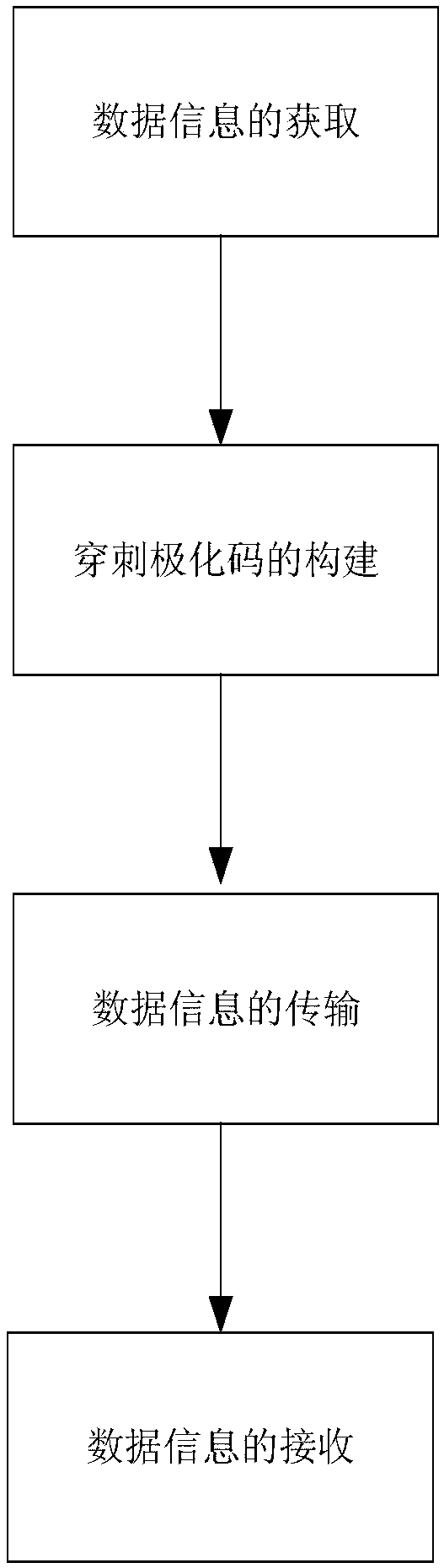
Information communication method based on puncture polarization code
An information communication method and polar code technology, applied in the field of information communication based on puncture polar codes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
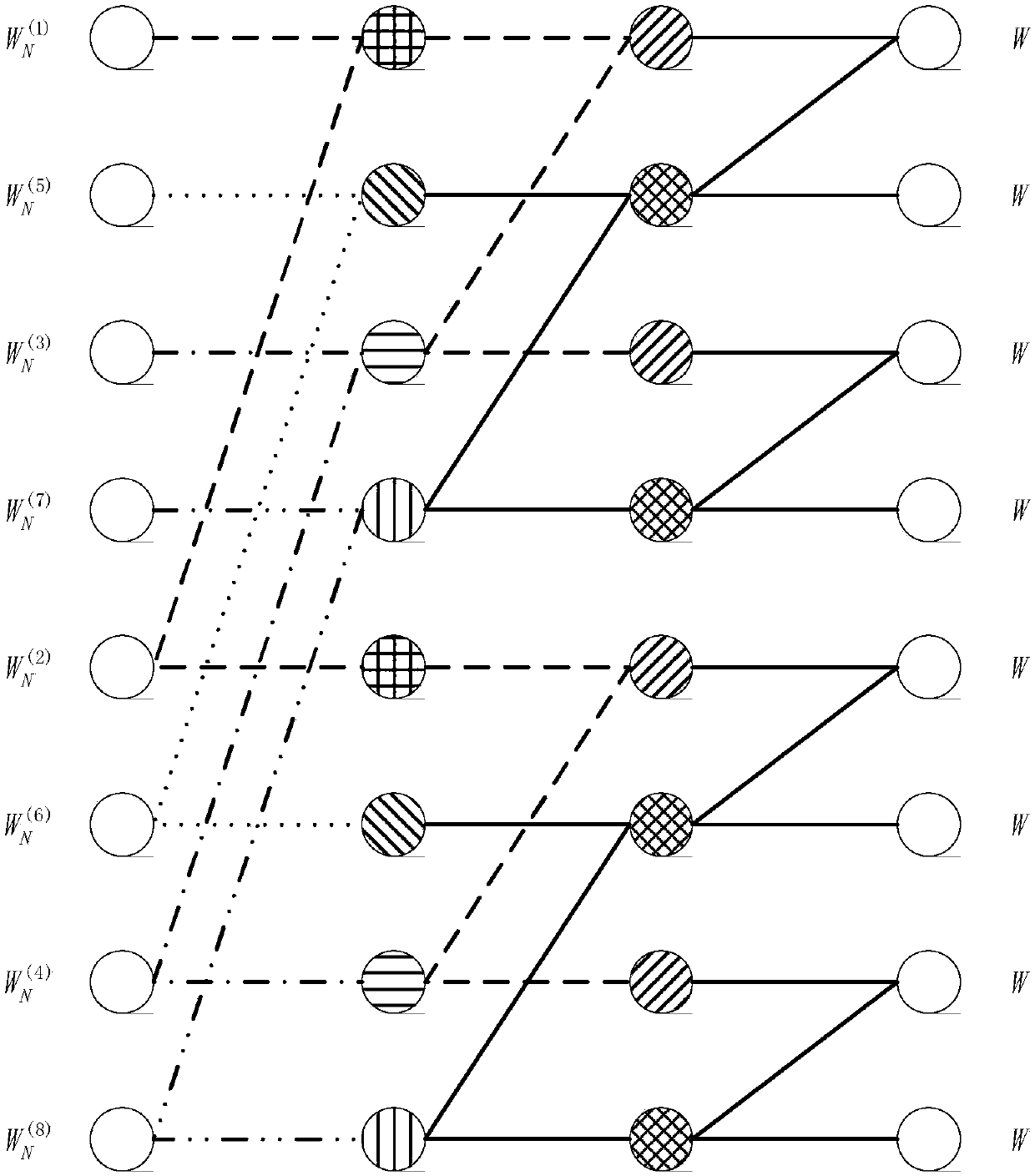
[0199] Example 1: The puncturing type is unknown puncturing, the puncturing polar code length M=6, the code rate R=0.5, then the number of information bits k=M*R=3. Select the original polar code with code length N=8, and then puncture it to obtain the corresponding punctured polar code with code length M=6.
[0200] First, the codeword puncture set Q is obtained: because the puncture type is unknown, the source puncture set B={1,2} is obtained according to the quasi-uniform puncture method, and then the bit flipping operation is performed on the set B to obtain the codeword puncture set Q;
[0201] The bit flip permutation operation is as follows: first divide the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} into two sets {1, 3, 5, 7} and {2, 4, 6, 8}, Then divide the two sets just obtained into two sets {1, 5}, {3, 7} and {2, 6}, {4, 8},
[0202] Finally, the four sets obtained above are divided into two sets: {1}, {5}, {3}, {7}, {2}, {6}, {4}, {8}, thus obtaining The bit flip set {1, 5,...
example 2
[0211] Example 2: The puncture type is a known type of puncture, the puncture polar code length M=7, the code rate R=0.5, then the number of information bits k=M*R=3, and the selected original code length N=8 The polar code is then punctured to obtain a corresponding polar code with code length M=7.
