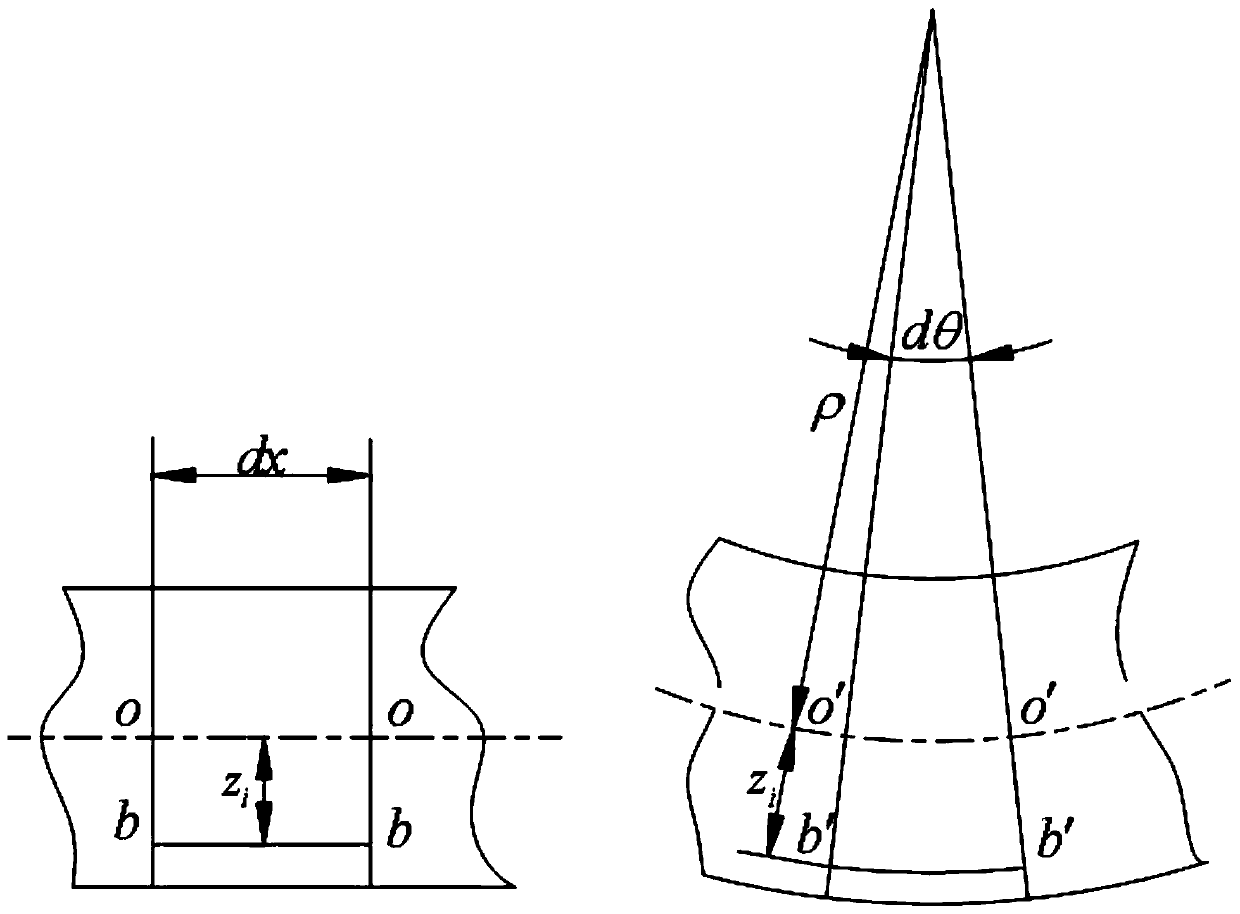
Method for calculating the composite stiffness of a main and auxiliary spring type composite material plate spring
A composite material plate and composite stiffness technology, which is applied in the field of leaf springs and can solve problems such as complex calculation of composite stiffness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
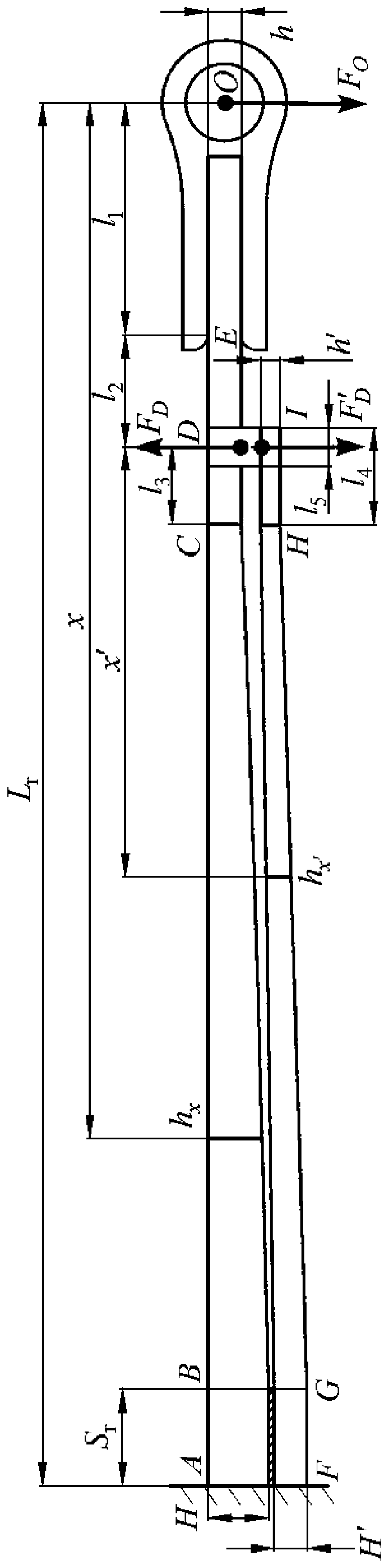
[0184] Such as figure 2 Schematic diagram of the structure and related geometric dimensions of the second half of the main and auxiliary spring composite leaf springs. In this example, the specific values of each parameter are:
[0185] Main spring: L r =715mm, leaf spring width b=70mm, H=31mm, l r =687mm, l 3 =50mm, l 2 =58mm, l 1 =92mm, h=17mm, the change law of the thickness of the parabola segment BC:
[0186]
[0187] Secondary spring: H'=31mm, l 5 =20mm, total length of auxiliary spring l 4 =100mm, h′=13.5mm, the change rule of GH thickness of parabola segment:
[0188]
[0189] The structure and related geometric dimensions of the first half of the main and auxiliary spring composite leaf springs are basically the same as those of the second half. The different parameters include: the length of the first half of the main spring is 700mm, and the length of the first half of the auxiliary spring is 560mm.
[0190] According to the calculation formula...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com