Engine intelligent idling control system and method
An engine controller, idle speed control technology, applied in the control device, transportation and packaging, driver input parameters and other directions, can solve the problem of vehicle braking and other problems, and achieve the effect of solving the effect of coasting braking.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
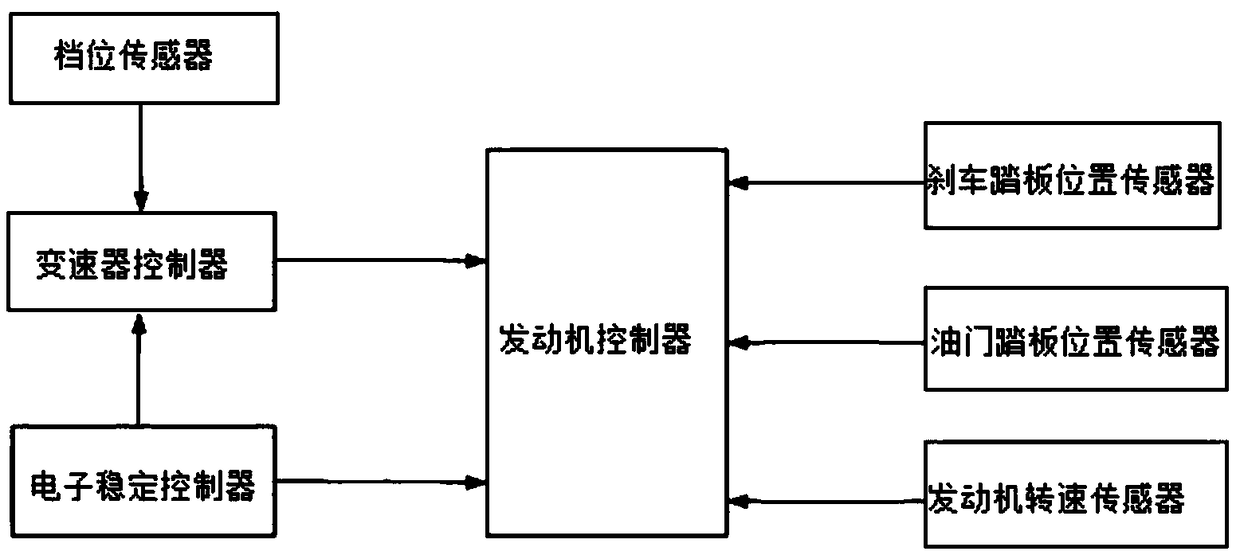
[0038] see figure 1 , which is a block diagram of the engine intelligent idle speed control system of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the engine intelligent idle speed control system of the present invention includes an engine speed sensor, an accelerator pedal position sensor, a brake pedal position sensor, an electronic stability controller, a gear sensor, a transmission controller and an engine controller.
[0039] The engine speed sensor is used to collect the idle speed of the engine.
[0040] The brake pedal position sensor is used to collect the brake pedal position.
[0041] The accelerator pedal position sensor is used to collect the accelerator pedal position.
[0042] The system also includes a gear position sensor, a wheel speed sensor and an electronic stability control system. The gear sensor is used to collect the current gear and the target gear. The electronic stability control system includes an electronic stability controller, a wheel ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com