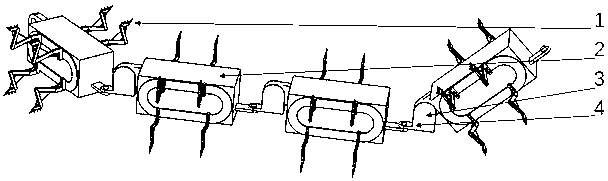
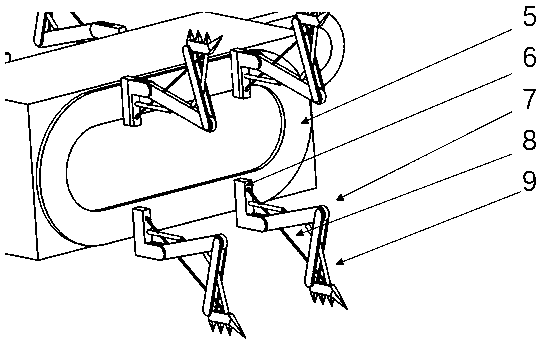
Multi-foot modular robot capable of being freely assembled
A robot and modular technology, applied in the field of mobile robots, can solve the problems of complex structure and insufficient obstacle-surmounting ability, and achieve the effect of solving obstacle-surmounting ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Robot multi-module assembly embodiment
[0030] 1. In this embodiment, the assembly mode of the robot module of the present invention is illustrated by taking the assembly of search and rescue robots after disasters such as earthquakes and fires as an example;
[0031] 2. After the disaster, the general terrain is more complex and there are many obstacles, and some places may need to drill holes for inspection by robots. Therefore, the walking mechanism adopts an attached figure 1 In the crawler and bionic multi-legged composite structure walking mechanism proposed in , the walking foot can be driven by a motor, and the joints of the walking foot are supplemented by springs to increase elasticity;
[0032] 3. Considering the needs of climbing, turning and even drilling, this embodiment takes 4 sections as an example to assemble the robot;
[0033] 4. Section 1: The head of the robot is used for exploration, search and detection. In addition to the power unit of the tra...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment of multi-joint robot going straight
[0040] 1. Take the 4-section robot in Embodiment 1 as an example to illustrate the process of the multi-joint robot going straight;
[0041] 2. The robot is named as the first section, the second section, the third section, and the fourth section from left to right. It is assumed that the robot needs to move forward at a certain speed v;
[0042] 3. In Example 1, the assembled robot has four sections with the ability to move autonomously. When the robot as a whole moves forward at a speed v, the robot at any one section will move straight at a speed v;
[0043] 4. Taking the robot in the second section as an example, before going straight, the robot has 2 pairs of walking feet on the ground and 2 pairs of walking feet in the air;
[0044]5. When the robot is going straight, the crawler drives the ground walking foot to move in the opposite direction of the forward direction. Because the relative position of the walking f...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Multi-joint robot turning embodiment
[0050] 1. The multi-joint robot needs to turn when it encounters an obstacle in the process of moving forward or backward. This example is used to illustrate the turning process;
[0051] 2. Take the 4-section robot in Embodiment 1 as an example, and name it as the first section, the second section, the third section, and the fourth section from left to right;
[0052] 3. The robot walks from right to left and needs to turn to the right;
[0053] 4. When turning, the left and right steering control devices between the joints of the first and second robots are driven, so that there is an angle between the axes of the first and second robots on the left;
[0054] 5. The upper end of the walking feet of the first and second robot landing on the ground is fixed to the robot body, and the lower end is fixed to the ground. Due to the elastic design of the walking feet, under the action of the steering device, the walking feet undergo el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com