Air vehicle
A technology for aircraft and ducted fans, applied in the field of aviation flight, can solve problems such as difficult trade-offs, and achieve the effects of reducing demand, improving flight aerodynamic efficiency, and high-level flight performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
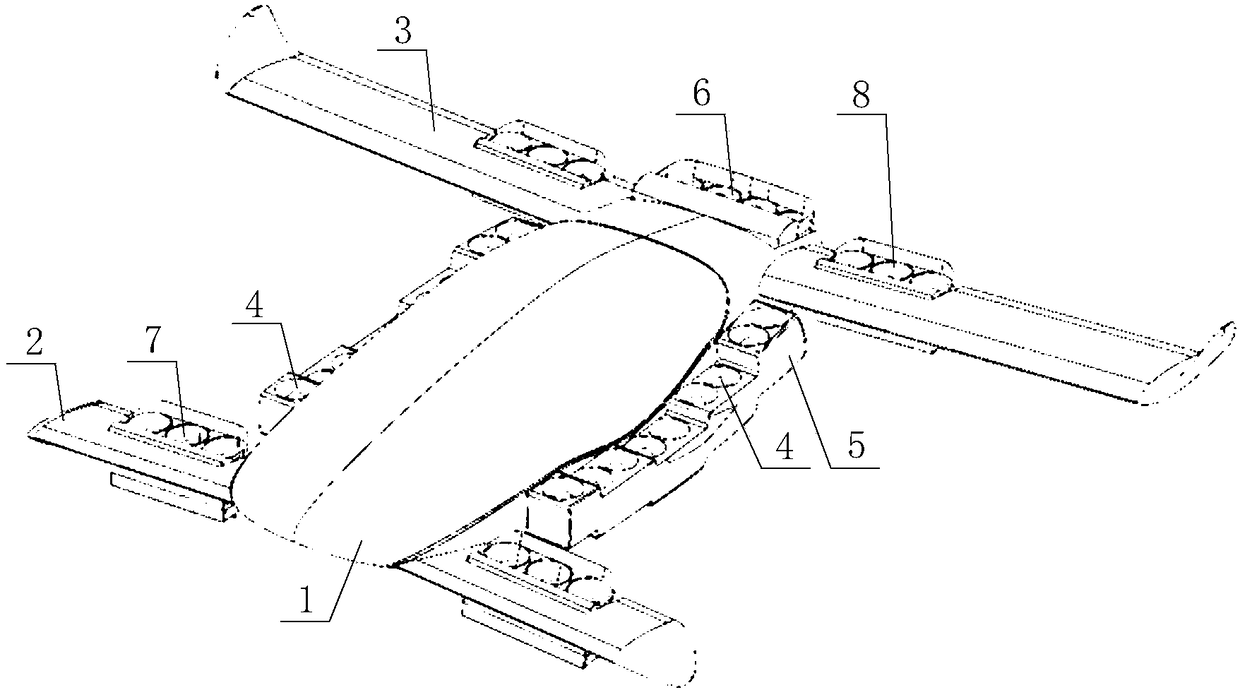
[0024] The core of the present invention is to provide an aircraft with improved comprehensive performance, which is embodied in that it has better level flight performance and vertical take-off and landing performance at the same time.
[0025] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the technical solutions of the present invention, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
