A Method for Identifying Virtual Backbone Nodes in Ad Hoc Networks
A backbone node and network virtualization technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as the inability to identify AdHoc network backbone nodes, and achieve the effect of shortening information workload, saving manpower and cost, and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
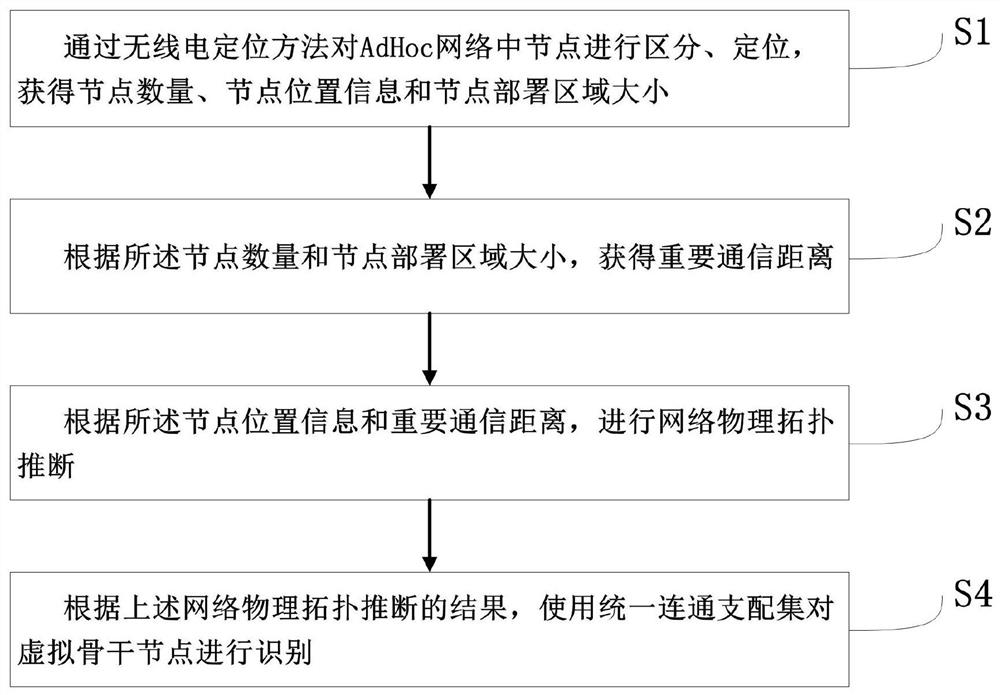
[0072] A specific embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for identifying a virtual backbone node in an Ad Hoc network, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0073] S1. Distinguish and locate the nodes in the Ad Hoc network through the radio positioning method, and obtain the number of nodes, node location information and the size of the node deployment area.
[0074] S2. Obtain an important communication distance according to the number of nodes and the size of the node deployment area.
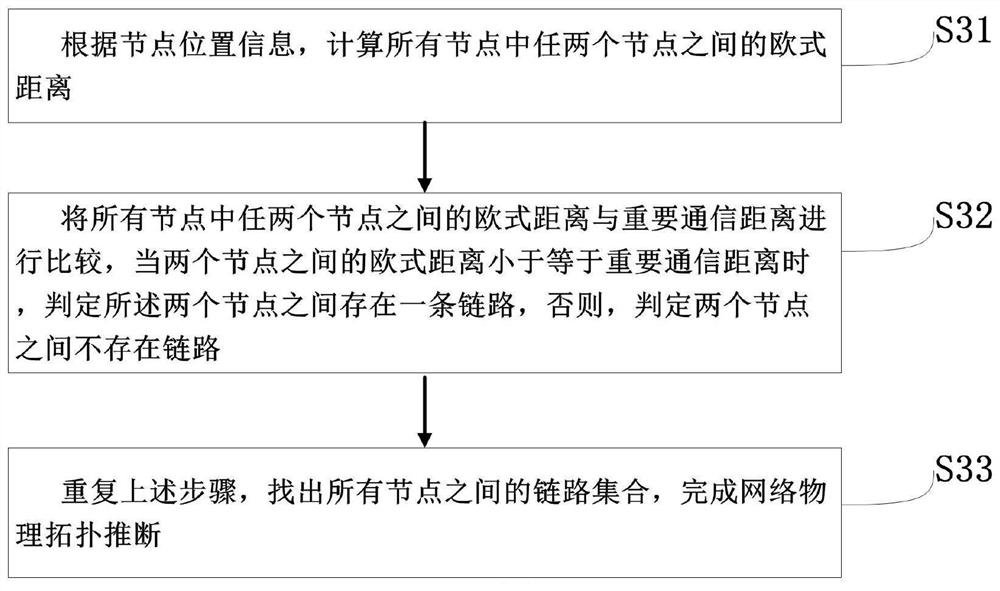
[0075] S3. Perform network physical topology inference according to the node location information and the important communication distance.
