Prosthetic valves with mechanically coupled leaflets
A valve leaflet and prosthesis technology, applied in the field of prosthetic valves, can solve the problems that the tension is not well controlled, dependent, and affects the local geometry of the valve leaflets, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0213] Example 1: Prosthetic Valve
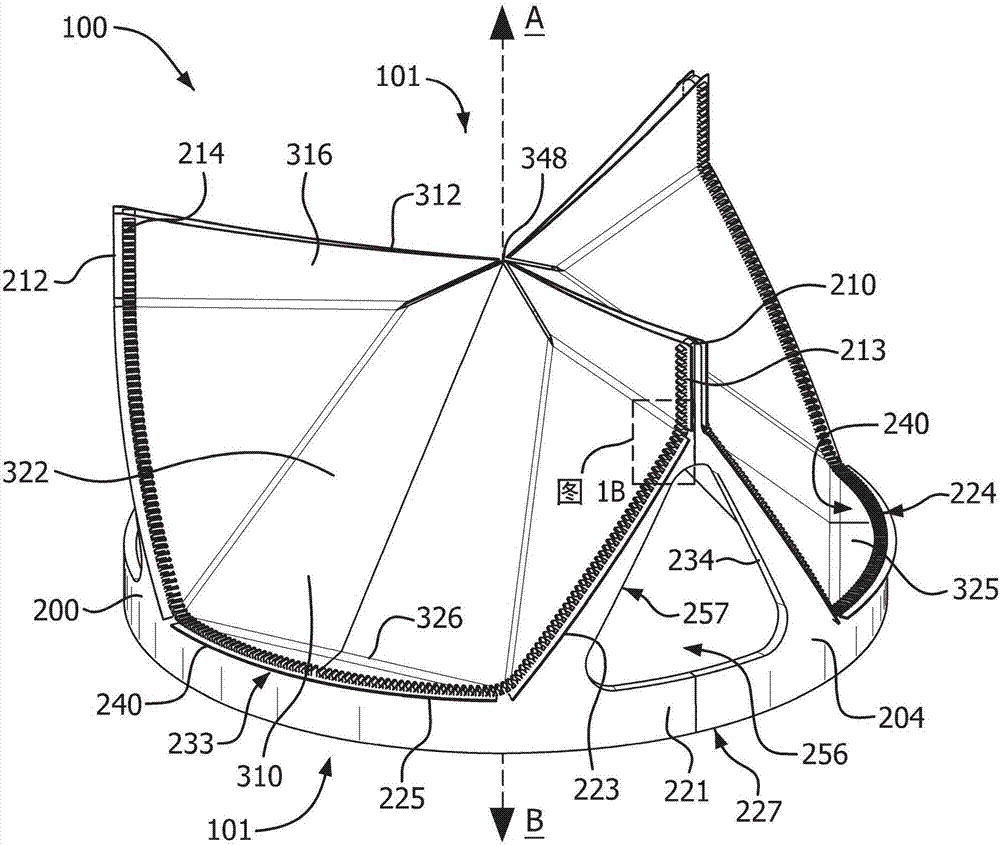
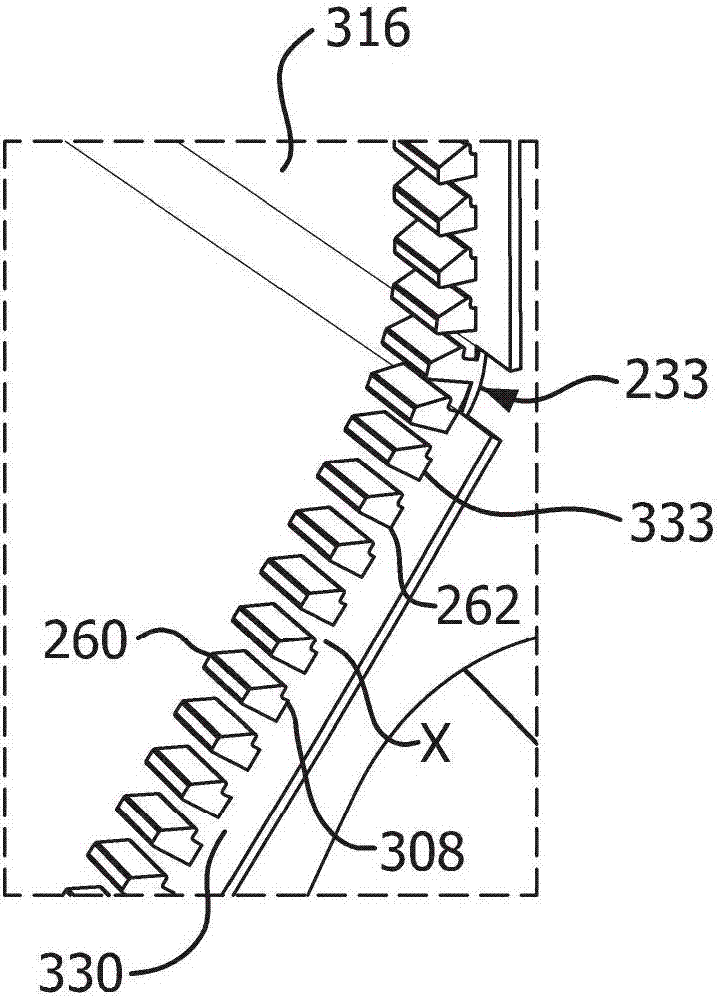
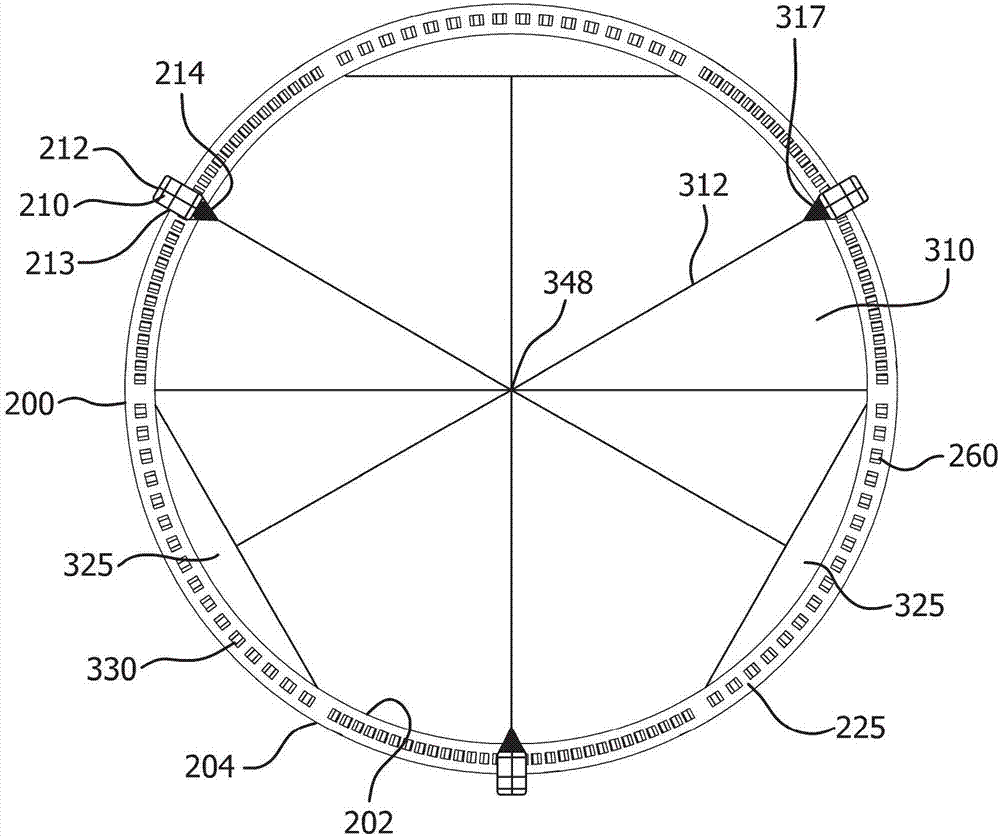
[0214] Leaflet Construction: Leaflet material was prepared with a multi-layered ePTFE membrane imbibed with fluoroelastomer. More specifically, ePTFE membranes subjected to PTFE's crystalline melting temperature or higher were fabricated according to the general teachings described in US Patent No. 7,306,729. The mass per unit area of the ePTFE diaphragm is about 0.5g / m 2 , the thickness is about 500nm, the IPA bubble point is about 200KPa, the matrix tensile strength is about 700MPa in the longitudinal direction and about 380MPa in the transverse direction. The diaphragm is imbibed with a fluoroelastomer configured according to the general teachings described in US Patent No. 7,462,675. The copolymer consists essentially of between about 60 and 65 weight percent perfluoromethyl vinyl ether and complementarily between about 40 and 35 weight percent tetrafluoroethylene.
[0215] The weight percent of fluoroelastomer relative to ePTFE wa...
example 2
[0228] Example 2: Pulmonary Valve Catheter
[0229] Leaflet frame and leaflet structure: Prepare the leaflet frame according to Example 1, except that the dimensions of the protruding part of the leaflet frame are as follows: base height 0.4 mm, base width 0.25 mm, base thickness 0.4 mm, head height 0.1mm, head width 0.375mm, and head thickness 0.4mm. Three leaflets were prepared as in Example 1, except that the leaflets did not have reinforcement bands.