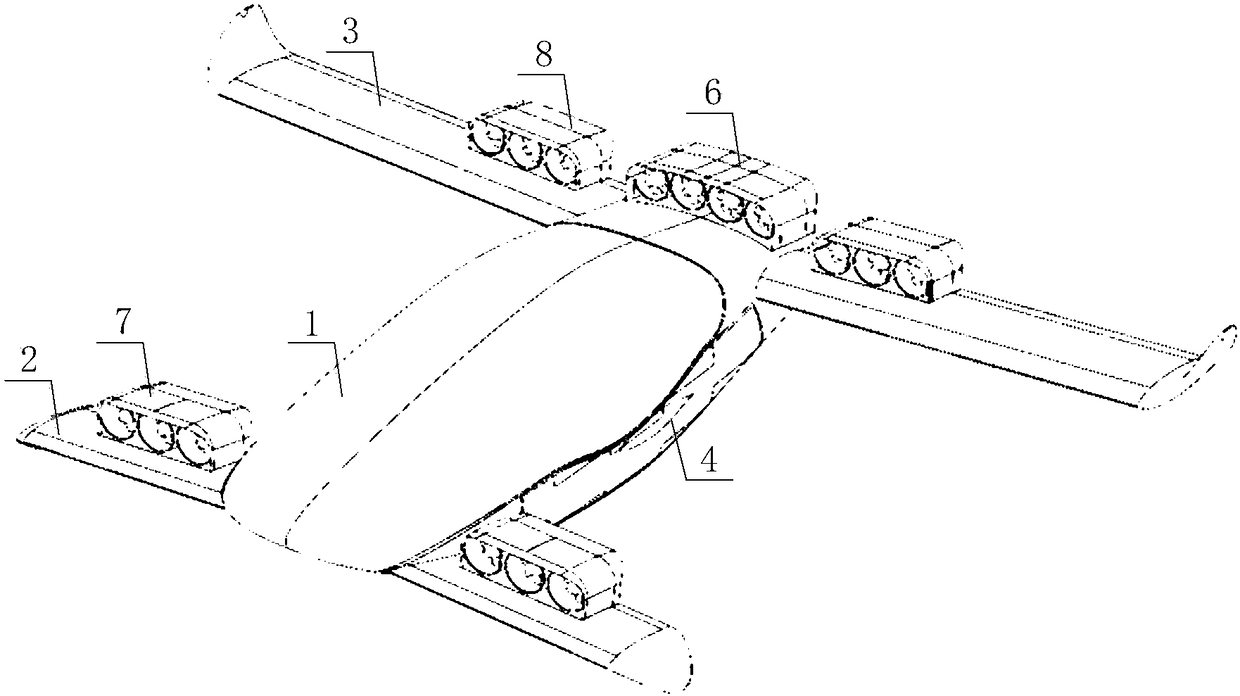
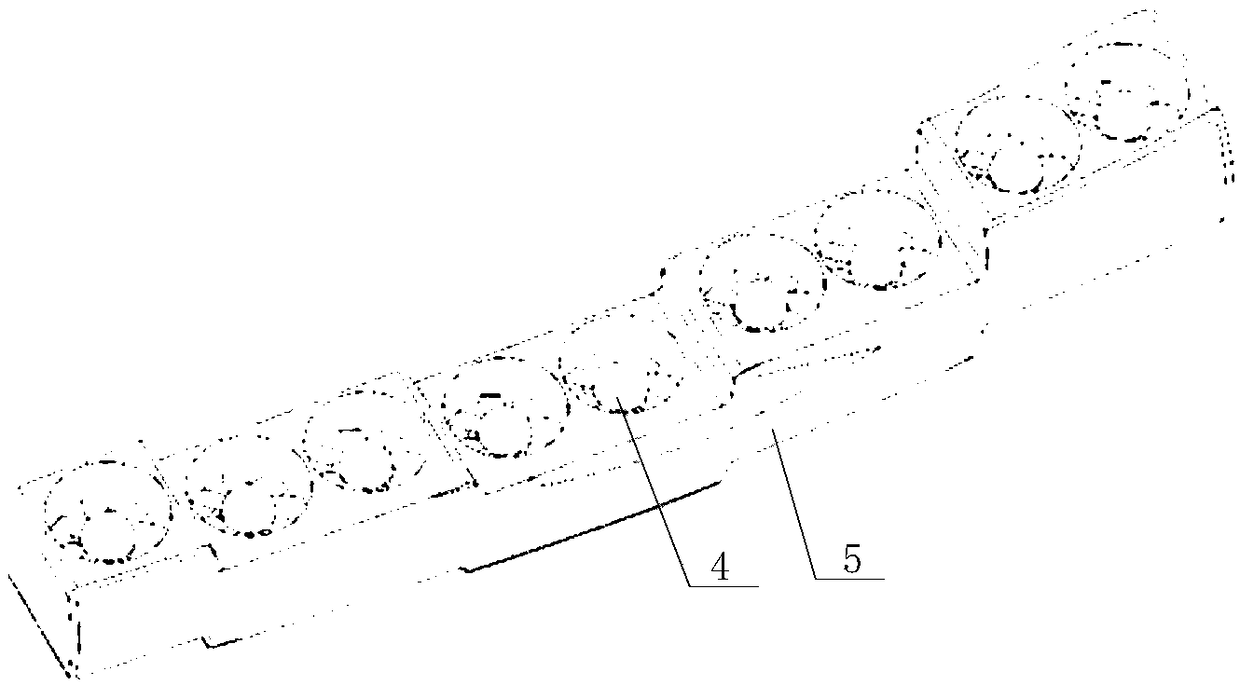
[0026] Please refer to Figure 1 to Figure 4 , in a specific embodiment, the aircraft provided by the specific embodiment of the present invention includes a fuselage body 1, two front wings 2 symmetrically arranged at the head of the fuselage body 1 and two symmetrically arranged at the tail of the fuselage body 1 The main wing 3, the front wing 2 is the lower wing, the main wing 3 is the upper wing, the root-to-tip ratio of the main wing 3 and the front wing 2 is 1:1, and there is no sweep angl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com