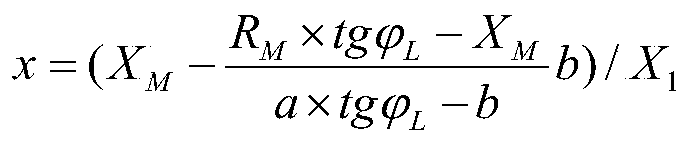A Fault Location Method Based on Fault Indicator Based on Traveling Wave-Impedance Method for Double-terminal Distribution Network with Branch
A technology for fault indicators and distribution network faults, which is applied to fault locations, instruments, and measuring circuits, and can solve problems such as positioning failures and positioning errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] In order to express the purpose and technical solution of the present invention simply and clearly, the following will be described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
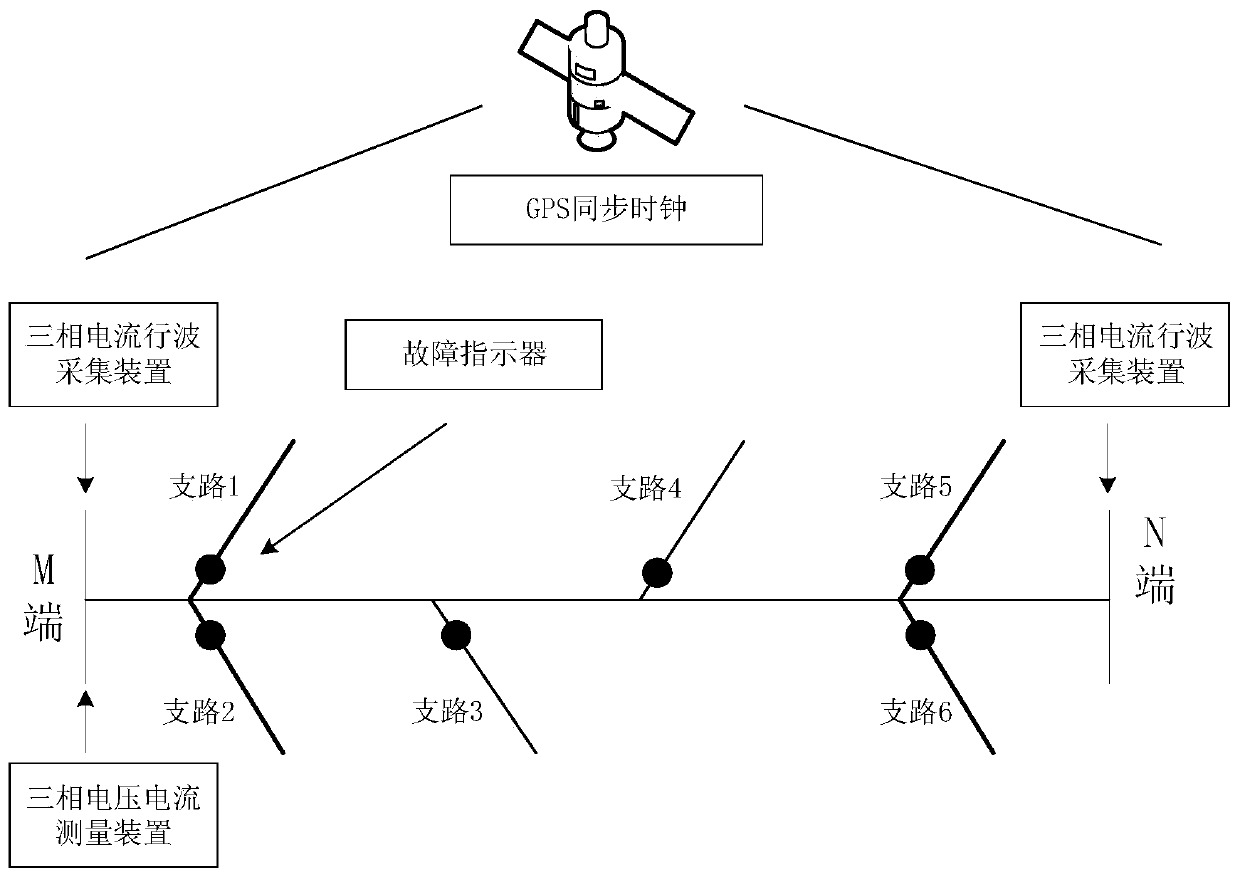
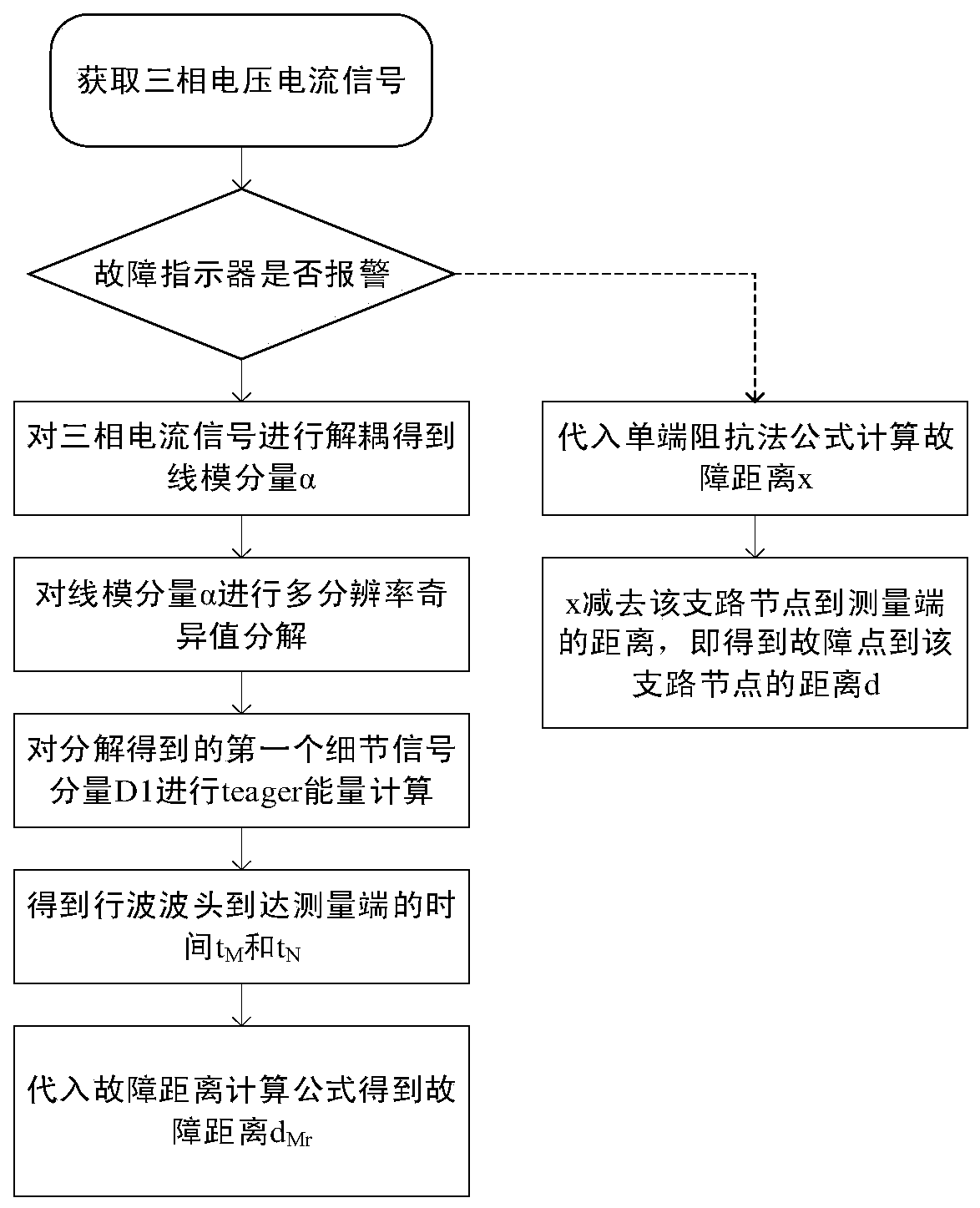
[0046] The transmission line system and positioning system of the double-ended distribution network with branches such as figure 1 As shown, it includes the installation of line system, fault indicator, double-ended traveling wave location system, and single-ended impedance location system. The positioning flow chart is as follows figure 2 shown, according to figure 2 The flow shown, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1: Install traveling wave signal acquisition devices at the first and last sections of the main line of the transmission line, that is, the M terminal and the N terminal, to obtain the three-phase current si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com