[0076] S4. According to the result of the above-mentioned network physical topology inference, the virtual backbone nodes are identified by using the unified connected dominance set.
[0077] The basic concepts involved in Embodiment 1 are briefly introduced below.
[0078] Ad Hoc network: a multi-hop, centerless, s...
Embodiment 2
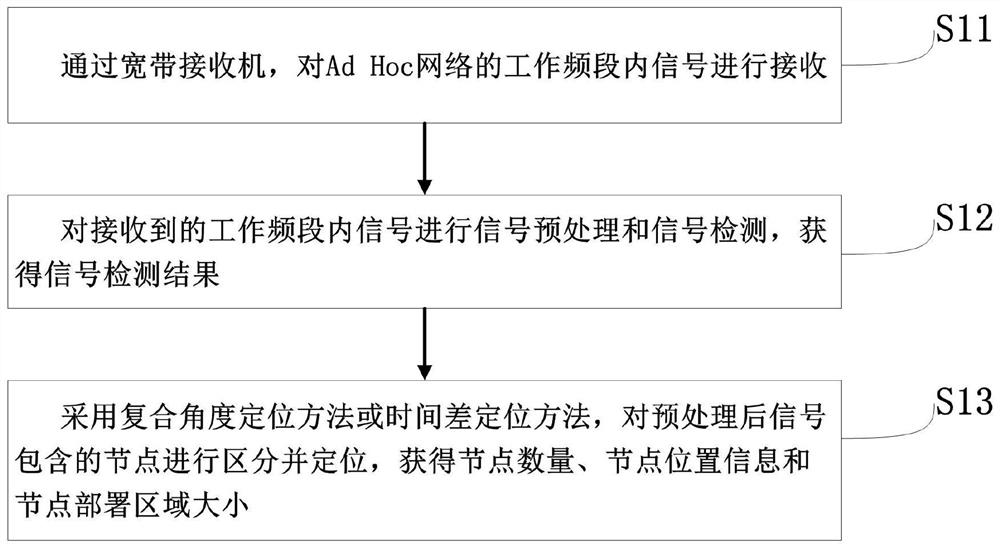
[0084] Optimizing on the basis of Example 1, such as figure 2 As shown, the above step S1 can be further refined into the following steps:
[0085] S11. Receive signals in the working frequency band of the Ad Hoc network through a broadband receiver;
[0086] S12. Perform signal preprocessing and signal detection on the received signals in the working frequency band, eliminate useless signals, and obtain signal detection results;
[0087] S13. Using the compound angle positioning method or the time difference positioning method, distinguish and locate the nodes included in the signal detection results, and obtain the number of nodes, node location information and the size of the node deployment area.
[0088] Specifically, the composite angle positioning method is based on radio direction finding, where multiple radio monitoring stations measure the direction of the same signal, and use the intersection of direction finding rays (angles) for positioning. The time difference...
Embodiment 3
[0149] An example of the method described in the application embodiment 2 is provided below, the technical effect of the Ad Hoc network virtual backbone node identification method is constructed as follows by using EXata software Figure 5 The simulation environment shown in the test method is verified. In the simulation scenario, 40 nodes are randomly deployed using the random deployment model, and the relevant parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0150] Table 1
[0151] parameter value Number of nodes 40 Deployment area size (1×1)km 2
Routing Protocol AODV fading value 4dB communication frequency 2.4GHz business type CBR
[0152] According to the size of the deployment area and the number of nodes, when the k value is set to 0.8, the network connectivity rate is close to 100%. Calculated by the important communication distance formula, R C ≈332m.
[0153] Combining node location information and important communica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com