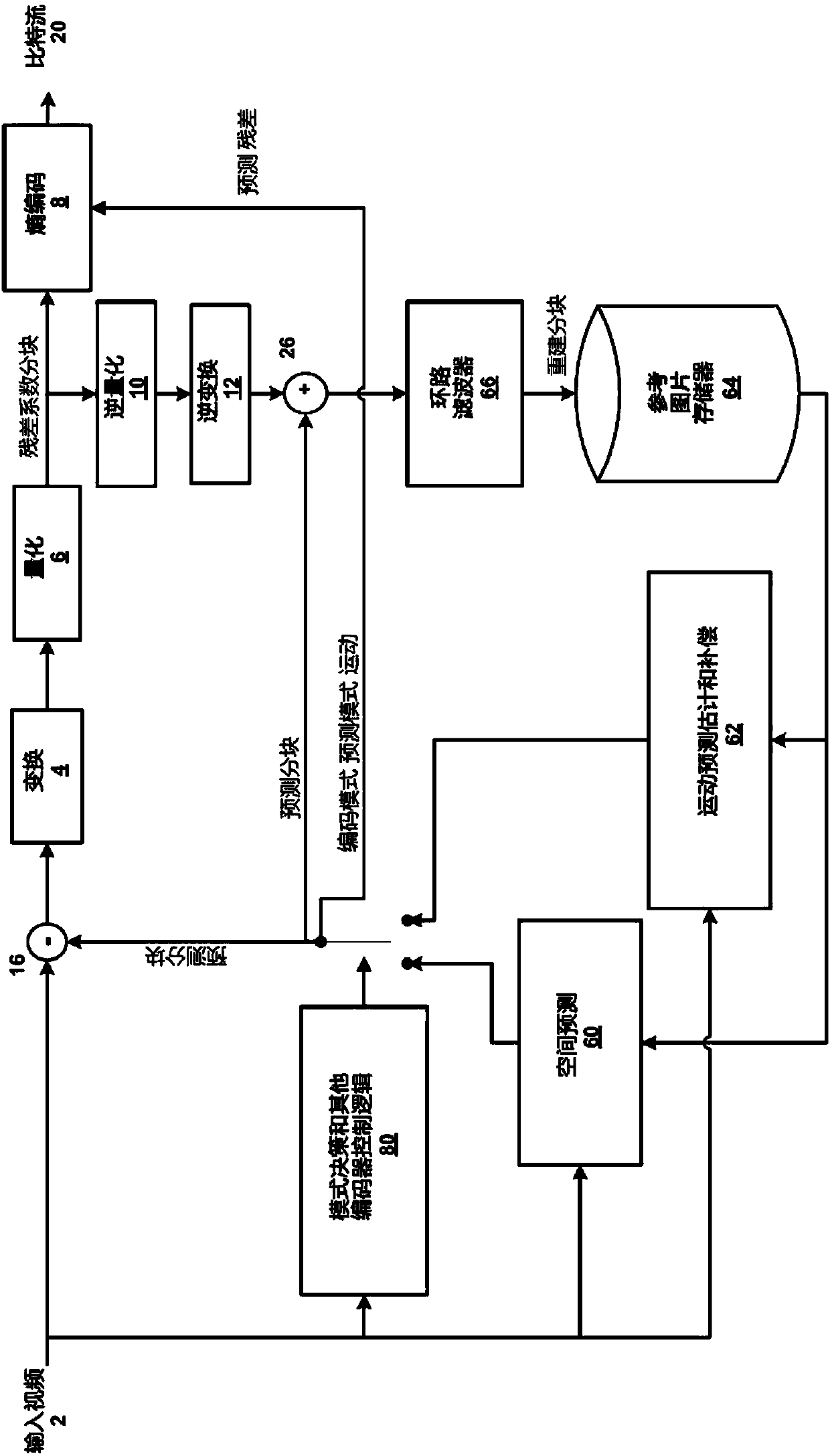
[0038] figure 1 An exemplary block-based hybrid video coding system is shown. As shown, the input video signal 2 may be processed in a block-by-block manner. These partitions may be referred to as macroblocks (MBs). In High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), video signals with high resolutions such as 1080p and higher can be compressed by using an extended block size called a coding unit (CU). As an example, a CU may be 64x64 pixels. A CU may be further divided into prediction units (PUs), on which individual prediction methods may be applied.
