A model for evaluating the prognosis of patients with Paget's disease and invasive ductal carcinoma and its application
An invasive and patient-friendly technology, which is applied in the field of models to evaluate the prognosis of breast Paget's disease patients with invasive ductal carcinoma, can solve the problem of inaccurate prognosis of PD-IDC population, and achieve the effect of efficient treatment plan and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
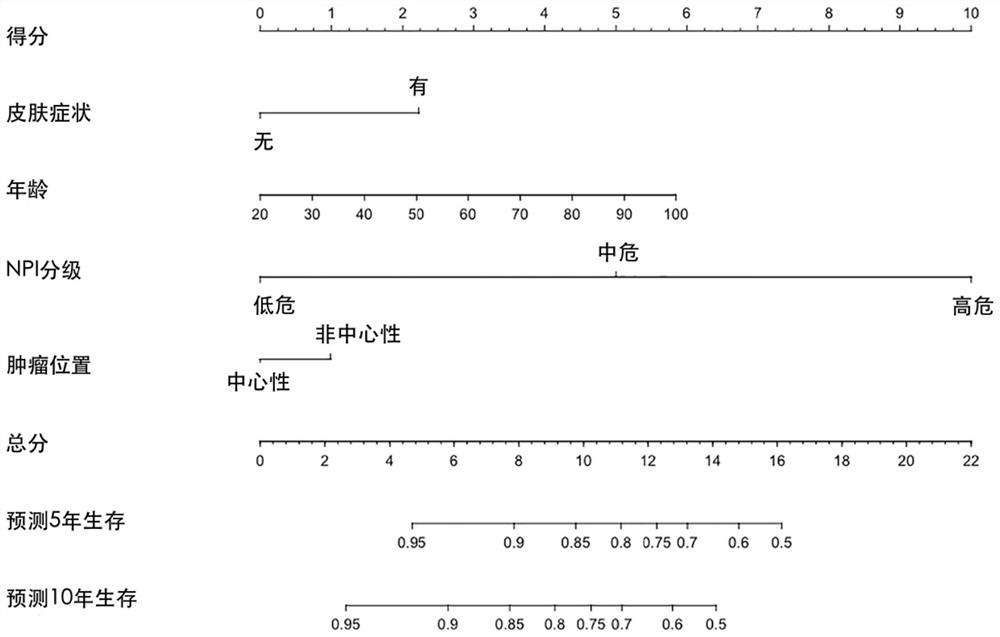
[0033] An embodiment of a method for constructing a prognostic model for assessing breast Paget's disease with invasive ductal carcinoma in the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0034](1) Modeling crowd screening:
[0035] A total of 2502 patients diagnosed with PD-ICD between 1988 and 2015 were included in the study cohort. The median follow-up time was 77 months, and the mean follow-up time was 92.9 months. By the study cutoff date, 477 patients with PD-IDC had died from breast cancer-related causes and 344 patients had died from other causes. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for this part of the population were: exclusion of stage IV breast cancer, exclusion of patients with incomplete records of clinicopathological information, exclusion of inflammatory breast cancer, and exclusion of patients who were followed up for less than 6 months after diagnosis.
