high frequency line
A high-frequency, line technology, applied in the field of high-frequency lines, to achieve the effect of suppressing impedance changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
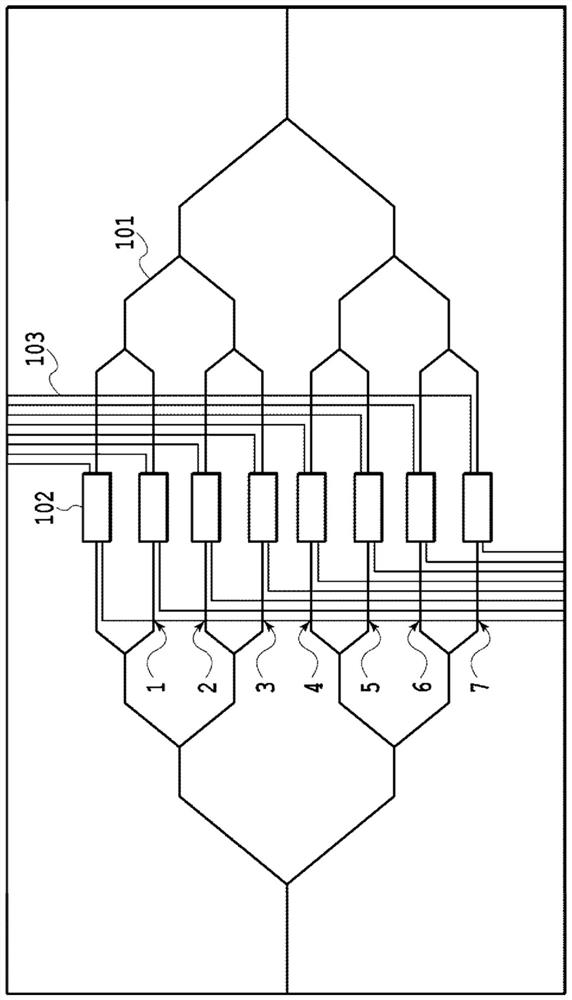
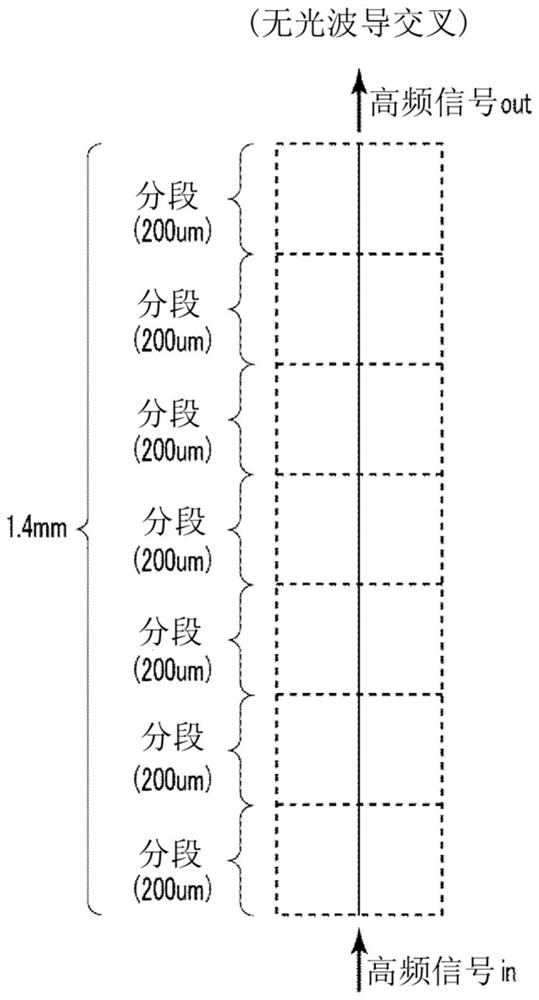
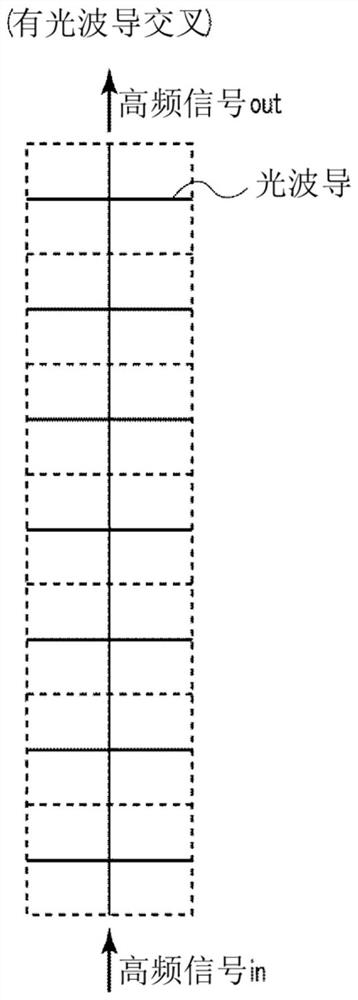
[0054] exist Figure 4A The top view of the segmented unit of the high-frequency line according to the first embodiment of the present invention is shown in Figure 4B Its IVB-IVB sectional view is shown in the Figure 4C Its IVC-IVC transverse section view is shown in Figure 4D Its IVD-IVD transverse cross-sectional view is shown in . The high-frequency line of this embodiment is a microstrip line, and its basic structure is formed by sequentially stacking a ground electrode 302 , a dielectric layer 304 , and a signal electrode 305 on a SI-InP substrate 301 . In addition, as shown in the transverse sectional view, the optical waveguide core 303 of the InP-based semiconductor intersects in the form of crossing the high-frequency line.
[0055] Such as Figure 4B sectional view of Figure 4D As shown in the cross-sectional view of the optical waveguide, the ground electrode 302 of the high-frequency line is partially interrupted along the transmission direction, and part ...
no. 2 approach
[0062] exist Figure 7A The top view of the segmented unit of the high-frequency line according to the second embodiment of the present invention is shown in Figure 7B Its VIIB-VIIB sectional view is shown in the Figure 7C Its VIIC-VIIC transverse sectional view is shown in the Figure 7D Shown in its VIID-VIID transverse cross-sectional view. The high-frequency line in this embodiment is a grounded coplanar line, and its basic structure is formed by sequentially stacking a lower ground electrode 702 , a dielectric layer 704 , a signal electrode 705 and an upper ground electrode 706 on a SI-InP substrate 701 . In addition, as shown in the cross-sectional view, the optical waveguide core 703 of the InP-based semiconductor intersects the high-frequency line.
[0063] As described in the first embodiment, due to the existence of this optical waveguide intersection, the dielectric constant between the lower layer ground electrode 702 and the signal electrode 705 is locally ch...
no. 3 approach
[0071] In addition, in Figure 9A A top view with grounded coplanar lines of a third embodiment of the present invention is shown in Figure 9B Its IXB-IXB sectional view is shown in the Figure 9C Its IXC-IXC transverse section view is shown in the Figure 9D Shown in its LCD-LCD transverse cross-sectional view. Such as Figure 9A As shown, the width of the signal electrode 905 is the same, but the width of the upper ground electrode 906 in the intersecting region of the optical waveguides may be enlarged, and the distance between the signal electrode 905 and the upper ground electrode 906 may be changed, specifically narrowed. In the case of this compensation structure (narrow SG gap electrode), such as Figure 8B As shown, the effect of suppressing the increase in characteristic impedance and the effect of suppressing the increase in excess electrical loss were also confirmed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com