Gait-based identity verification method, apparatus and device, and storage medium
An identity verification method and gait technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of wrong recognition results, too many non-personal sample data, and reduce the effect of user identity recognition, so as to reduce the amount of calculation and improve the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
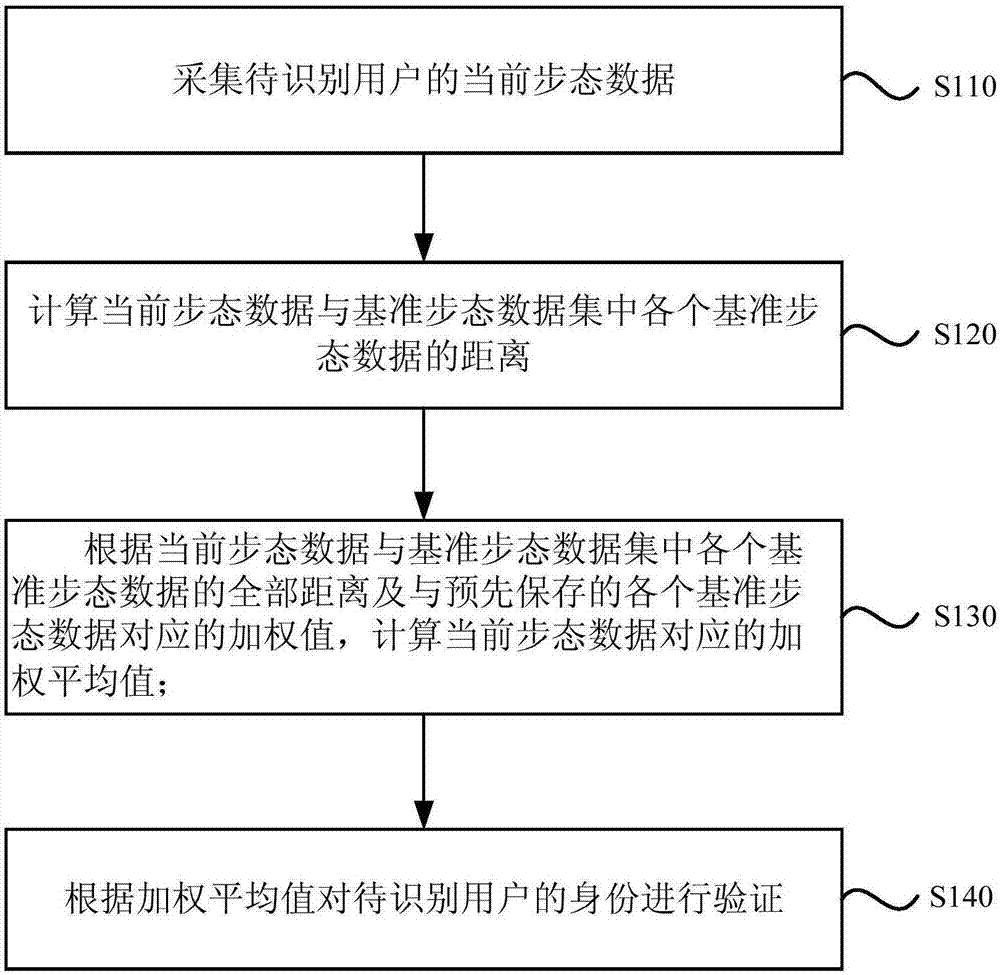
[0029] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the gait-based identity verification method provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to identity verification, and the method can be executed by a gait-based identity verification device, such as figure 1 As shown, the gait-based authentication method may include the following steps:
[0030] S110. Collect current gait data of the user to be identified.
[0031] In this embodiment, the current gait data refers to a gait cycle data in the current state of the user to be identified, and a gait cycle refers to the time when one heel strikes the ground until the same heel strikes the ground again during walking. The current gait data of the user to be recognized is collected through the sensor in the terminal device. Exemplarily, the sensor may be an acceleration sensor, a gyroscope sensor, or a gravity sensor.
[0032] S120. Calculate the distance between the current gait data and each reference gait...
Embodiment 2
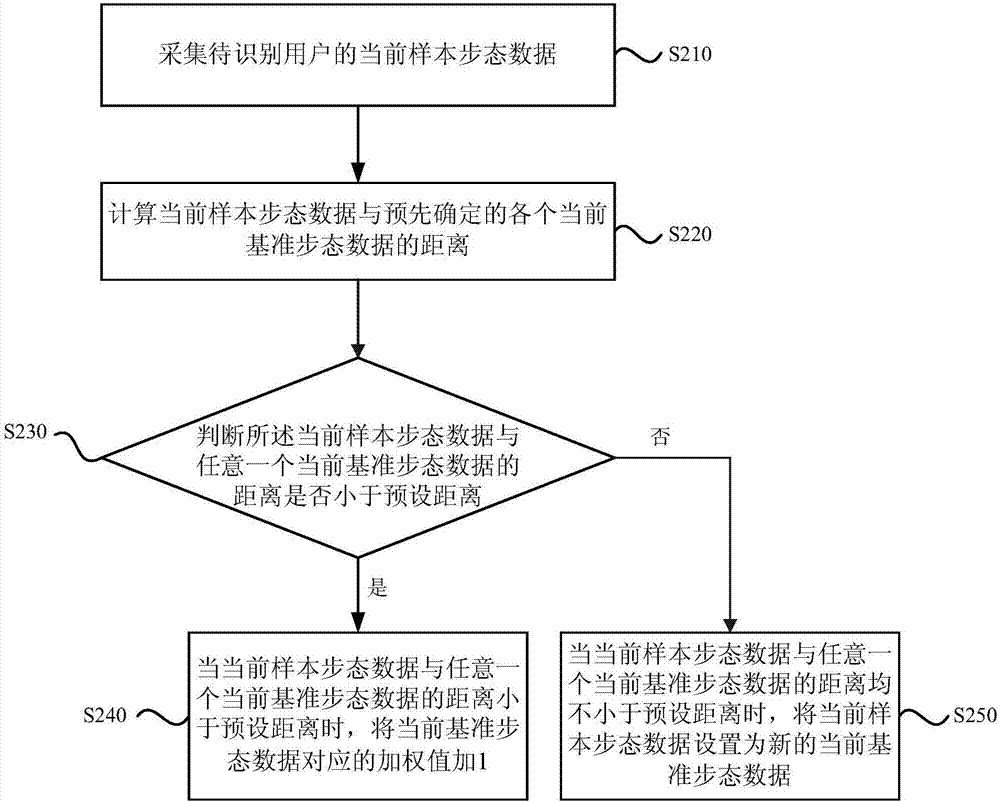
[0051] figure 2 It is a flowchart of model training in the gait-based identity verification method provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment further adds a model training method in the gait-based identity verification method on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments. Such as figure 2 shown. Model training in the gait-based identity verification method may include the following steps:
[0052] S210. Collect current sample gait data of the user to be identified.
