Design method for data-driven posture controller of non-cooperative target assembled spacecraft
A non-cooperative target and attitude controller technology, applied in attitude control, space navigation equipment, space navigation equipment, etc., can solve problems such as complex spacecraft design process and unknown parameters of combined spacecraft
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0023] Embodiment one: a data-driven attitude controller design method of a non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1: Establish the attitude kinematics equation and attitude dynamics equation of the attitude control of the non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft;
[0025] Step 2: Obtain a linearized attitude equation according to the attitude kinematics equation and attitude dynamics equation of the non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft attitude control established in step 1, wherein the system matrix parameters are unknown;
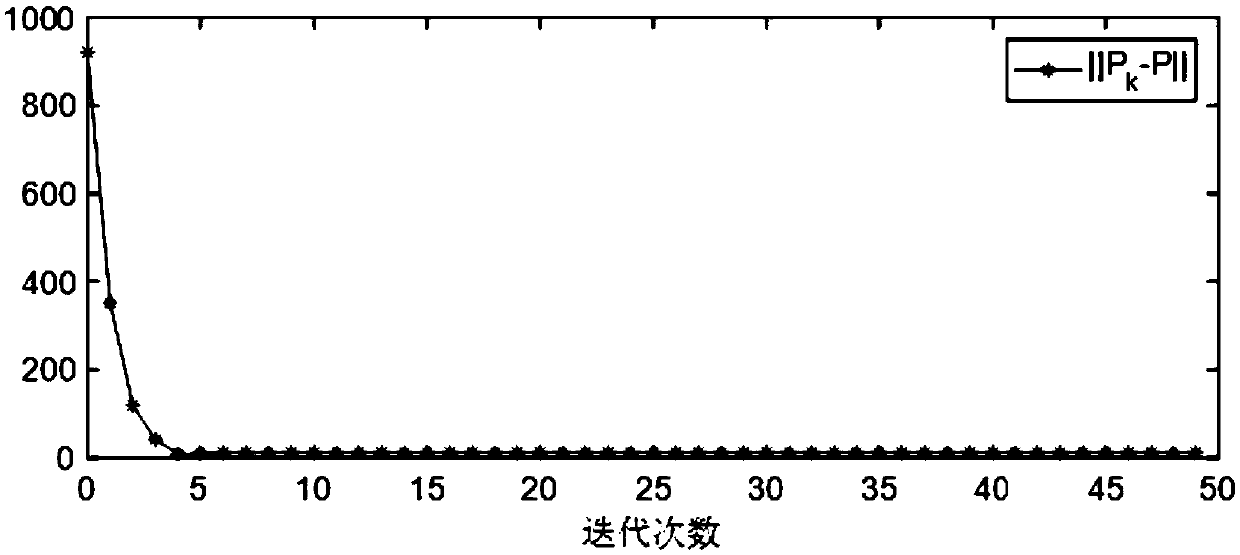
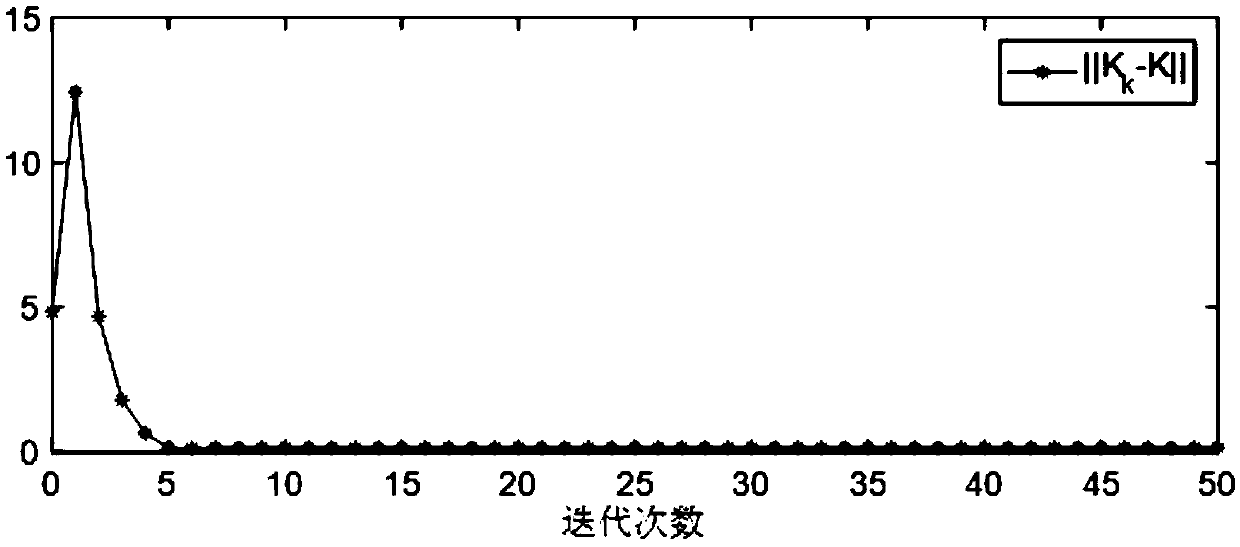
[0026] Step 3: According to the linearized attitude equation obtained in Step 2, use the parameter Lyapunov equation to design the initial feedback gain K of the Kleinman iterative algorithm 0 ;
[0027] Step 4: According to the initial feedback gain K designed in step 3 0 Using a data-driven approach, an attitude controller for a non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft is designed.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the specific process of establishing the attitude kinematics equation and the attitude dynamics equation of the attitude control of the non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft in the step one is:
