Method for reprogramming cancer cells into non-cancer cells in vivo and application thereof
A technology for reprogramming and purpose, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as poor prognosis and recurrence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
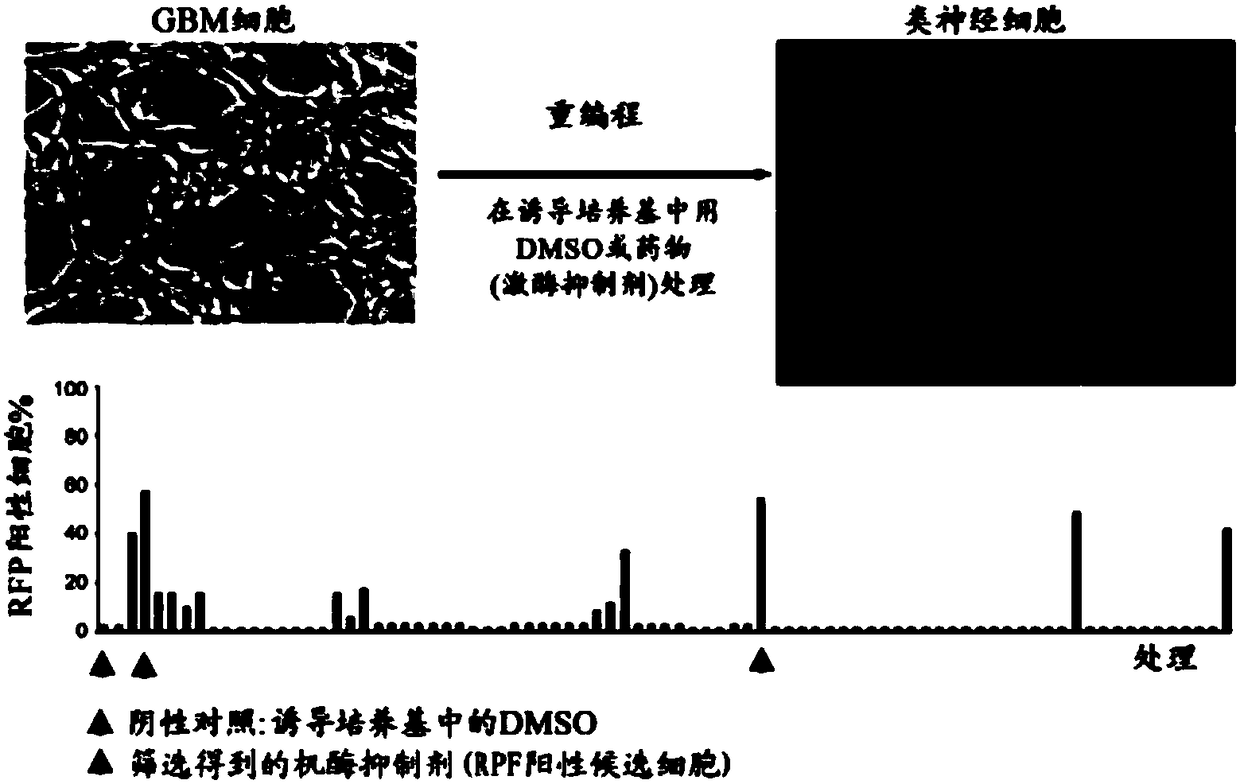
[0116] Example 1: Screening of a library of protein kinase inhibitors against reprogrammed GBM cells
[0117] Because many protein kinases are known to be involved in aging and proliferation processes and thus have important functions in cancer cell reprogramming, a protein kinase inhibitor library (Calbiochem) containing 355 inhibitors was screened to identify potential inhibitors capable of reprogramming cancer cells. candidate compound.
[0118] Screening is performed by culturing cancer cells, in particular GBM cell lines, in induction media in combination with candidate protein kinase inhibitors and monitoring changes in cell morphology. A candidate protein kinase inhibitor has the ability to reprogram and transform cancer cells into normal cells when detectable morphological changes in cultured cancer cells are observed.
[0119] Materials used for screening are described in detail below.
[0120] Material
[0121] Cells: GBM cell lines U138, U118, U87, GM139 and GM97...