[0212] First, the codeword puncture set Q is obtained: because the puncture type is a known type, the source puncture set B={8} is obtained according to the anti-aligned uniform puncture method, and then the bit flipping operation is performed on the set B to obtain the codeword puncture set ;
[0213] The bit flip permutation operation is as follows: first divide the set {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} into two sets {1, 3, 5, 7} and {2, 4, 6, 8}, Then divide the two sets just obtained into two sets {1, 5}, {3, 7} and {2, 6}, {4, 8},
[0214] Finally, the four sets obtained above are divided into two sets: {1}, {5}, {3}, {7}, {2}, {6}, {4}, {8}, thus obtaining The bit flip set {1, 5,...
example 3
[0221] Example 3: code length M=8, code rate R=0.5, then the number of information bits k=M*R=4; so in this case no puncture is needed, and the original polar code with code length N=8 is selected.
[0222] First, the initial transition probability set W is obtained: the transition probability of the BSC channel is set to p=0.2, then the corresponding channel transition probability is w(0|0)=w(1|1)=1-p=0.8, w( 1|0)=w(0|1)=p=0.2. Because each channel has the same initial transition probability, that is, W (i) ={0.8,0,...,0,0.2,0,...,0}, where 1≤i≤8,
[0223] Thus the initial transition probability set W={W (1) ,W (2) ,...,W (8)}.
[0224] Secondly, calculate and obtain the error probability set Pe={P 1 ,P 2 ,...,P 8}: According to our modified Tal-Vardy algorithm, calculate P e ={P 1 ,P 2 ,...,P 8} = {0.2458 0.2176 0.2176 0.12080.2176 0.1116 0.0932 0.0167}.
[0225] Finally, the information bit set I and the fixed bit set F are obtained:
[0226] For the obtaine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com