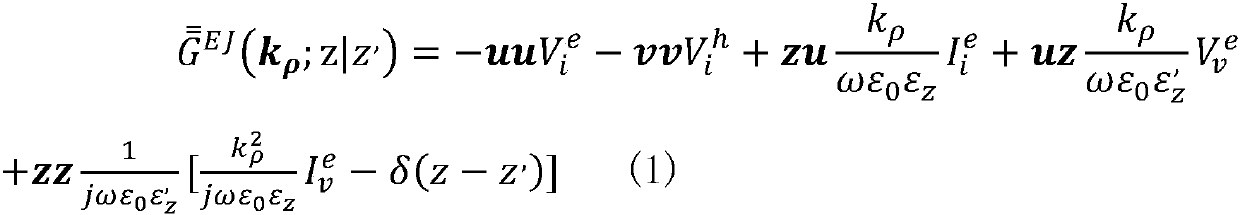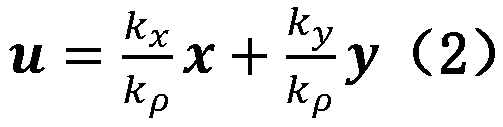Frequency domain reverse time migration algorithm based on layered medium Green's function
A technology of Green's function and layered media, which is applied to the re-radiation of sound waves, the reflection/re-radiation of radio waves, and instruments, etc., which can solve the problems of limited engineering applications, high computational cost of time-domain reverse time migration algorithm, and incapable of real-time data Dealing with and other issues to achieve the effect of saving computing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
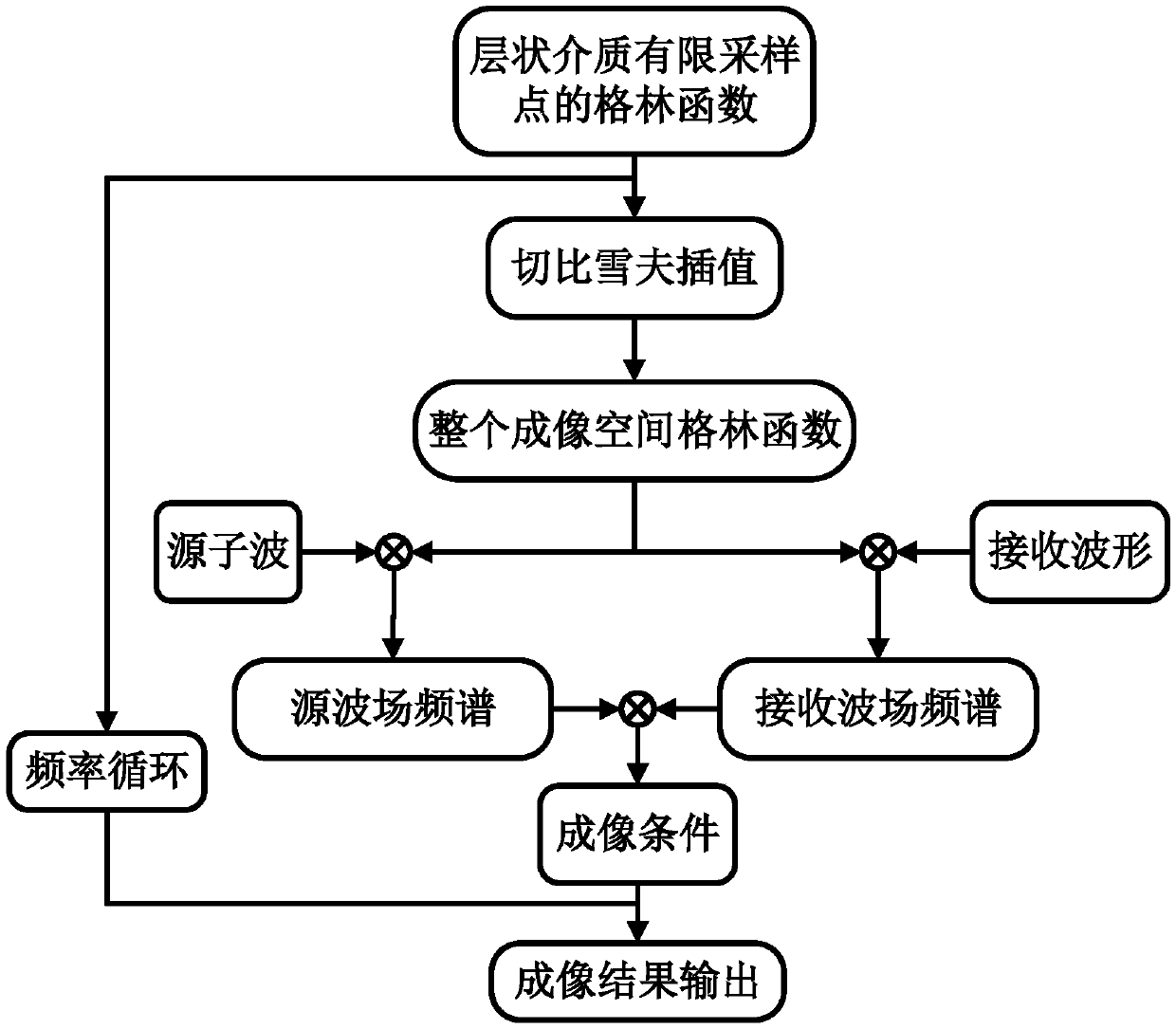
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, a frequency domain reverse time migration algorithm based on layered medium Green's function includes the following steps:
[0033] Step 1. First calculate the dyadic Green's function of the diagonal sampling points in the layered medium space within the effective frequency band, and obtain the Green's function of the entire imaging space through Chebyshev interpolation. Taking the electromagnetic field as an example, the specific steps to calculate the dyadic Green's function of the diagonal sampling point in the layered medium space are as follows:
[0034] Set the propagation direction of the wave as z, since the transverse medium perpendicular to z is uniform and infinitely extended, calculate the electric field type Green's function of the electric field E generated by the current source J
[0035]
[0036] The unit vector (u, v) in formula (1) is the rotation coordinate vector defined in the spectrum domain, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com