A method for measuring the spatial position of traffic signs based on two-dimensional images
A traffic sign and spatial location technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of measuring equipment, low data processing efficiency, and heavy data collection workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
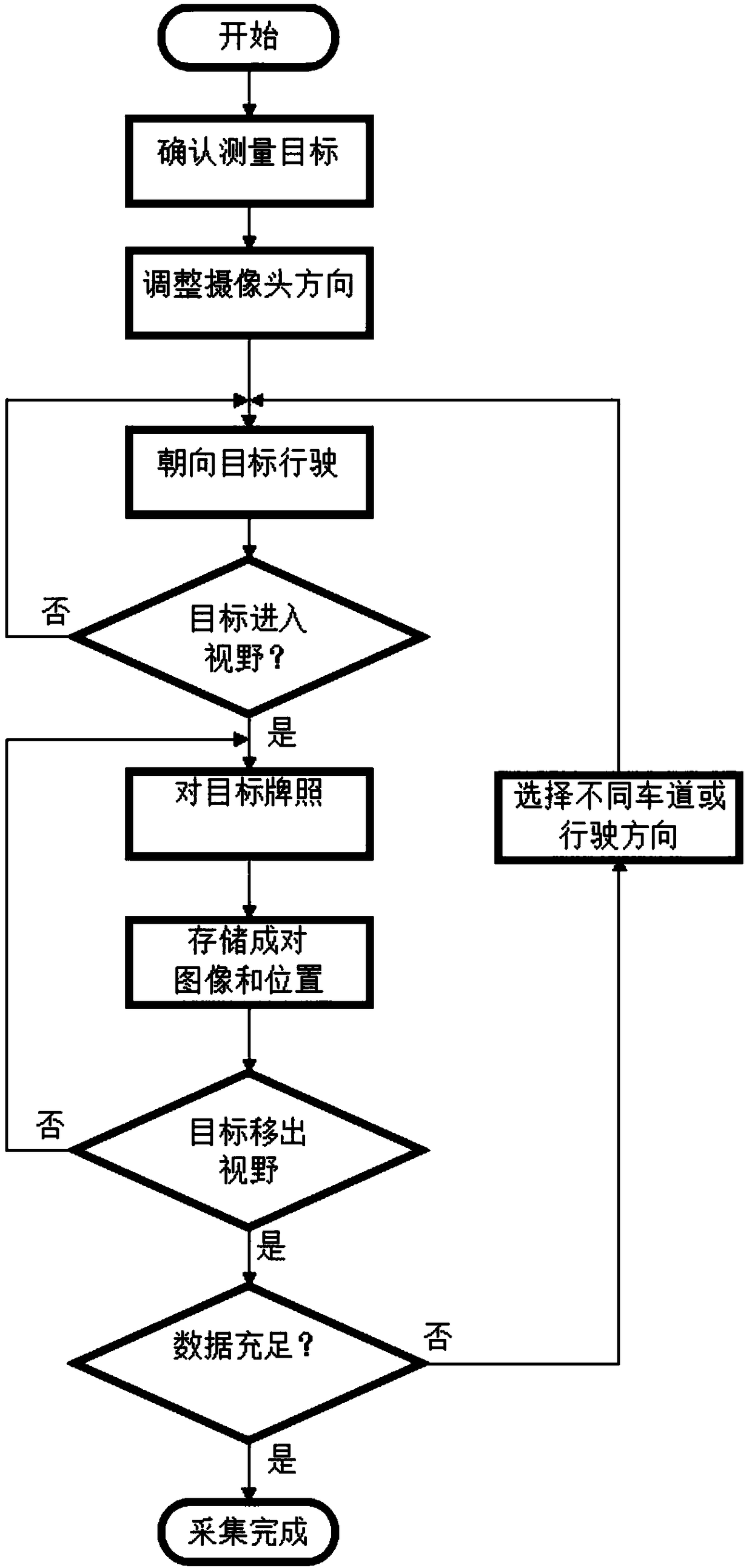
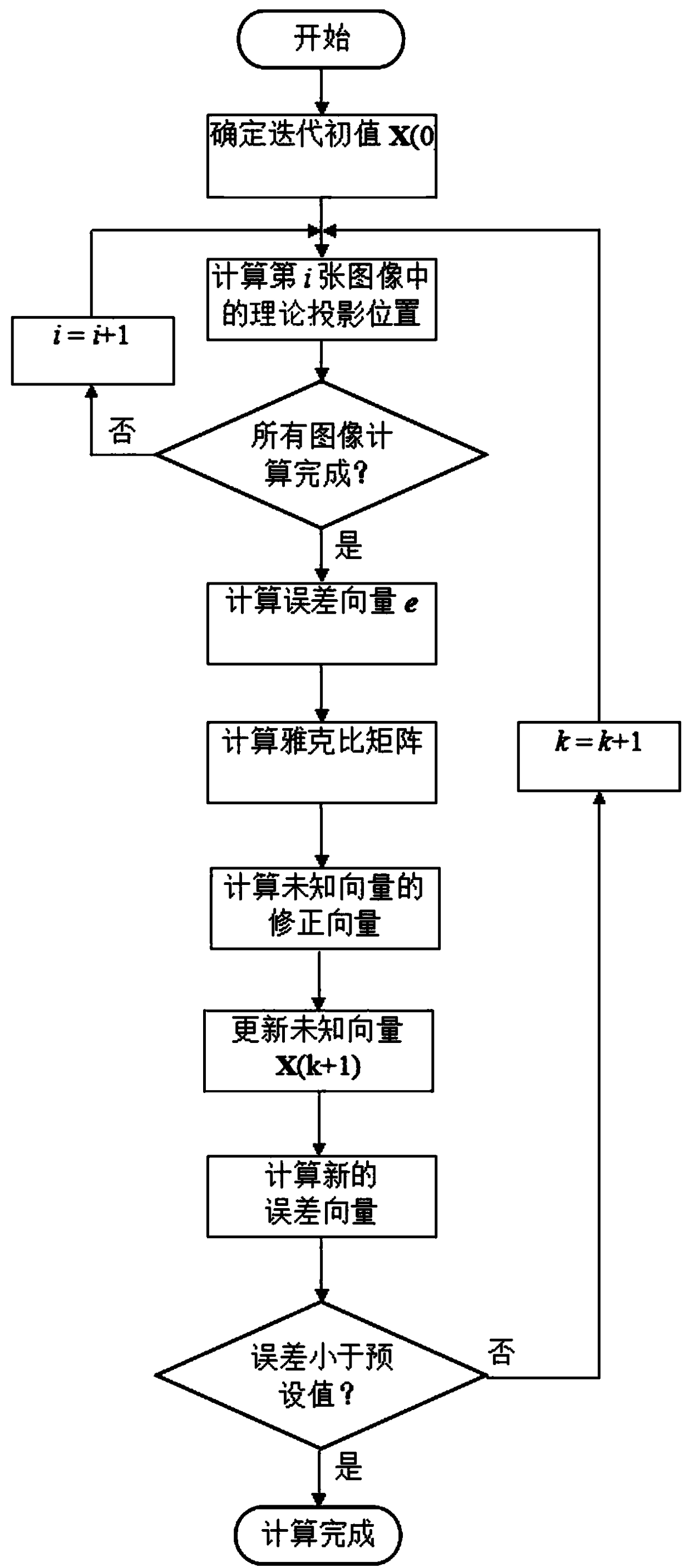
[0064] The traffic sign targeted by this method can be any place that can be captured by the camera.
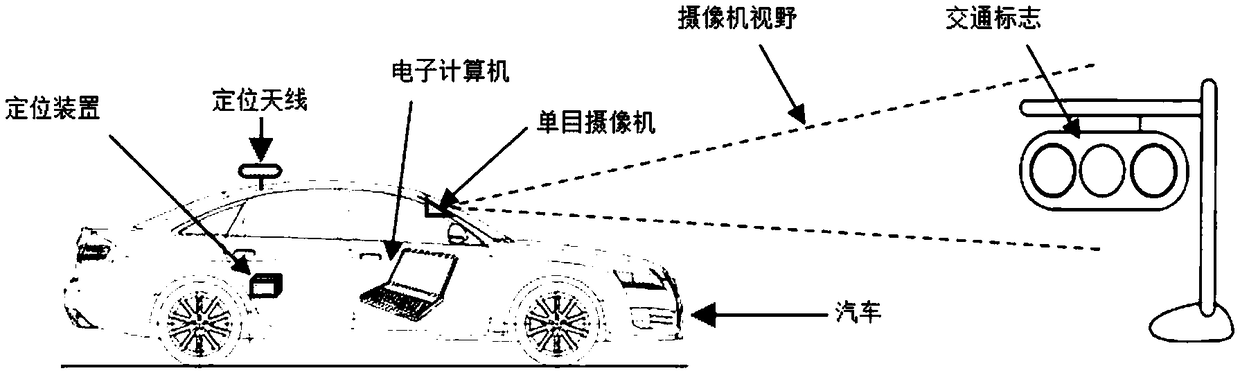
[0065] 1.1 Measuring device
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, the device for measuring the spatial position of a traffic sign proposed by the present invention includes:
[0067] a. One vehicle that can run normally on the road (measurement vehicle, no special requirements).
[0068] b. One ordinary monocular camera / camera, which can be installed at any position on the car, and can photograph the external environment to generate two-dimensional digital images. There is no requirement for the installation position of the camera. You can shoot forward or sideways. The device can be installed anywhere in a, such as the inside of the front windshield, or the roof of a car. But it needs to be connected to the body stably. The user can flexibly choose the camera installation location according to the location characteristics of the target to be tested. For example, when measuring a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com