[0053] In this embodiment, the sample gait data refers to all gait data of the user to be identified.
[0054] S220. Calculate the distance between the current sample gait data and each predetermined current reference gait data.
[0055] S230, judging whether the distance between the current sample gait data and any current reference gait data is less than the preset distance; if so, execute S240; otherwise, execute S250;
[0056] S240. When the distance between the current sample ga...
Embodiment 3
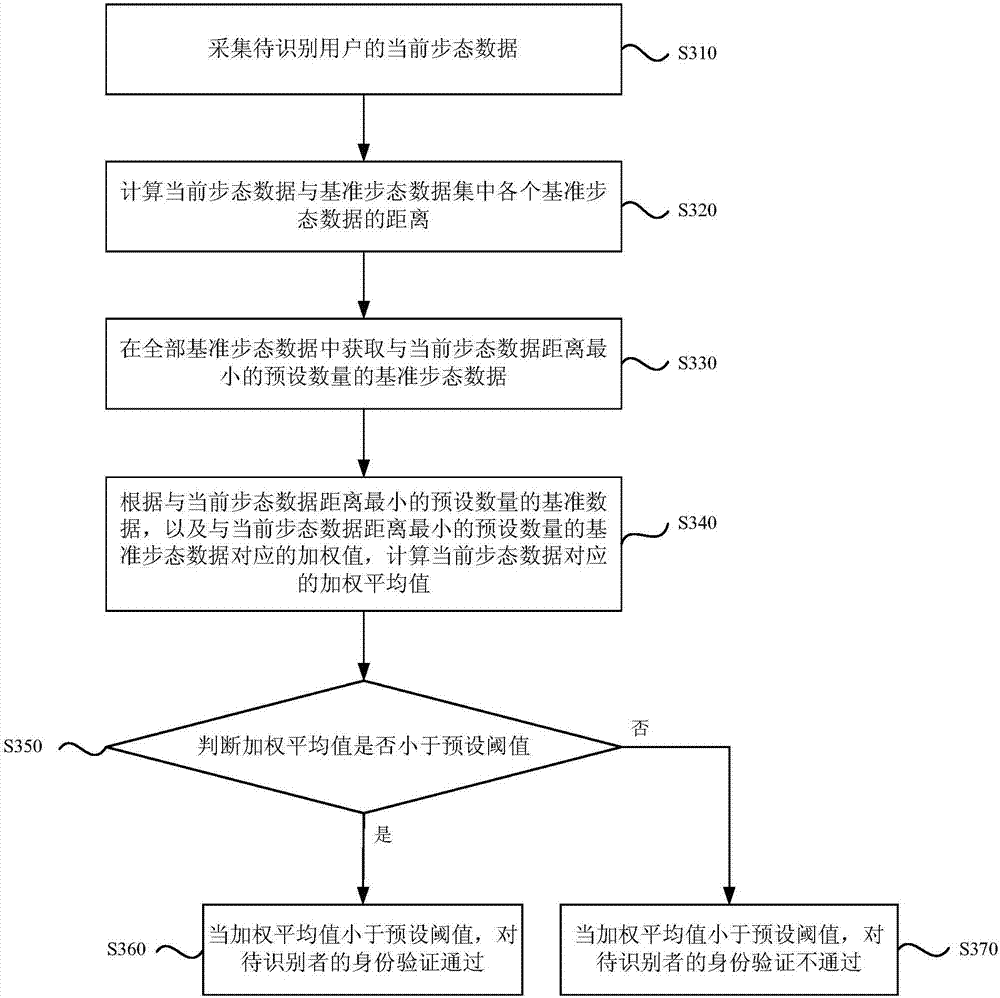
[0073] image 3 It is a flow chart of the gait-based identity verification method provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention. On the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment optimizes the gait-based identity verification method, such as image 3 As shown, the gait-based authentication method may include the following steps:
[0074] S310. Collect current gait data of the user to be identified.
[0075] S320. Calculate the distance between the current gait data and each reference gait data in the reference gait data set.
[0076] S330. Obtain a preset number of reference gait data with the smallest distance from the current gait data among all the reference gait data.
[0077] S340. Calculate the weighted average value corresponding to the current gait data according to the preset number of reference data with the smallest distance from the current gait data and the weighted value corresponding to the preset number of reference gait data with the small...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com