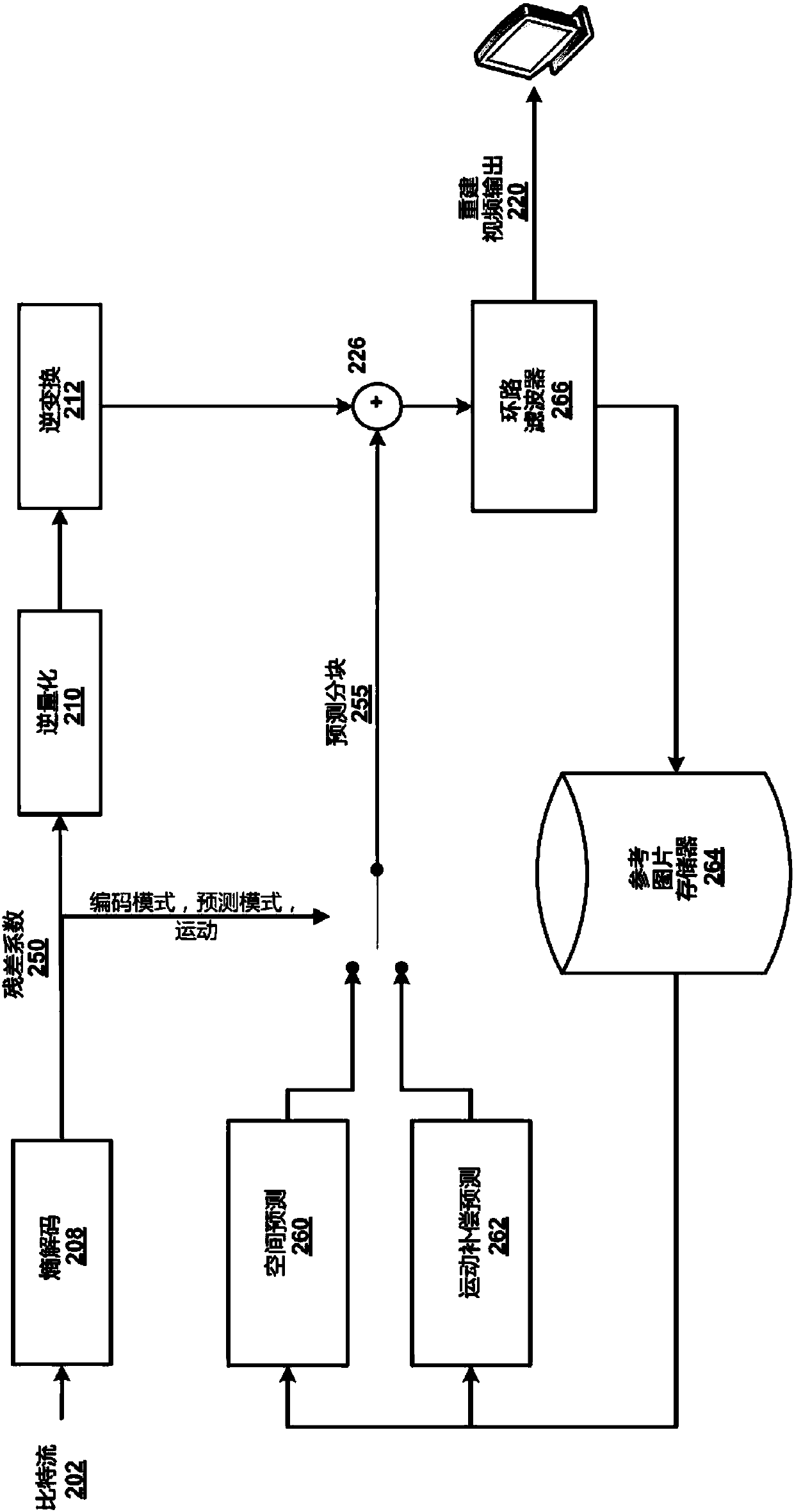
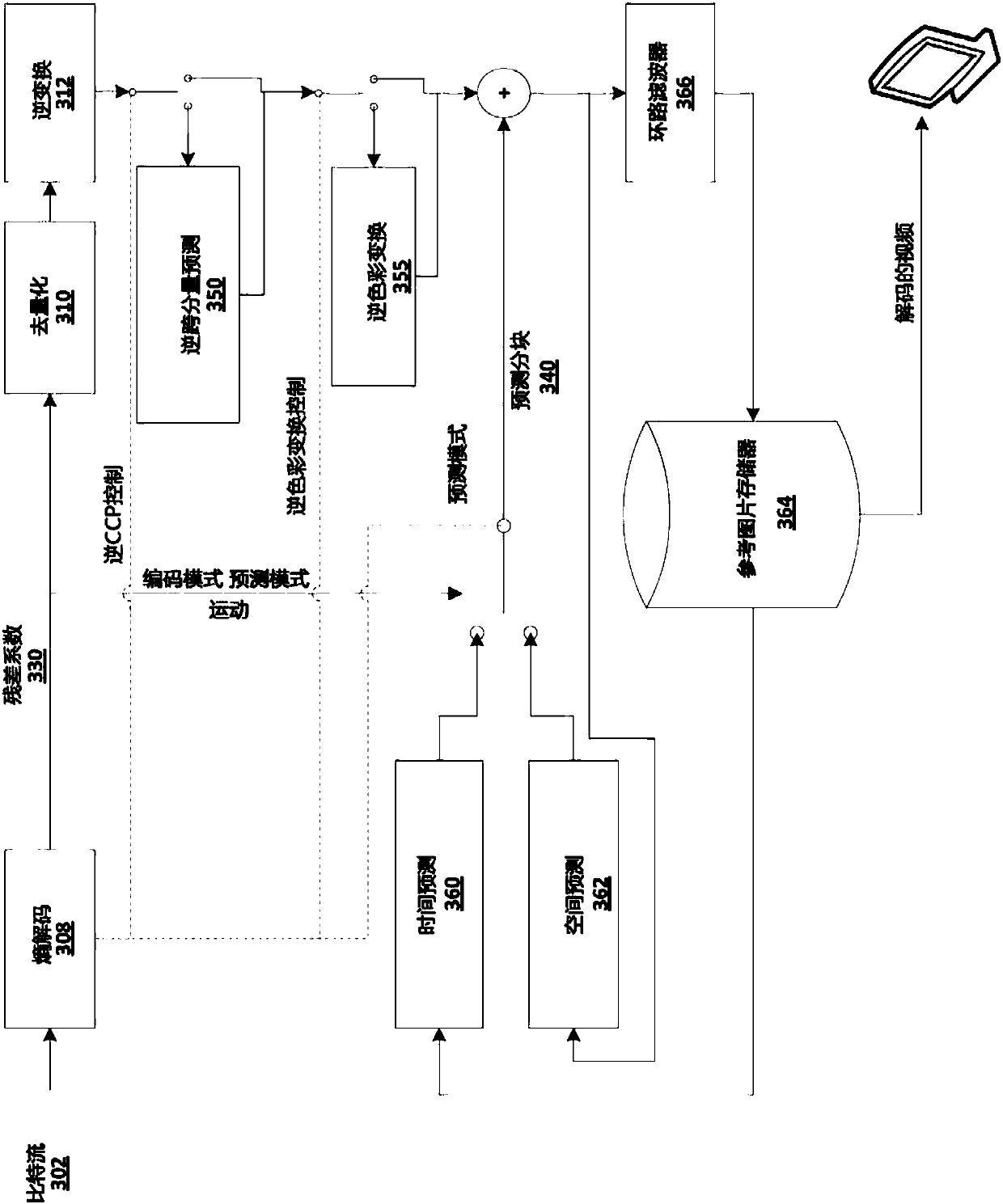
[0039] like figure 1 As shown, input video partitions (eg, MBs and / or CUs) may be analyzed by spatial prediction 60 and / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com