Variable stiffness control device for rope driving robot
A control device and robot technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, manufacturing tools, joints, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to adjust stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
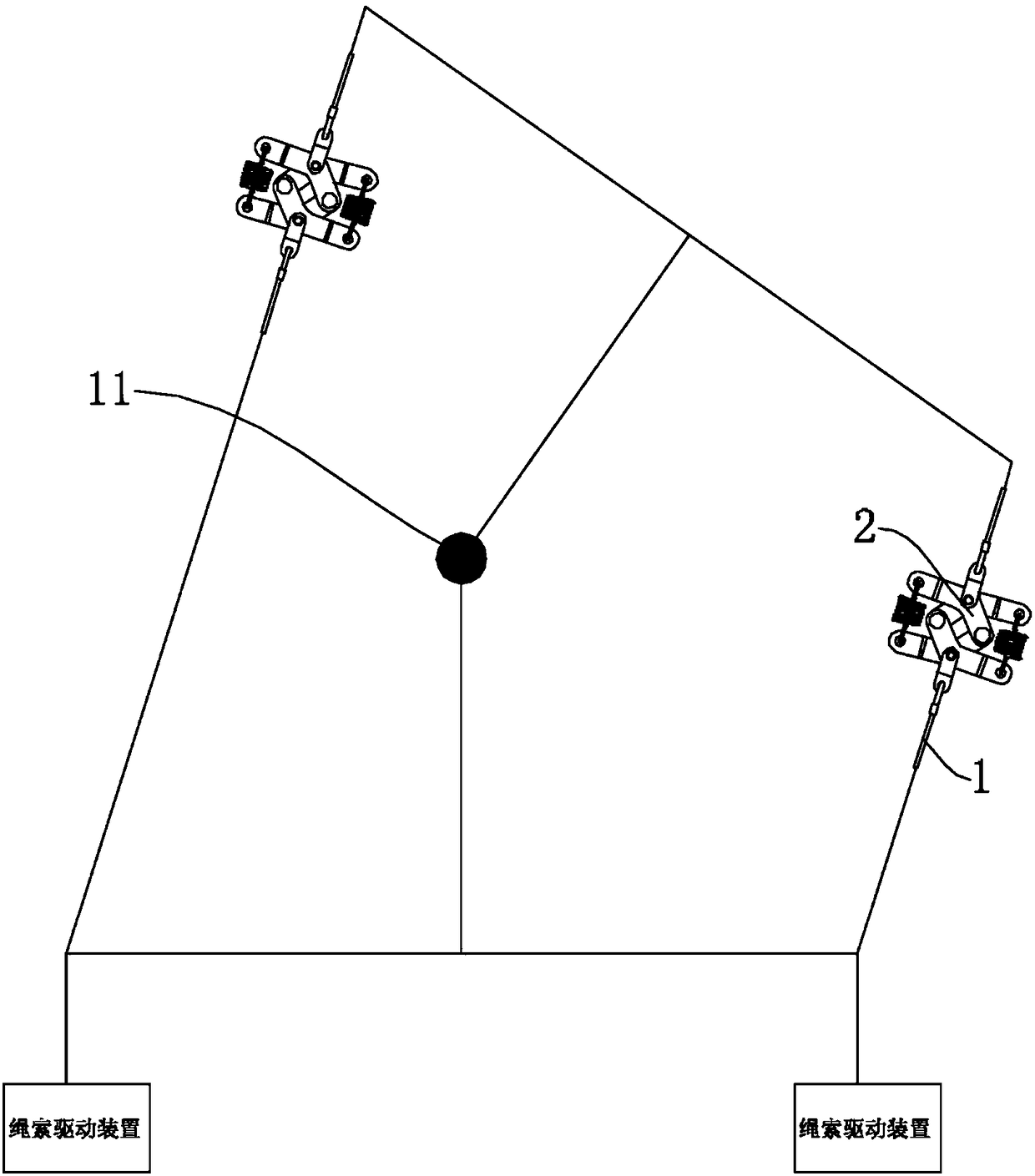
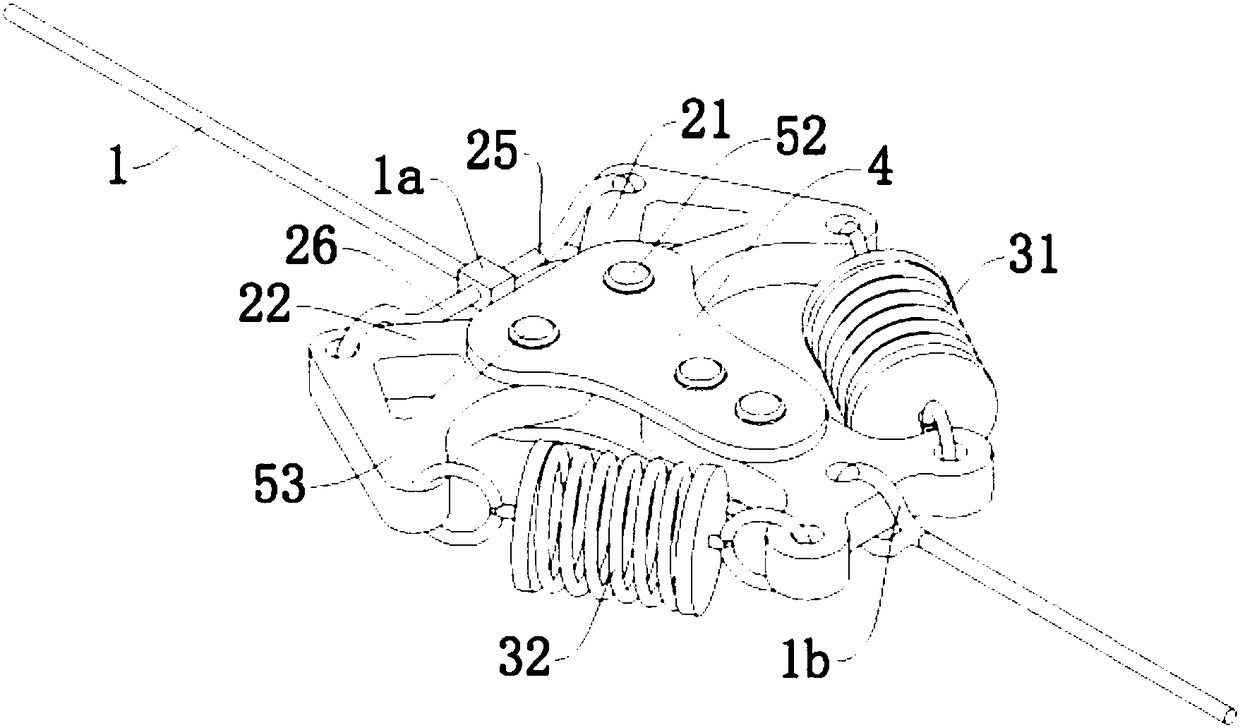
[0037] Such as image 3 with Figure 4 As shown, the diamond-shaped telescopic mechanism 2 in this embodiment has a mounting base 4 . The first rigid adjustment arm 21 and the second rigid adjustment arm 22 are rotatably arranged on the mounting base 4 . The first connection end 1 a is connected to the first rigid adjustment arm 21 through a third arm 25 constituted by a rope segment. The first connection end 1 a is connected to the second rigid adjustment arm 22 through a fourth arm 26 formed by a rope segment.
[0038] The first rigidity adjusting arm 21, the second rigidity adjusting arm 22, the third arm 25 and the fourth arm 26 constitute the four sides of the diamond telescoping mechanism 2, and the rhombus telescoping mechanism is determined by the first rigidity regulating arm 21 and the second rigidity regulating arm 22 2 stretching state. The third arm 25 and the fourth arm 26 can be rope segments or rigid arms, which do not affect the telescopic state between th...
