Watermelon grain size gene and its SNP molecular marker and application
A technology of molecular markers and watermelon seeds, which is applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as the inability to determine the position and effect of a single quality/quantity trait gene, difficulty in screening, and many candidate genes, so as to achieve accurate directional genetic improvement, improve accuracy and The effect of selecting efficiency and accelerating the improvement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Determination of watermelon seed size genes and development of molecular markers
[0038] 1. Fine mapping of main effect QTL for watermelon seed size
[0039] F 2 The high-density genetic linkage map constructed by the population, the parents, F 1 and F 2 Visual identification of grain size in 93 single melons from the population; combined genetic linkage map and F 2 As a result of population phenotype identification, the Rqtl-IM-binary method was used for initial QTL mapping, and the main QTL for grain size was identified, with a peak LOD of 46.94, explaining 26.16% of the phenotypic variation, and a confidence interval (2-LOD) of 3.68 ~31.67 cM.
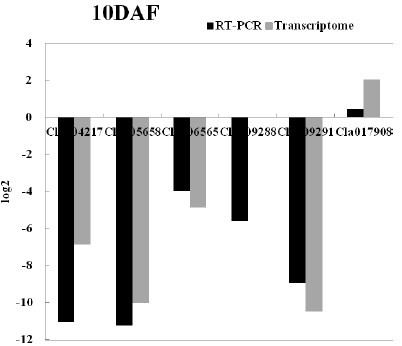
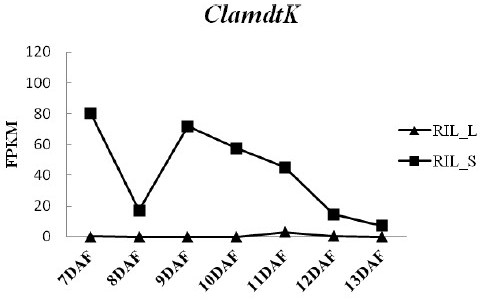
[0040] 2. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of kernel size correlation
[0041] (1) Construct recombinant inbred lines (RILs) by using the watermelon large-grain female parent "ZXG01478" and small-grain male parent "14CB11", and screen one of the large-grain (RIL_L) and small-grain (RIL_S) postanthesis 7, 8...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: Watermelon F 2 Population molecular marker analysis
[0054] 1. Using CTAB method to extract watermelon F 2 The total DNA of the leaves of the population, the specific steps are as follows:
[0055] (1) Put 1 g of fresh leaves into a mortar, add liquid nitrogen to grind into powder, then transfer to a centrifuge tube with 1 ml of CTAB extraction solution, mix the two thoroughly, and then place in a constant temperature water bath at 65°C 60 min, during which the mixture was inverted 2 to 3 times;
[0056] (2) After taking it out from the water bath, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 1 min;
[0057] (3) Take the supernatant and put it in another centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform: isoamyl alcohol, and gently invert to mix well; the volume ratio of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol is 24:1;
[0058] (4) Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 min, and take the supernatant;
[0059] (5) Add 0.7 times the volume of pre-cooled isopropanol and mix well, then f...
Embodiment 3
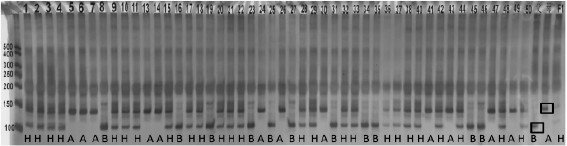
[0091] Embodiment three: F 2 Population genotype analysis
[0092] Carry out dcaps9_S6 molecular marker through embodiment 2 in constructing F by " ZXG01478 " and " 14CB11 " 2 After genotype identification in the population, examine the dcaps9_S6 molecular marker for both genotypes at 93 F 2 distribution across populations, the dcaps9_S6 genotype was found to completely co-segregate with the kernel size phenotype. The results are shown in Table 2, where A represents the maternal band type, B represents the paternal band type, and H represents the heterozygous genotype.
[0093] The genotype of the molecular marker dcaps9_S6 was B (113bp) in 24 of the 69 small-grain (thousand-grain weight<37g) lines, and H in 44. In the 24 large-grain lines, all of them were A (142bp).
[0094] The 24 strains with molecular marker InDel14_S6 genotype A are all large-grained strains, while the 24 strains with genotype B are all small-grained strains. The accuracy rate of genotype identifica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com