A method for selective hydrogenation of cracked C6-C8 cuts
A C6-C8, selective technology, which is applied in the field of one-stage selective hydrogenation of pyrolysis gasoline and the selective hydrogenation of cracked C6-C8 fractions, can solve the inability to achieve controllable adjustment of macropore-mesoporous pore diameter and diene hydrogenation. The problem of low selectivity, etc., can achieve the effect of strong coking inhibition ability, improved diene hydrogenation selectivity, and good low temperature activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] First, 8.0 g of the water-soluble chitosan pore-enlarging agent was added to deionized water at 50° C., and then acetic acid was added dropwise until the chitosan was completely dissolved to obtain an acid solution containing the pore-enlarging agent. Weigh 1.46g of phosphoric acid and 7.35g of magnesium nitrate respectively, and completely dissolve phosphoric acid and magnesium nitrate in 70g of distilled water to form an aqueous solution containing phosphorus and magnesium. Weigh 350g of pseudo-boehmite powder and 20.0g of fennel powder into the kneader, mix well, then add the mixed solution of phosphoric acid and magnesium nitrate, and finally add the acid solution containing chitosan to the pseudo-boehmite Knead evenly in the stone, and shape it into a clover shape through kneading-extrusion. Dry at 120° C. for 8 hours, and calcined at 700° C. for 4 hours to obtain an alumina carrier 1 containing phosphorus and magnesium. In carrier 1, phosphorus pentoxide is 0.5wt...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Add 8.0 g of the water-soluble chitosan pore-enlarging agent into deionized water at 50° C., and then add acetic acid dropwise until the chitosan is completely dissolved to obtain an acid solution containing the pore-enlarging agent. Weigh 