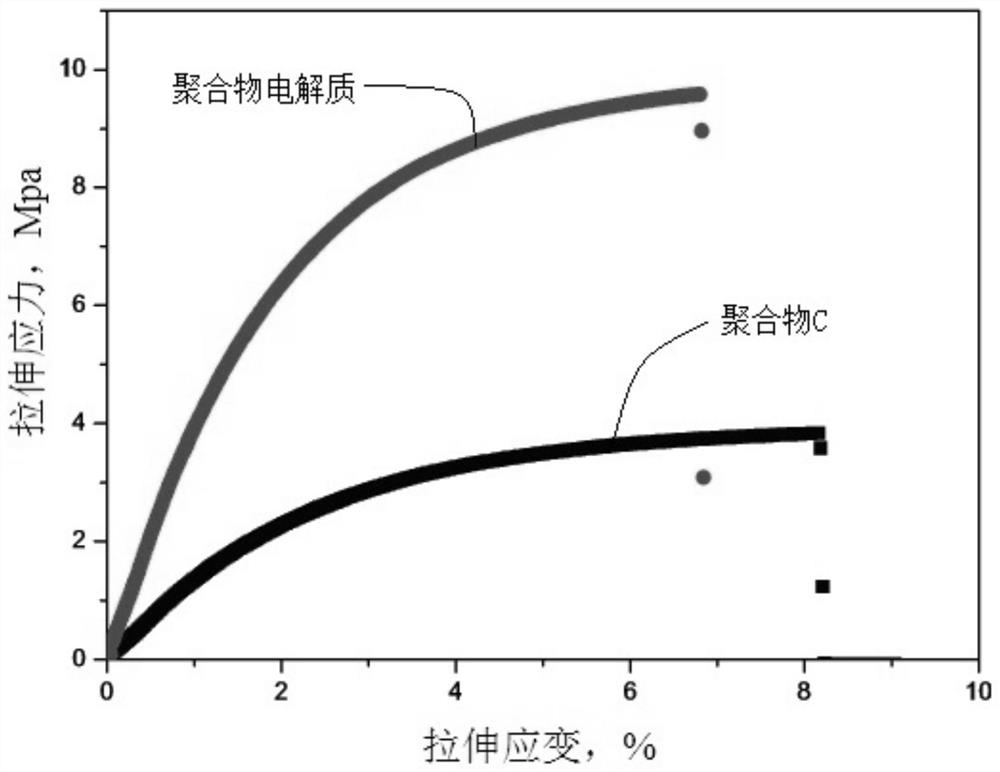
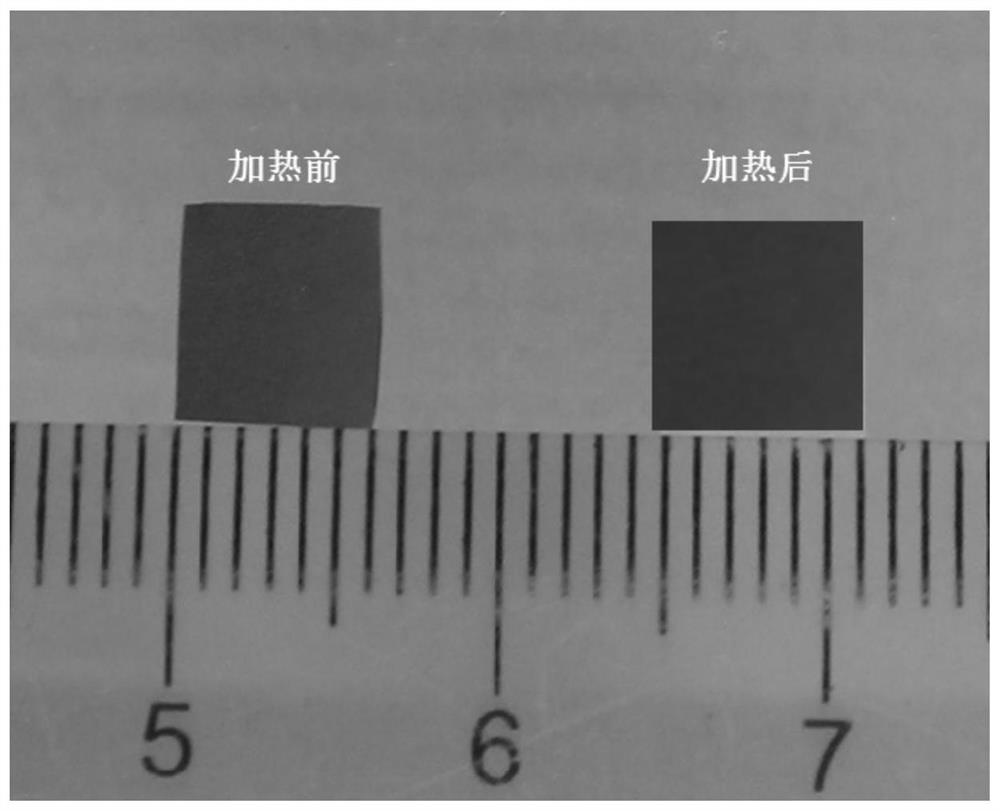
A kind of polymer electrolyte and its preparation method and application
A polymer and electrolyte technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as poor lithium dendrite effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The polymer electrolyte of this embodiment is prepared by the following steps:
[0041] 1) Dissolve 5.66mg of Grubbs in 1.33mL of dichloromethane to obtain a catalyst solution;
[0042] 202mg 5-norbornene-2-dimethyl phosphate (M1), 187mg 5-norbornene-2-polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (M2), 100mg bis-norbornene grafted polyethylene glycol Alcohol (M3) was dissolved in 30mL of dichloromethane to obtain a monomer solution;
[0043] Mix the catalyst solution and the monomer solution, stir and react at room temperature for 10 hours, when the system turns from pink to dark brown, add vinyl ether to terminate the reaction, and distill off the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain polymer A;
[0044] 2) Dissolve polymer A and bromotrimethylsilane in 5 mL of dichloromethane respectively, mix the dissolved two solutions and react at room temperature for 16 h, then add methanol (5-norbornene-2-dimethyl The molar ratio of base phosphate, trimethylbromosilane, and methanol...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The preparation process of the polymer electrolyte in this example is basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that in step 1), the amounts of M1, M2, and M3 added are 202 