Rate matching method and device
A rate matching and bit rate technology, applied in the field of rate matching, can solve problems such as performance loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The specific embodiments of the present application will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
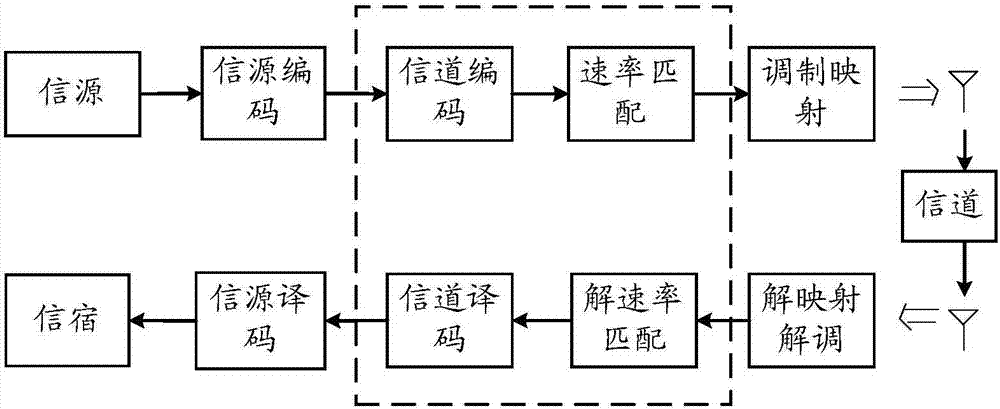
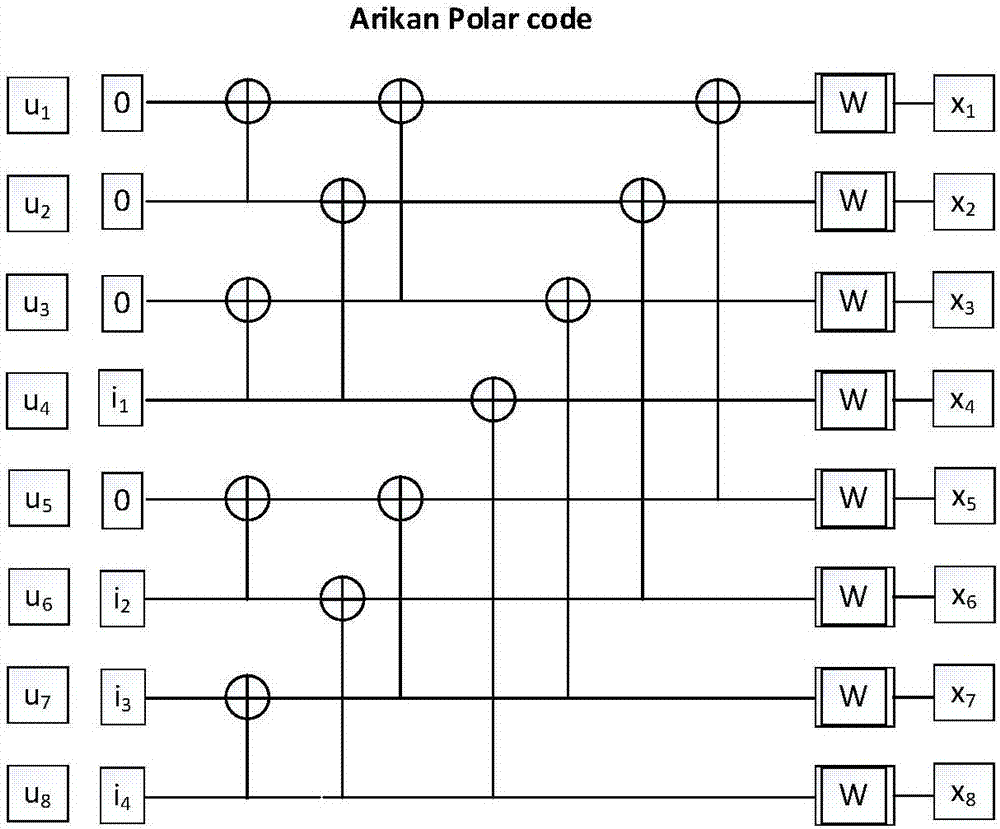
[0027] figure 1 It is the basic process of wireless communication. At the sending end, the source is sent out after sequentially undergoing source coding, channel coding, rate matching and modulation mapping. At the receiving end, the destination is output through demapping and demodulation, derate matching, channel decoding and source decoding in sequence. Polar codes can be used for channel coding and decoding. Since the code length of the original Polar code (mother code) is an integer power of 2, it is necessary to implement a Polar code with any code length through rate matching in practical applications. The sending end performs rate matching after channel encoding to achieve any target code length, and at the receiving end, de-rate matching is performed before channel decoding. It should be noted that the basic process o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com