[0230] First and Second Conduits: Each conduit was a round ePTFE tube with an inner diameter of about 23.7 mm and a wall thickness of about 1.2 mm. The length of each extruded tube is about 150 mm.
[0231] First frame construction: The first frame was formed from cobalt chrome (fully hardened and aged MP35N) tube with an outer diameter of 25 mm and a wall thickness of 0.35 mm. Tubes are laser cut to form as Figure 20E The first frame shown in . The laser cut first frame is electropolished to complete the formation of ...
example 3
[0239] Example 3: Transcatheter self-expanding prosthetic valve
[0240] frame preparation
[0241] A cylindrical stainless steel hollow mandrel with a diameter of 23.6 mm was obtained. The mandrel had about 1 mm diameter perforations through the wall distributed over a length of about 100 mm of the mandrel. An approximately 90 mm length of sacrificial release material (4:1 PTFE heat shrink tubing from Zeus, Inc., Orangeburg, SC, 25.4 mm initial ID, Cat. No. 96974) is placed on the mandrel, and Leave the perforations at the ends exposed and shrink to the mandrel by heating in an air oven set at 300°C for 15 minutes. Components were allowed to cool to room temperature.
[0242] A FEP / ePTFE member having the following characteristics: a mass per unit area of 50.6 grams per square meter and a tensile strength at break of 1.7 kgf / cm in the longitudinal direction and 1.64 kgf / cm in the transverse direction was obtained. Tensile testing was performed at 23°C on 25.4 mm wide sp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com