mg, 236 mg, and 339 mg, respectively, and the molar ratio of M1:Grubbs second-generation catalyst 150:1; step 2), the reduction reaction is to stir the reaction at room temperature for 18h, add methanol and then stir the reaction at room temperature for 28h; step 3), stir the reaction at 85°C for 30h; step 4), in Under 140°C and 4.5MPa, hydrogenation reaction was carried out for 24h.
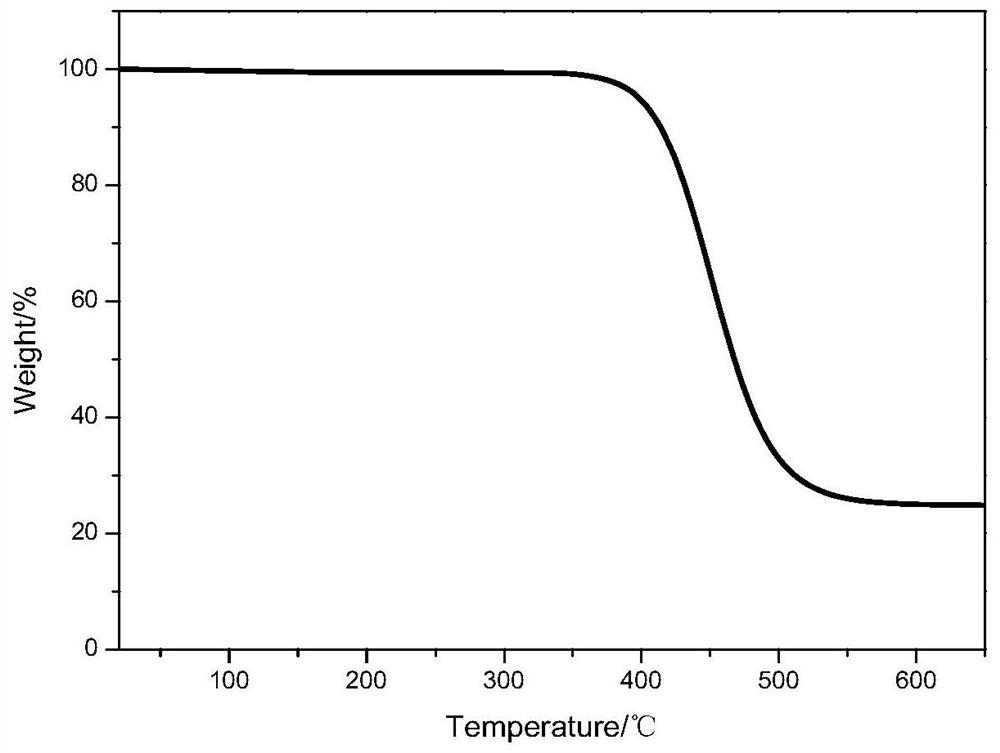
[0053] The initial thermal decomposition temperature of the polymer electrolyte obtained in Example 2 is 356.8°C, and the average polymerization degree ratio of structural unit A (m=10), structural unit B (n=15), and structural unit C is 2:1:1.
Embodiment 3
[0055] The preparation process of the polymer electrolyte in this example is basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that in step 1), the amounts of M1, M2, and M3 added are 202 mg, 340 mg, and 370 mg, respectively, and the molar ratio of M1:Grubbs second-generation catalyst 150:1; in step 2), the reduction reaction is to stir the reaction at room temperature for 20h, add methanol and then stir the reaction at room temperature for 30h; in step 3), stir the reaction at 95°C for 28h; in step 4), in Under 160°C and 5.0MPa, hydrogenation reaction was carried out for 24h.
[0056] The initial thermal decomposition temperature of the polymer electrolyte obtained in Example 2 is 360.2°C, and the average polymerization degree ratio of structural unit A (m=7), structural unit B (n=8), and structural unit C is 1:1:1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com