1.09g of phosphoric acid and 9.12g of magnesium nitrate respectively, completely dissolve phosphoric acid and magnesium nitrate in 70g of distilled water to form an aqueous solution containing phosphorus and magnesium. Weigh 350g of pseudo-boehmite powder and 20.0g of fennel powder into the kneader, mix well, then add the mixed solution of phosphoric acid and magnesium nitrate, and finally add the acid solution containing chitosan to the pseudo-boehmite Knead evenly in the stone, and shape it into a clover shape through kneading-extrusion. Dry at 120° C. for 8 hours, and calcined at 700° C. for 4 hours to obtain an alumina carrier 1 containing phosphorus and magnesium. Then use phosphorus and magnesium to modify the surface of the ca...
Embodiment 3
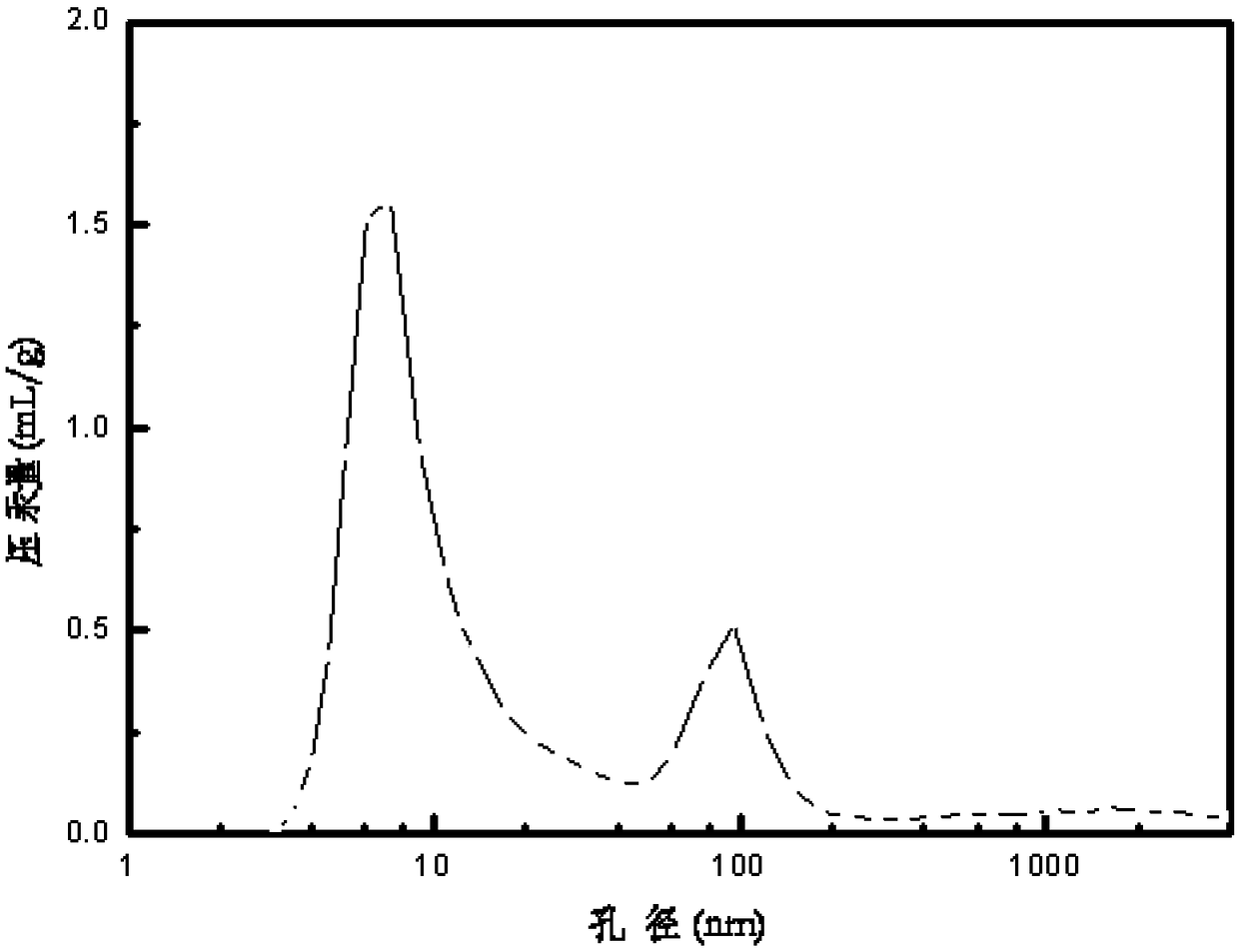
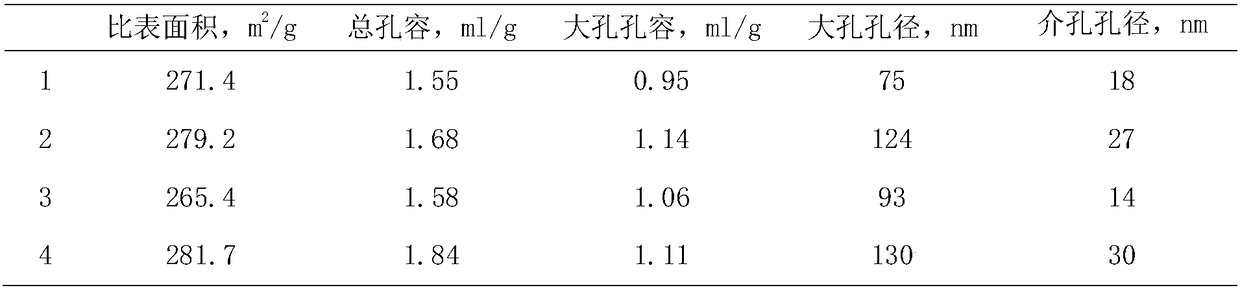
[0045] The preparation method of the carrier was carried out according to Example 1. The difference is that the auxiliary component in the carrier also contains cerium, and the water-soluble chitosan pore-enlarging agent is replaced with a non-water-soluble chitosan pore-enlarging agent, and the chitosan formic acid solution is stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 30 minutes to obtain Alumina support with macroporous structure3. The contents of the auxiliary components phosphorus, magnesium and cerium in the carrier are respectively 1.8wt%, 2.0wt%, and 0.6wt% of the weight of the carrier. Its specific surface area and pore size distribution are shown in Table 1.
[0046] A palladium solution was prepared to impregnate the alumina carrier 3, dried at 120° C. for 6 hours, and calcined at 500° C. for 5 hours to obtain the catalyst 3 . Catalyst 3 had a palladium content of 0.29 wt%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mesopore | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com