Ink jet printing method
An inkjet printing and print-driven technology, applied in the field of inkjet printing, can solve problems such as inability to print images of qualified quality, and achieve the effects of improving printing efficiency, ensuring printing quality, and avoiding paper waste.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
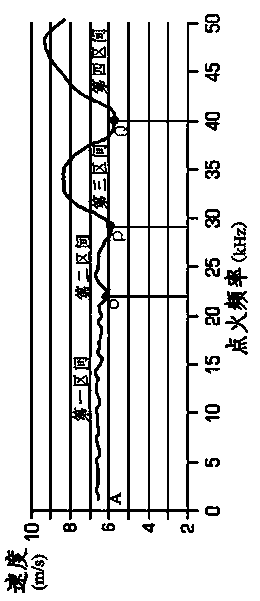
[0030] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the relationship curve between the ignition frequency of the nozzle and the ejection speed of ink droplets. Specifically, the ignition frequency of the nozzle is within the range of 0 to 50kHz (50kHz is the maximum ignition frequency of the nozzle), and most of the ink droplets (more than 90%) from The velocity injection curve of the nozzle ejection. It can be seen from the figure that the ignition frequency reaches 6.5m / s from position A, and then basically tends to be stable, and the speed does not change significantly until point O. The corresponding nozzle ignition frequency at point O is 22kHz. This section of ignition frequency interval is defined as the first interval, the ignition frequency of the first interval is greater than 0kHz and less than 22kHz; after point O, the waveform representing the change in speed begins to have a small amount of fluctuation, and the corresponding nozzle ignition frequency at point P is 29kH...
Embodiment 2
[0036] For the above figure 1 When using the nozzle with the characteristics of the nozzle shown in , you can also reduce the image printing resolution to avoid the problem of poor printing quality in the third interval and the fourth interval. Specifically, if the resolution of the original printed image is 600dpi, the image effect printed by the nozzle at the beginning of the acceleration stage meets the requirements, and there is a problem with the print quality after the ignition frequency reaches 29kHz, that is, point P, then the printer’s print quality at 29kHz Speed V 29kHz =29000Hz / 600dpi×2.54=122.8cm / s. After 29kHz, that is, the P point, start to use the resolution of 400dpi for inkjet printing, and the image that meets the requirements can be printed. Similarly, at the position of point Q when the ignition frequency is 40kHz, the printing speed of the printer V 40kHz =40000Hz / 600dpi×2.54≈169cm / s, if the third interval uses 400dpi for printing, then the actual re...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Such as Figure 6 As shown, it is the nozzle characteristic curve of another nozzle when printing. It can be seen from the curve that the ink droplet ejection speed tends to be stable when the ignition frequency of the nozzle is less than 10kHz. This section is defined as the first interval; ignition When the frequency ranges from 10kHz to 16kHz, the ink droplet ejection speed fluctuates significantly, and this interval is defined as the second interval; after the ignition frequency is greater than 16kHz, the ink droplet ejection speed becomes stable again until the maximum ignition frequency of the nozzle is 20kHz , define this interval as the third interval.
[0040] In the process of accelerating the transmission of the printing medium, the ignition frequency gradually increases. In the first interval, since the ejection speed of the ink droplets is basically stable, the effect of the printed image can also be guaranteed. If the image resolution printed by the nozzle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com