Embodiment 2
[0152] Example 2: Characterization of neurons generated by transformation of GBM cells with a combination of P529 and Y27632
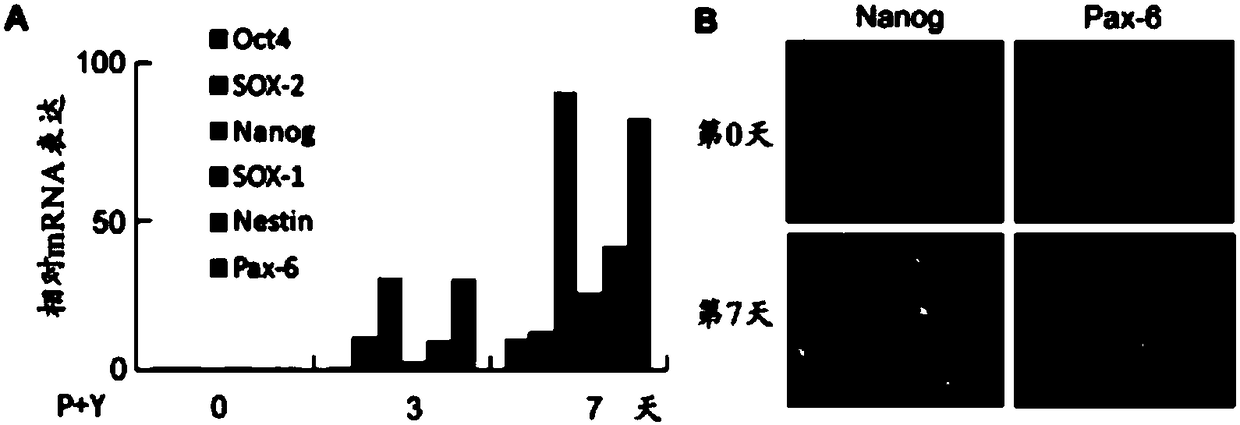
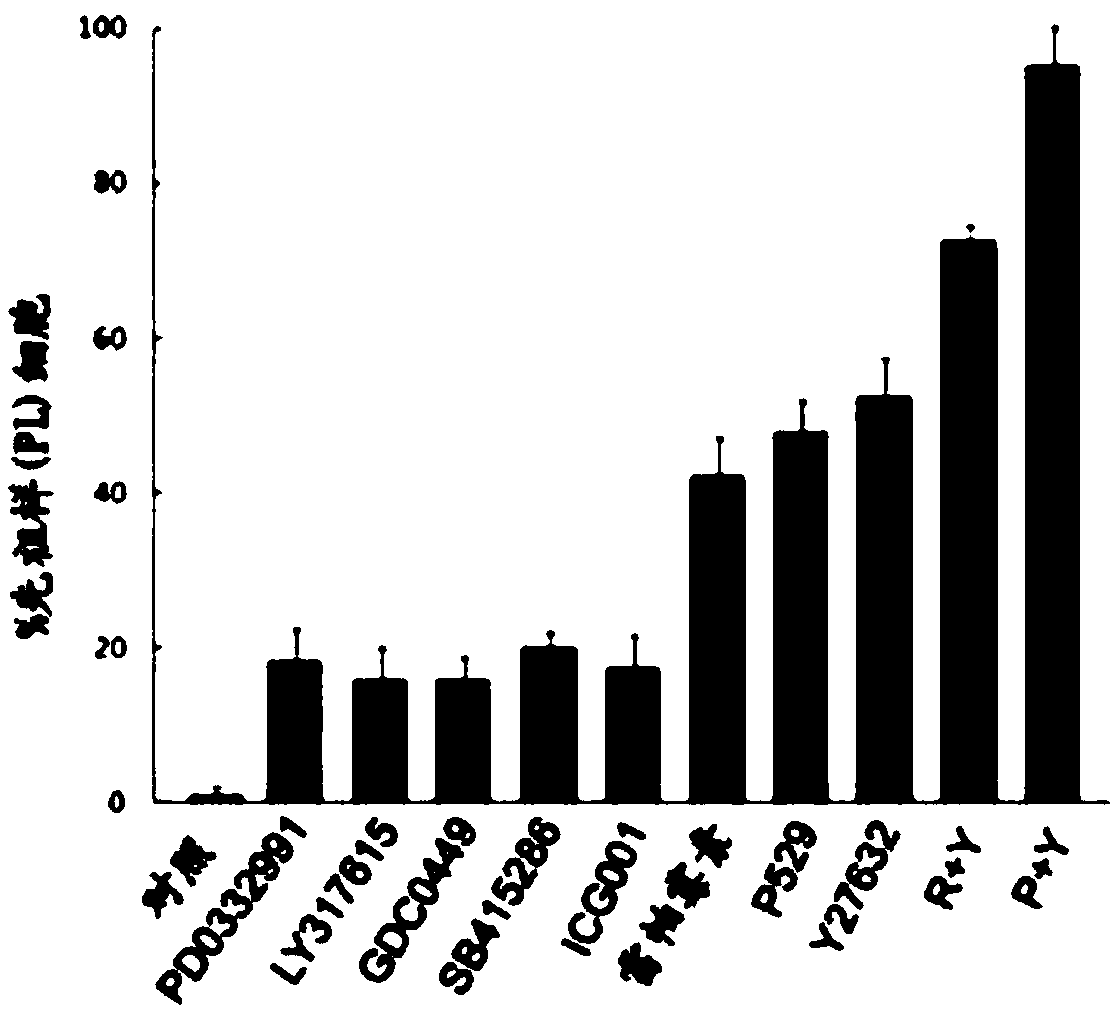
[0153] Using the same method as in Example 1, the transformation efficiency using the combination of P529 and Y27632 was tested and the characteristics of the neuronal products transformed from GBM cells were verified ( Figure 4 ).
[0154] It was observed that in 1-2 weeks, 70%-85% of GBM cells were induced to become neuron-like cells and become iN cells ( Figure 4 A). These iN cells possess the morphology of awakened mature neurons, and the expression of neuronal markers including Tuj1, synapsin, MAP2, vGluT1, GABA and TBR1 ( Figure 4 B). After three weeks of induction, whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings at iNs revealed that 70% of iNs had functional voltage-dependent sodium and potassium currents and were capable of firing multiple action potentials ( Figure 4 C-E). These data suggest that iNs are functional neurons.
Embodiment 3
[0155] Example 3: Treatment of normal neurons and astrocytes with protein kinase inhibitors
[0156] Following the same procedure described in Example 1, mTOR-ROCK inhibitor (P+Y) treatment was also tested on normal neurons and astrocytes to assess whether the treatment had any inducing effect on normal cells. Primary mouse neurons / astrocytes were prepared for testing. Culture properties, neural markers (including MAP2, Prominin, GFAP and S100) and electrophysiological characterization were assessed compared to no-treatment controls (data not shown). found that mTOR‐ROCK treatment did not affect normal neuronal or astrocyte properties. Thus, the reprogramming conditions described in this disclosure are cancer cell specific.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com