Embodiment 2
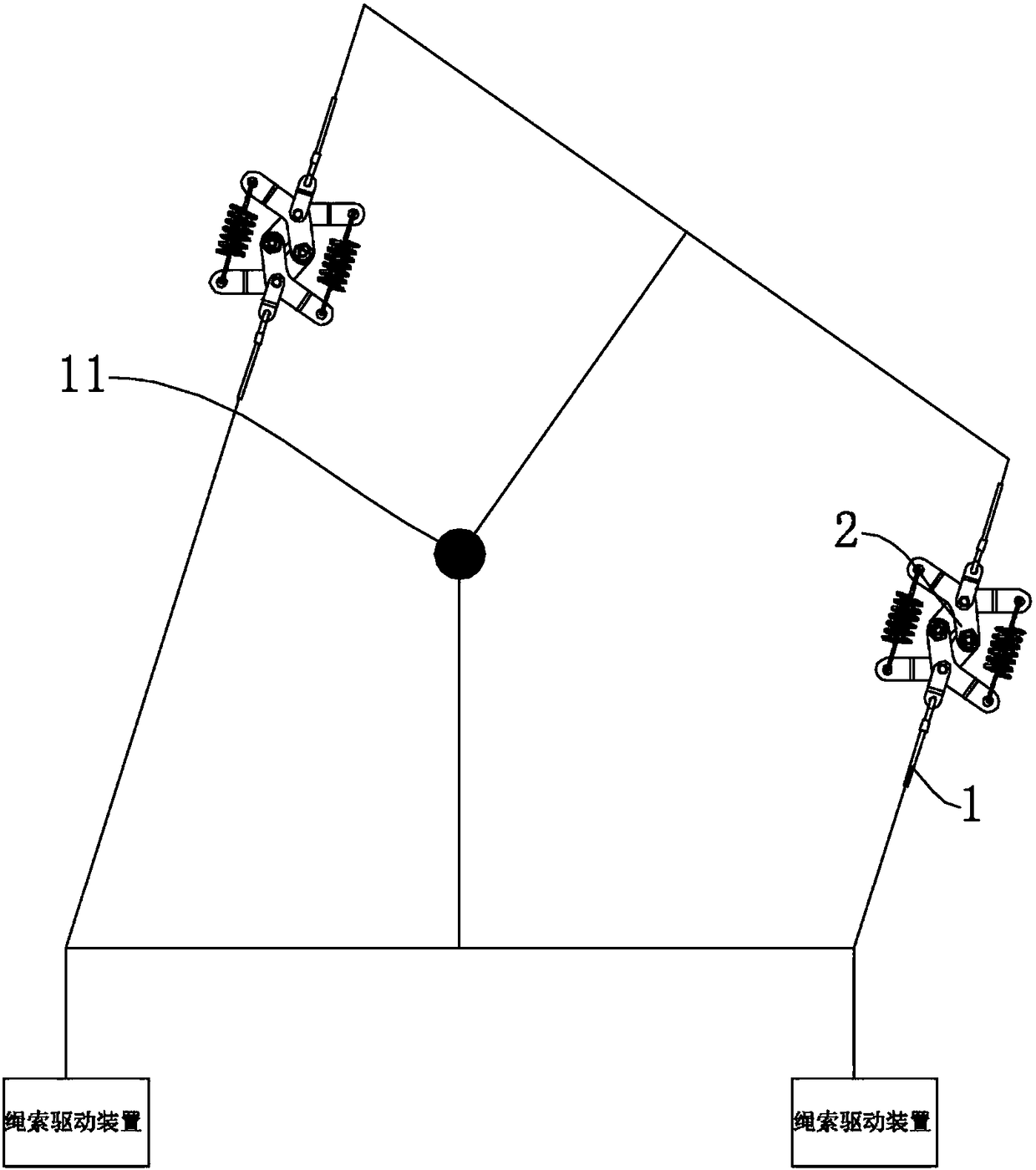
[0043] Such as Figure 5 with Image 6 As shown, in this embodiment, the diamond-shaped telescopic mechanism 2 includes a third rigid adjustment arm 23 and a fourth rigid adjustment arm 24 arranged in a rhombus shape with the first rigid adjustment arm 21 , the second rigid adjustment arm 22 .
[0044] Both ends of the first tension spring 31 are respectively connected to the first extension 21 a of the first rigid adjustment arm 21 and the third extension 23 a of the third rigid adjustment arm 23 .
[0045] Both ends of the second tension spring 32 are respectively connected to the second extension 22 a of the second rigid adjustment arm 22 and the fourth extension 24 a of the fourth rigid adjustment arm 24 .
[0046] The first rigid adjustment arm 21 and the first extension 21a, the second rigid adjustment arm 22 and the second extension 22a, the third rigid adjustment arm 23 and the third extension 23a, the fourth rigid adjustment arm 24 and the fourth extension 24a are L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com