A metal nanomaterial with high strength linear elasticity in a wide temperature range and its preparation method and application
A metal nano and nano crystal technology, applied in the field of nano materials, can solve the problems of precisely controlling the deformation of devices, shortening the operating temperature range, dissipating mechanical energy, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] The present embodiment provides the wire material (composition is Ti) of the metal nanomaterial of wide temperature domain high strength linear superelasticity 45 Ni 55 ), which is prepared by the following steps:
[0056] (1) Titanium with a purity of 99.9wt.% and nickel with a purity of 99.9wt.% are selected according to the ratio of Ti and Ni atomic ratio 0.9:1, wherein the sum of the atomic percentages of Ti and Ni is 100%;
[0057] (2) Put the above material components into a vacuum melting furnace, melt and cast them into NiTi binary alloy ingots under the protection of 0.5MPa argon;
[0058] (3) In a vacuum furnace, the obtained NiTi binary alloy ingot is subjected to homogenization annealing treatment for 10 hours at 950° C.;
[0059] (4) Hot forging the ingot after homogenizing annealing into a rod-shaped profile at 850°C;
[0060] (5) At 550°C, the rod-shaped profile obtained by hot forging is hot-drawn to obtain a wire with a diameter of 0.55 mm;
[0061]...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The present embodiment provides the wire material (composition is Ti) of the metal nanomaterial of wide temperature domain high strength linear superelasticity 45 Ni 55 ), which is prepared by the following steps:
[0073] The steps (1)-(8) in this embodiment are the same as the steps (1)-(8) in Example 1.
[0074] (9) The wire material obtained in step (8) was subjected to a 10% uniaxial tensile deformation treatment at 20° C. to obtain the metal nanomaterial wire material of this embodiment.
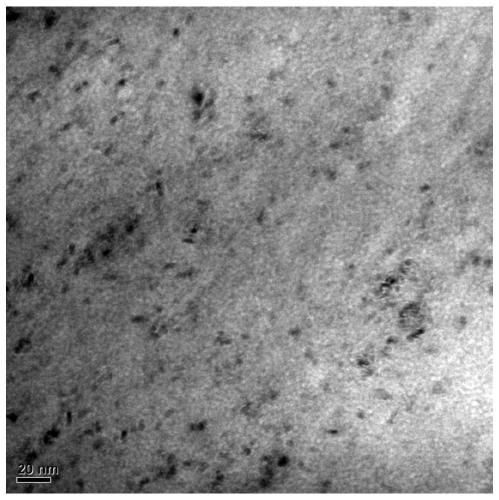
[0075] Figure 7 For the two-dimensional high-energy X-ray diffraction spectrum of the metal nanomaterial wire in this embodiment after implementing uniaxial stretching and 10% deformation, from Figure 7 It can be seen that after the metal nanomaterial wire is deformed by 10% uniaxial stretching, the metal nanomaterial is in the martensitic phase (B19'-NiTi) at 20 °C, which is composed of preferentially oriented martensite variants.
[0076] Figure 8 The tensile stress-st...
Embodiment 3
[0078] The present embodiment provides the wire material (composition is Ti) of the metal nanomaterial of wide temperature domain high strength linear superelasticity 45 Ni 55 ), which is prepared by the following steps:
[0079] Steps (1)-(7) of this embodiment are the same as steps (1)-(7) in Embodiment 1.
[0080] (8) Carrying out crystallization annealing treatment at 450° C. for 10 minutes on the wire material obtained in step (7);
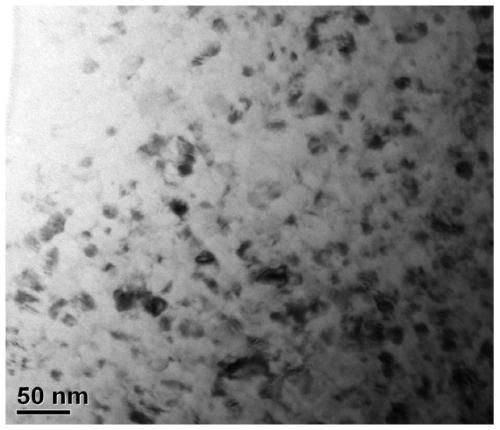
[0081] Figure 9 It is the bright-field image of the transmission electron microscope of the longitudinal section of the cold-drawn wire after crystallization and annealing at 450 ° C for 10 minutes. Figure 9 It can be seen that the metal nanomaterial is composed of uniformly distributed NiTi nanocrystals, and the average diameter of the grains is 100nm.
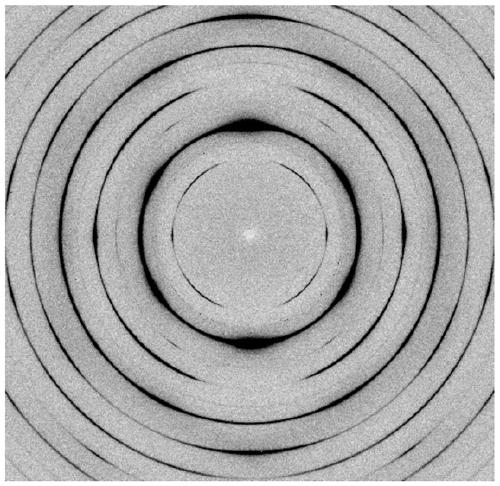
[0082] Figure 10 It is the two-dimensional high-energy X-ray diffraction spectrum of the wire after the cold-drawn wire is crystallized and annealed at 450 ° C for 10 minutes, from ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com