Turnout action reference curve selection method and application thereof
A technology of reference curves and actions, applied in the field of rail transit, can solve problems such as missed and false reports of turnout faults
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
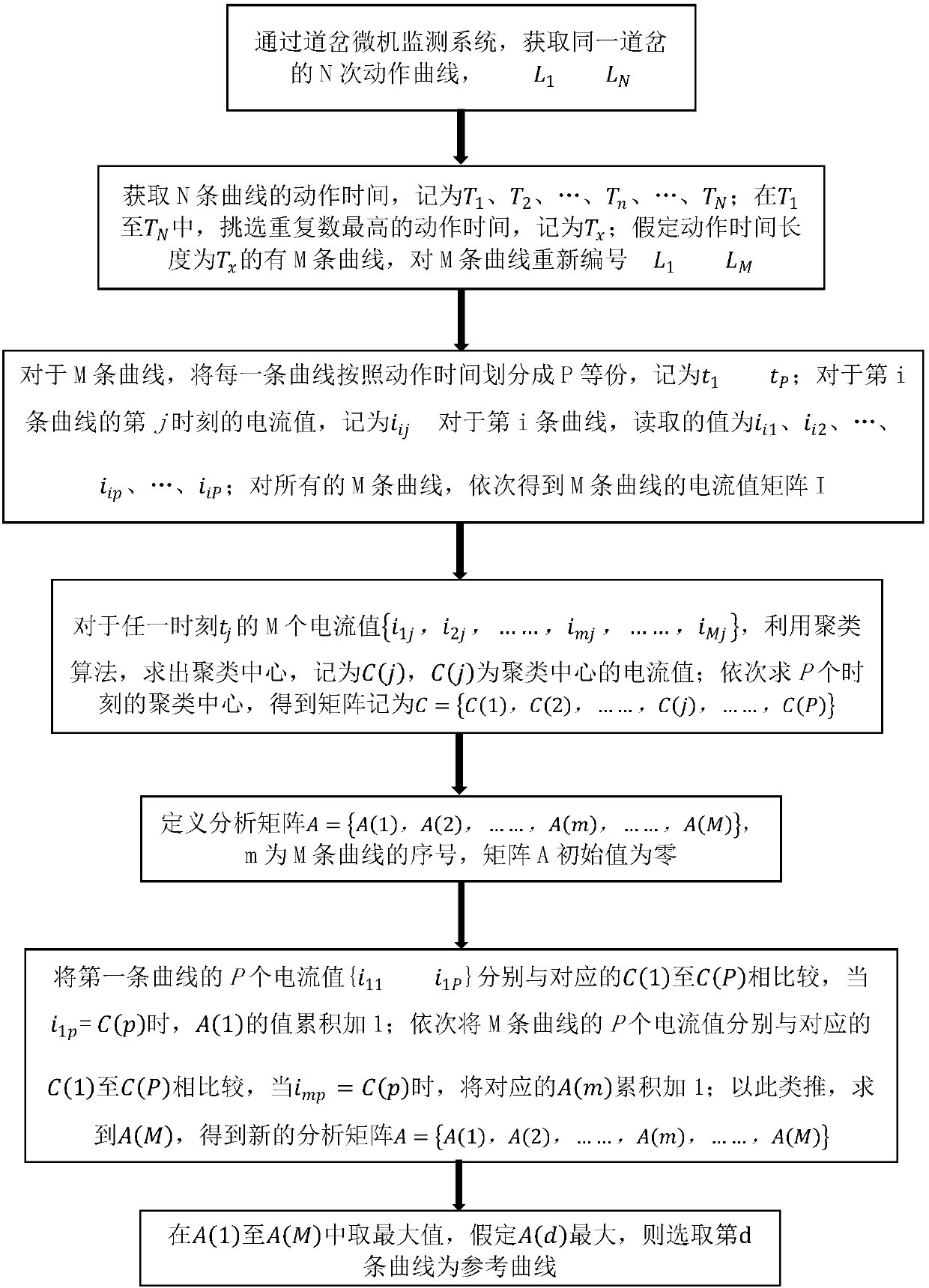
[0066] In this embodiment, a method for selecting a reference curve for a turnout action is provided. figure 1 is a flow chart of a method for selecting a reference curve for a turnout action according to an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in figure 1 As shown, the flowchart includes the following steps:
[0067] Step 1: Obtain the N times action curve of the same turnout through the turnout microcomputer monitoring system, denoted as L 1 ,...,L N ;
[0068] Step 2: Obtain the action time of N curves, denoted as T 1 , T 2 ,...,T n ,...,T N ; at T 1 to T N Among them, select the action time with the highest number of repetitions, and record it as T x ;Assume that the action time length is T x There are M curves, and the M curves are renumbered as L 1 ,...,L M ;
[0069] Step 3: For M curves, divide each curve into P equal parts according to the action time, denoted as t 1 ,...,t P ; For the current value at the jth moment of the i-th curve, denoted ...
