Polarization SAR image classification method for polarization scattering non-stationary modeling
A technology of non-stationarity and classification method, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of inability to balance accuracy and operation time, inaccurate classification of scattering mechanism, and large influence of noise in classification results, so as to achieve reliable classification results and reduce the probability of misclassification. , to ensure the effect of the classification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
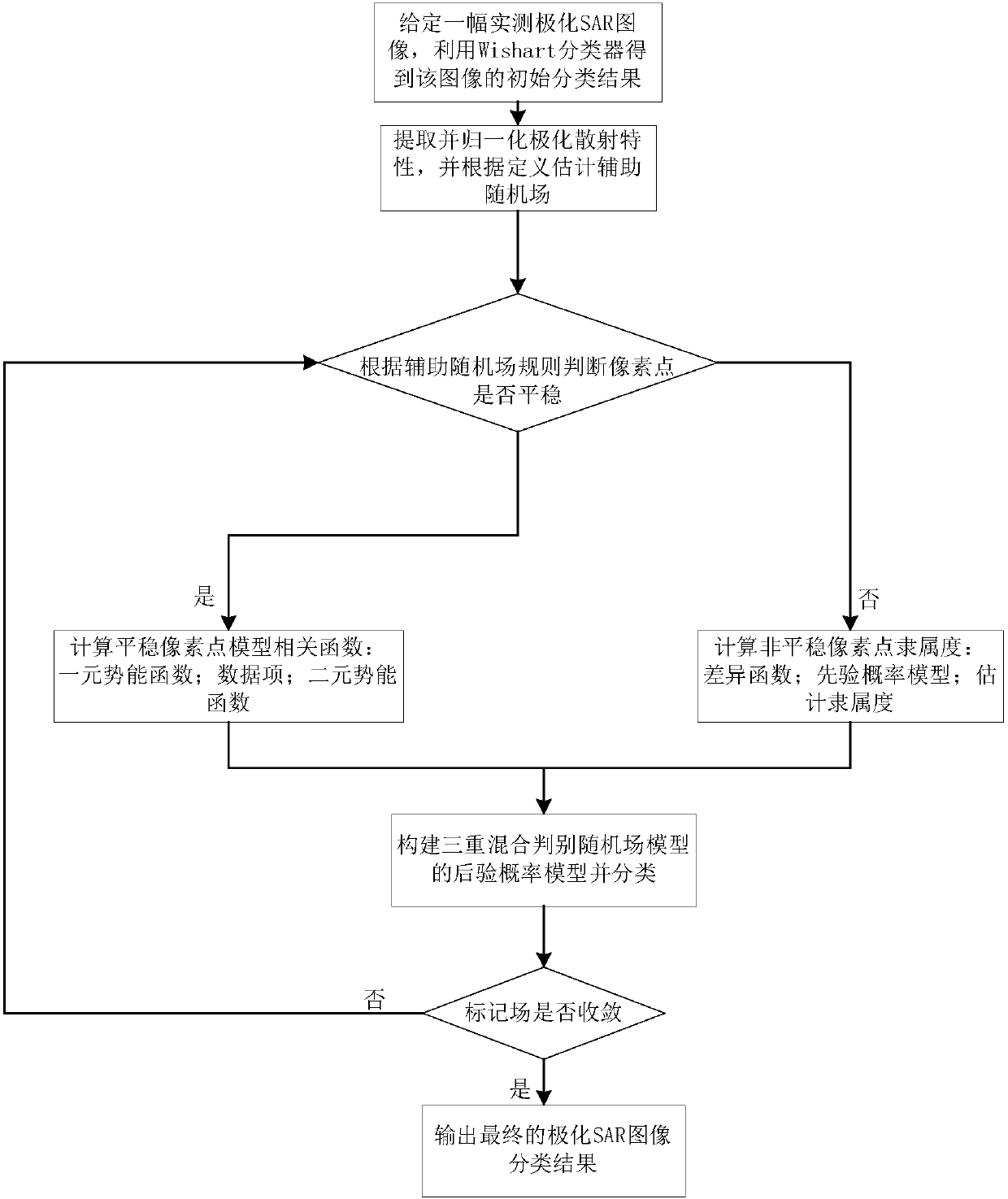
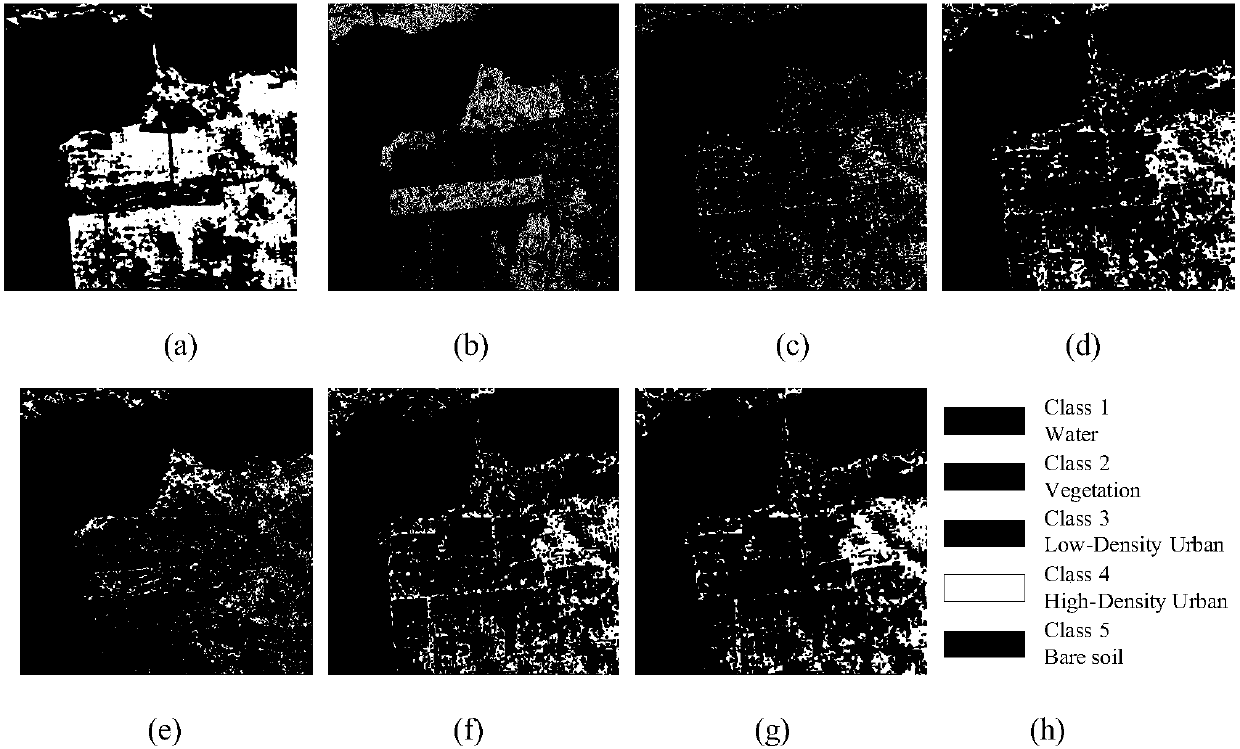
[0030] In the classification of polarimetric SAR images, the main scattering mechanism, that is, the scattering component with the largest proportion, is introduced to better preserve the information of the main scattering mechanism in the classification. However, there are often a large number of mixed pixels in the image, and the type of scattering mechanism at the mixed pixel is extremely complex, and it is difficult to determine which scattering component plays a decisive role. Therefore, it is not accurate to define the scattering component with the largest proportion as the main scattering mechanism of. Benboudjema et al. defined that if the group potential energy function of the label field composed of the category to which the pixel belongs changes with the position of the group, the image is called non-stationary, and the real image is often non-stationary. However, it is difficult to study the non-stationary characteristics of polarimetric SAR data due to factors suc...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The polarization SAR image classification method based on the non-stationary modeling of polarization scattering mechanism is the same as embodiment 1, and the estimation auxiliary random field process described in step (2) includes the following steps to complete:
[0042] a) Divide the polarimetric SAR image into four scattering categories using the following formula: volume scattering P v , dihedral scattering P d , surface scattering P s and mixed scattering P m , this decomposition method has a clear physical meaning, and the classification criterion for the polarization scattering mechanism is easy to define:
[0043]
[0044] Among them, P i is the main scattering mechanism at the pixel point i, η is the preset threshold, take η=0.5, P s ,P d and P v Respectively indicate that the main scattering mechanism categories at pixel i are surface scattering, dihedral scattering and volume scattering, and P m Indicates that there is no obvious main scattering m...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The polarimetric SAR image classification method based on the non-stationarity modeling of the polarimetric scattering mechanism is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2. The specific rules for classifying and iterating pixels in the iterative process are:
[0050] Auxiliary random field u 1 , u 2 , u 3 The pixels in the set are all stable and have their own clear main scattering mechanism. In order to better preserve the information of the main scattering mechanism in the classification process, the iteration rule of the present invention is: during iteration, the constrained stationary pixels belong to a main scattering mechanism. The pixels of the scattering mechanism category can only be classified with the pixels belonging to the same main scattering mechanism category in the next classification process, and the unstable pixels without the main scattering mechanism category can be classified according to the specific results in the next classification process. categ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com