Improved EMD algorithm based on polynomial
A polynomial and polynomial fitting technology, applied in the field of improved EMD algorithm, can solve problems such as polluting data sequences, achieve smooth signals, improve modal aliasing problems, and smooth EEG signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0039] Method of the present invention comprises the steps:
[0040] Step 1: Taking the starting point of the signal as the center point, select a window with a length of 5 (such as figure 1 Shown), polynomial fitting is carried out on the signal value in this window;
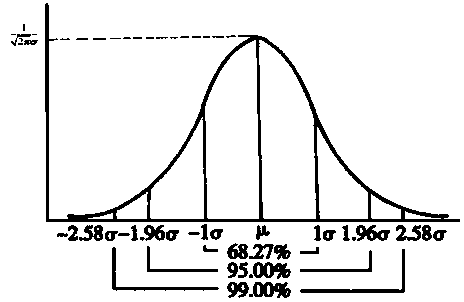
[0041] Step 2: Take the starting point of the signal as the mean point and the variance as 1 to construct a discrete Gaussian signal, Among them, μ is the mean value, that is, the signal value that needs to be denoised, σ is the standard deviation, and the value of the article is 1 (such as figure 2 shown);
[0042] Step 3: The sequence value obtained by fitting in the window is multiplied by the corresponding Gaussian signal value as the denoising value of the central signal;
[0043] Step 4: Slide the window with a step size of 1, and repeat the above steps to complete the denoising of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com