Embodiment 2
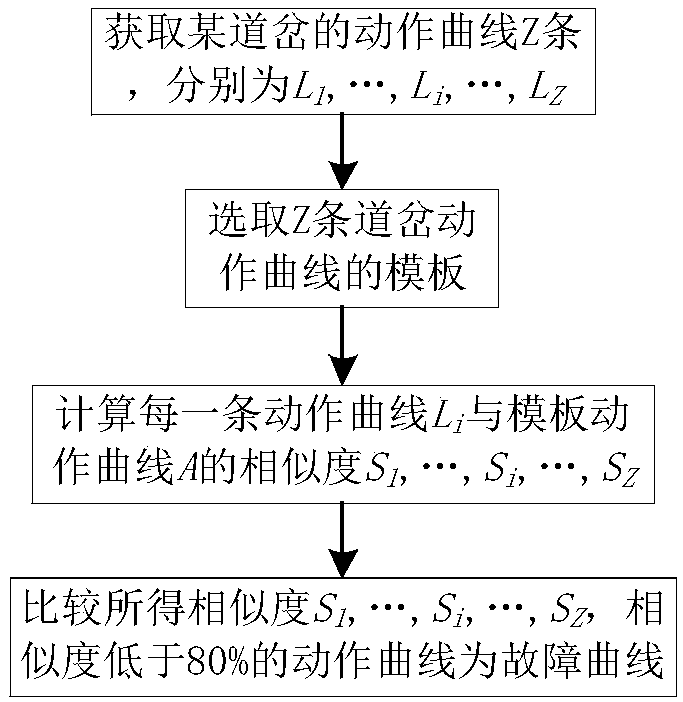
[0088] In this embodiment, a template-based fault diagnosis method is provided, figure 2 It is a flowchart of the template-based fault diagnosis method according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the flowchart includes the following steps:
[0089] Step 1: Obtain the action curve Z of a turnout, which are L respectively 1 ,...,L i ,...,L Z ;
[0090] Step 2: Select the template of Z turnout action curves;
[0091] Step 3: Calculate each action curve L i The similarity S with the template action curve A 1 ,...,S i ,...,S Z ;
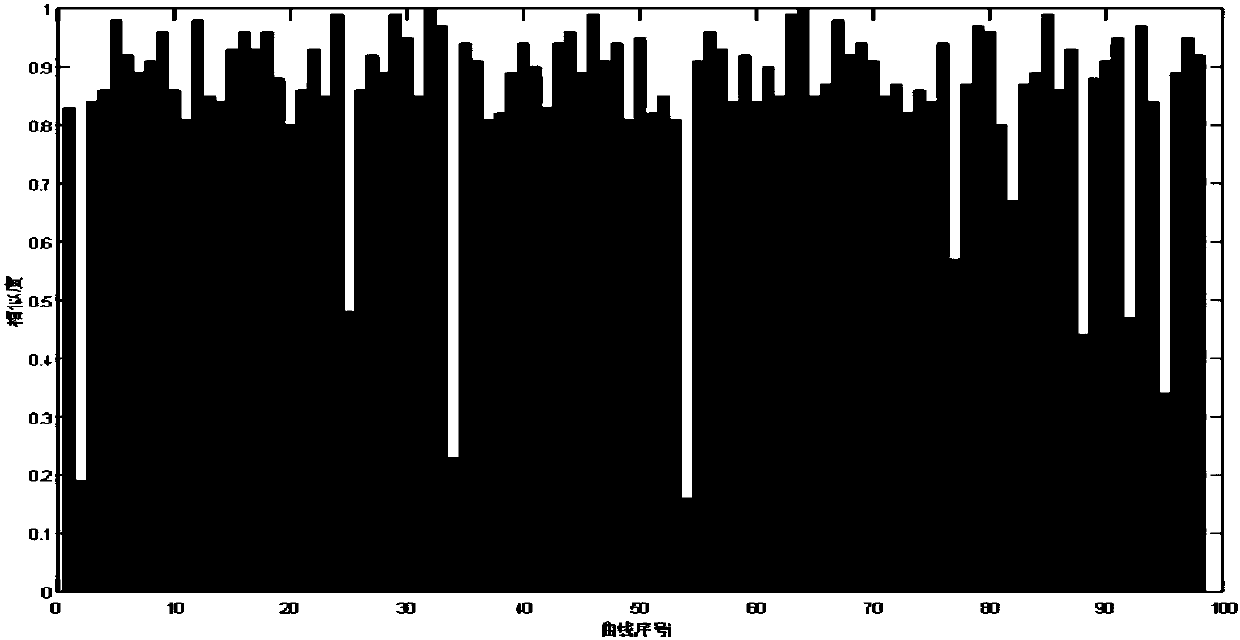
[0092] Step 4: Compare the obtained similarity S 1 ,...,S i ,...,S Z , the action curve whose similarity is lower than 80% is the failure curve.
[0093] Through the above steps, the fault state of the turnout is diagnosed. Compared with the prior art, the inefficiency and unreliability caused by judging the fault state of the turnout through manual experience are solved by the above steps. The problem of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com