Data forwarding method and data forwarding apparatus based on clusters
A forwarding method and data technology, applied in the field of Internet of Things, can solve problems such as poor real-time performance, and achieve the effect of improving real-time performance, improving real-time performance, and shortening the time for forwarding data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
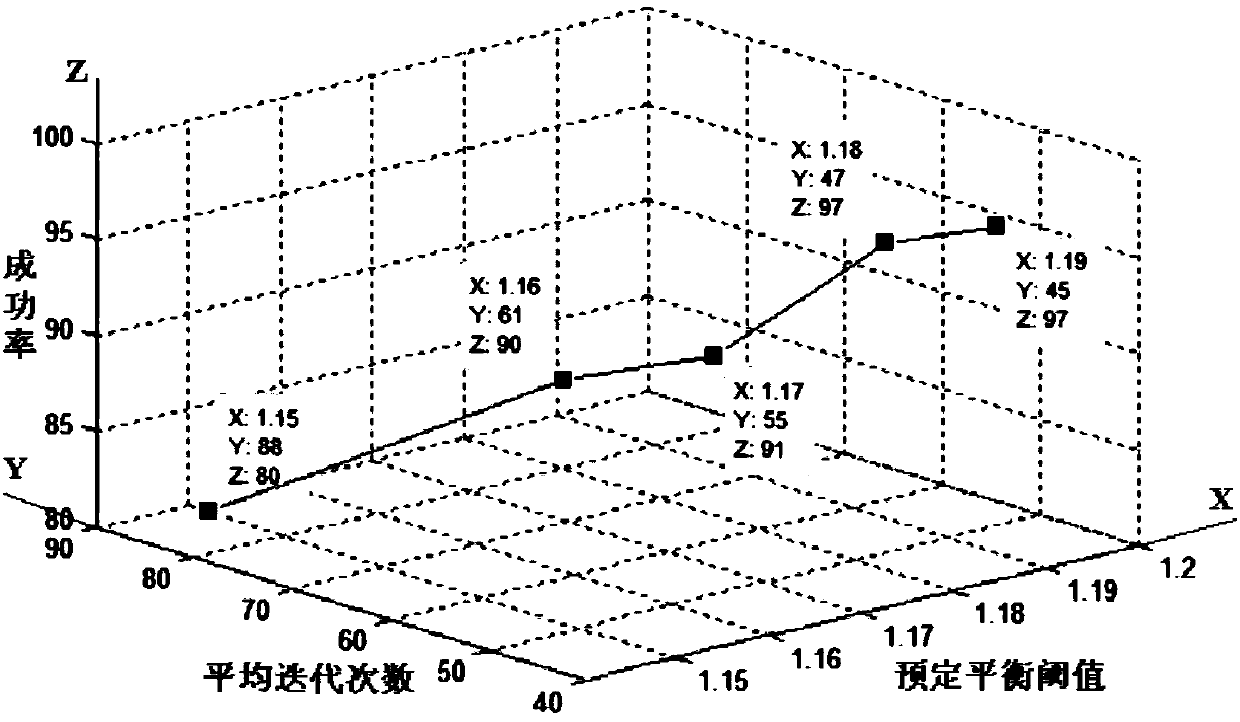
[0196] In this embodiment, the size of the rectangular area is 200m×200m, and the number of nodes is 200; the number of partitions is represented by M and ranges from 1 to 10; θ is 1.15.
[0197] Figure 7 A schematic diagram of the relationship between the number of partitions (that is, the number of divided sub-regions) and the average number of iterations is exemplarily shown. Such as Figure 7 As shown, as the number of partitions increases, the average number of iterations also shows an upward trend. This is because as the number of partitions increases, it is necessary to ensure that the lengths of access paths in more sub-regions are balanced. Therefore, more sub-region adjustments are required to meet the requirements. And because of the random distribution of nodes, the more the number of partitions, the more likely it is that the partition cannot be completed within the specified number of iterations, so the increase in the number of partitions will increase the n...
Embodiment 2
[0200] In this embodiment, the size of the rectangular area is 200m×200m; the number of cluster head nodes is 80, 100, 120, 140, 160, 180, and 200, and the cluster head nodes are randomly distributed; the number of partitions is 1, 2, 3, respectively. ..., 10; θ is 1.15.
[0201] Figure 9 A schematic diagram exemplarily showing the relationship between the cluster head node, the number of partitions and the average moving distance of the mobile sink node. It can be seen that, in the case of a certain number of partitions, if the number of nodes is larger, the average moving distance of the mobile sink nodes in each partition will be greater. Similarly, when the number of nodes is fixed, if the number of partitions increases, the average moving distance of the mobile sink nodes in each partition will be smaller.
[0202] Figure 10 A schematic diagram exemplarily showing the relationship between the cluster head node, the number of partitions and the average number of itera...
Embodiment 3
[0204] In this embodiment, the side lengths of the square area of the wireless sensor network are 1000m, 2000m, 3000m, 4000m, and 5000m respectively; the number of cluster head nodes is 200; the number of partitions is 1, 2, 3, ..., 10; θ = 1.18.
[0205] Figure 11 A schematic diagram exemplarily showing the relationship among the side length of the wireless sensor network area, the number of partitions and the average number of iterations of the partitions. It can be seen that in the case of relatively sparse cluster head nodes, the number of iterations required for partitioning is relatively large.
[0206] Figure 12 A schematic diagram exemplarily showing the relationship between the side length of the wireless sensor network area, the number of partitions and the average moving distance of the mobile sink node. combine Figure 9 and Figure 12 It can be seen that the average moving distance of the mobile sink node is directly proportional to the size of the entire...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com