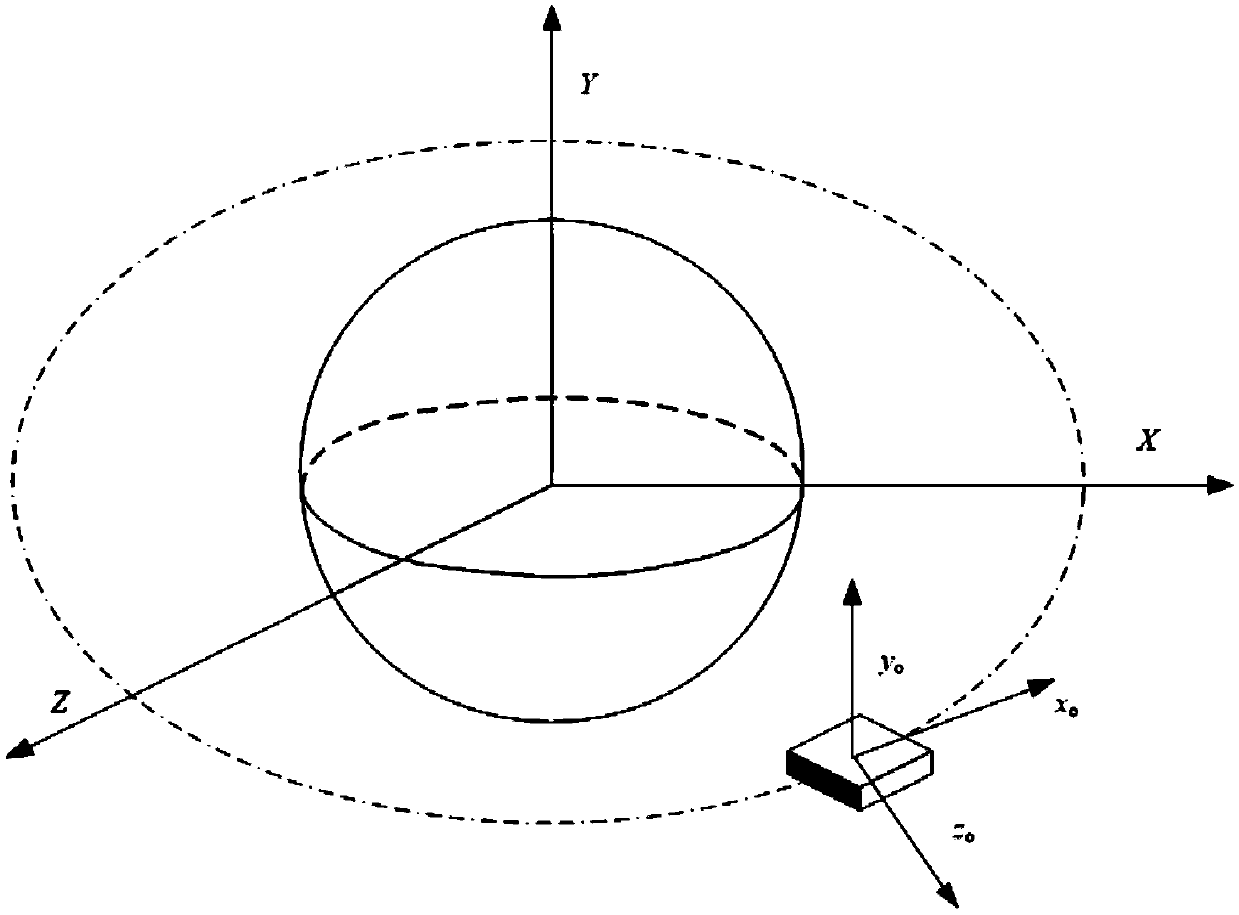
[0029] (1) Coordinate system definition:
[0030] Define the geocentric equatorial inertial coordinate system as OX i Y i Z i , where the origin of the coordinate system is set at the center of the earth O, OX i The axis points to the equinox in the equatorial plane, O i Pointing perpendicular to the equatorial plane to the Earth's North Pole, OY i with OX i and OZ i The two axes form a right-handed vertical coordinate system;
[0031] The orbital coordinate system is O'X o Y o Z o , the coordinate origin is located at the center of mass of the spacecraft, O′X o in the orbital plane, perpendicular to O'Z o axis and point to the spacecraft velocity direction, O′Z o P...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the attitude kinematics equation and the attitude dynamics equation of the attitude control of the non-cooperative target assembly spacecraft established according to the step 1 in the step 2 are linear The specific process of transforming the attitude equation is:
[0052] at the equilibrium point q * =[0 0 0 1] T and ω * =[0-ω 0 0] T Linearize attitude kinematics equation (1) and attitude dynamics equation (2) to get:
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] in for q 1 The first derivative of , for q 2 The first derivative of , for q 3 The first derivative of , ω 0 represents the angular velocity of the spacecraft revolving around the earth, for ω rx The first derivative of , for ω ry The first derivative of , for ω rz The first derivative of ;
[0056] Spacecraft roll angle ψ, pitch angle θ, yaw angle The relationship with the quaternion q is: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com