[0036] (2) Index establishment: In the study cohort, 10.31% had T4 tumors, of which 8 (3.1%) wer...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2 calibration curve and C index are used to verify the predictive accuracy of model in embodiment 1
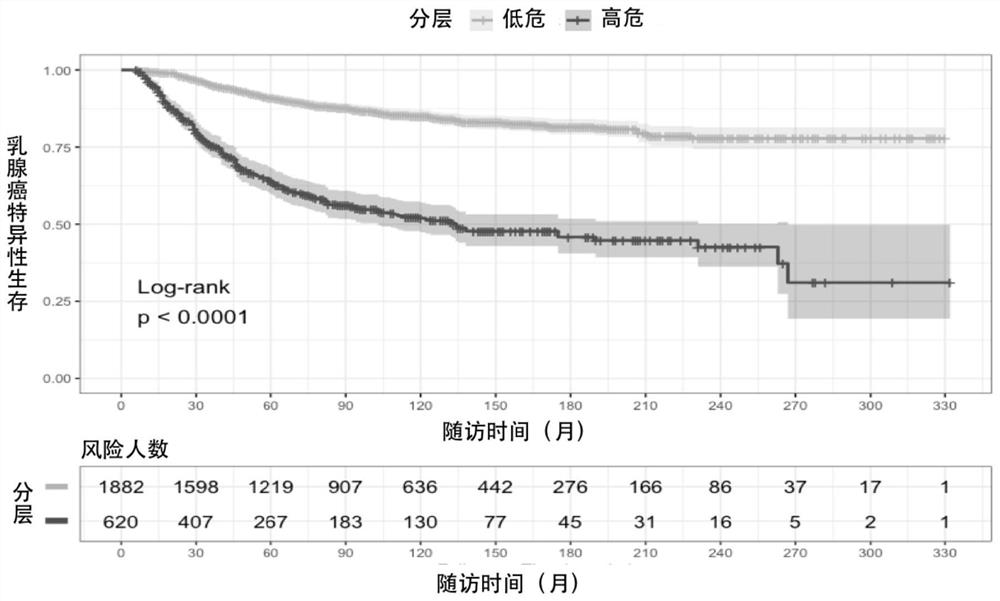
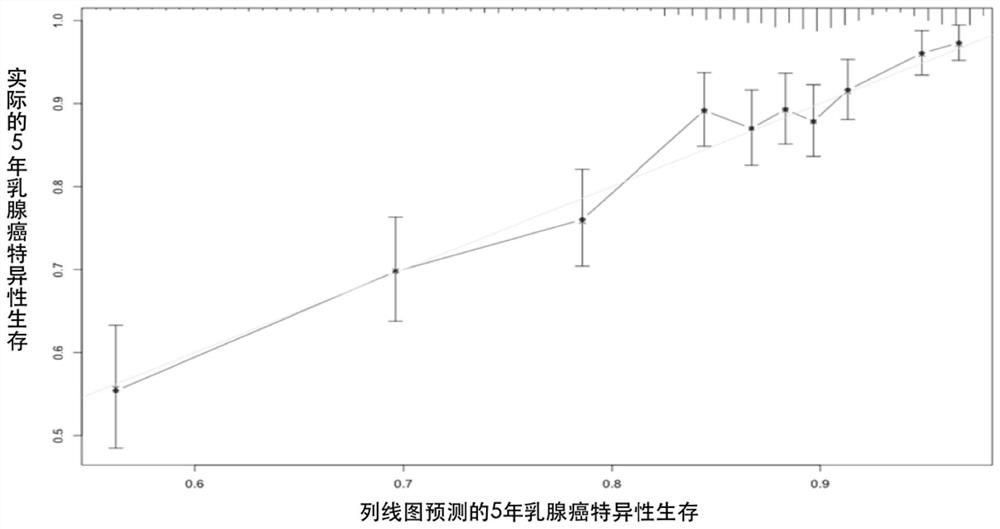
[0048] The C index ranges from 0 to 1, and greater than 0.5 indicates that the model has a better discrimination, and the closer to 1, the better the discrimination of the model. Based on the patient population data screened in Example 1, the inventors used the Bootstrap method for internal validation of the model in Example 1, wherein 500 random samples were replaced 1000 times from the original data set, and the C index was recalculated and corrected with 1000 iterations. After verification, the average C index is 0.739 (95% CI, 0.692-0.746), suggesting that the model of Example 1 has good discrimination. The inventors then plotted calibration curves of predicted and observed 5- and 10-year survival using 1000 bootstrap runs.
[0049] image 3 The predicted 5-year survival probability and the patient's real 5-year survival probability, the abscissa is the...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3 Comparing the PD-IDC nomogram of Example 1 with AJCC staging and NPI grading
[0051] Based on the patient population data screened in Example 1, the inventors compared the PD-IDC nomogram of Example 1 with the AUC (area under the receiver operating curve) between the AJCC staging and NPI grading, and the NPI grading predicted 5 years respectively and 10-year BCSS. Furthermore, a C-index is calculated to compare the performance of the three forecasting methods.
[0052] The predicted results show that the C index of the PD-IDC nomogram is 0.791 (95% CI, 0.783-0.818), the AJCC stage is 0.718 (95% CI, 0.695-0.741), and the NPI classification is 0.691 (95% CI, 0.650 -0.735). The C index of PD-IDC was significantly better than that of AJCC staging (P=0.000) and NPI classification (P=0.000).
[0053] Figure 5 In the figure, the light gray solid line is the ROC curve of the PD-IDC nomogram, the black solid line is the ROC curve of the AJCC staging, and the dott...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com