Method for combining resource allocation and content caching in F-RAN architecture
A technology for content caching and resource allocation, which is applied in the field of joint resource allocation and content caching, can solve problems such as waste of cache resources, inability to guarantee service delay, waste of spectrum resources, etc., and achieve the goal of reducing the pressure on fronthaul links and improving resource utilization Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
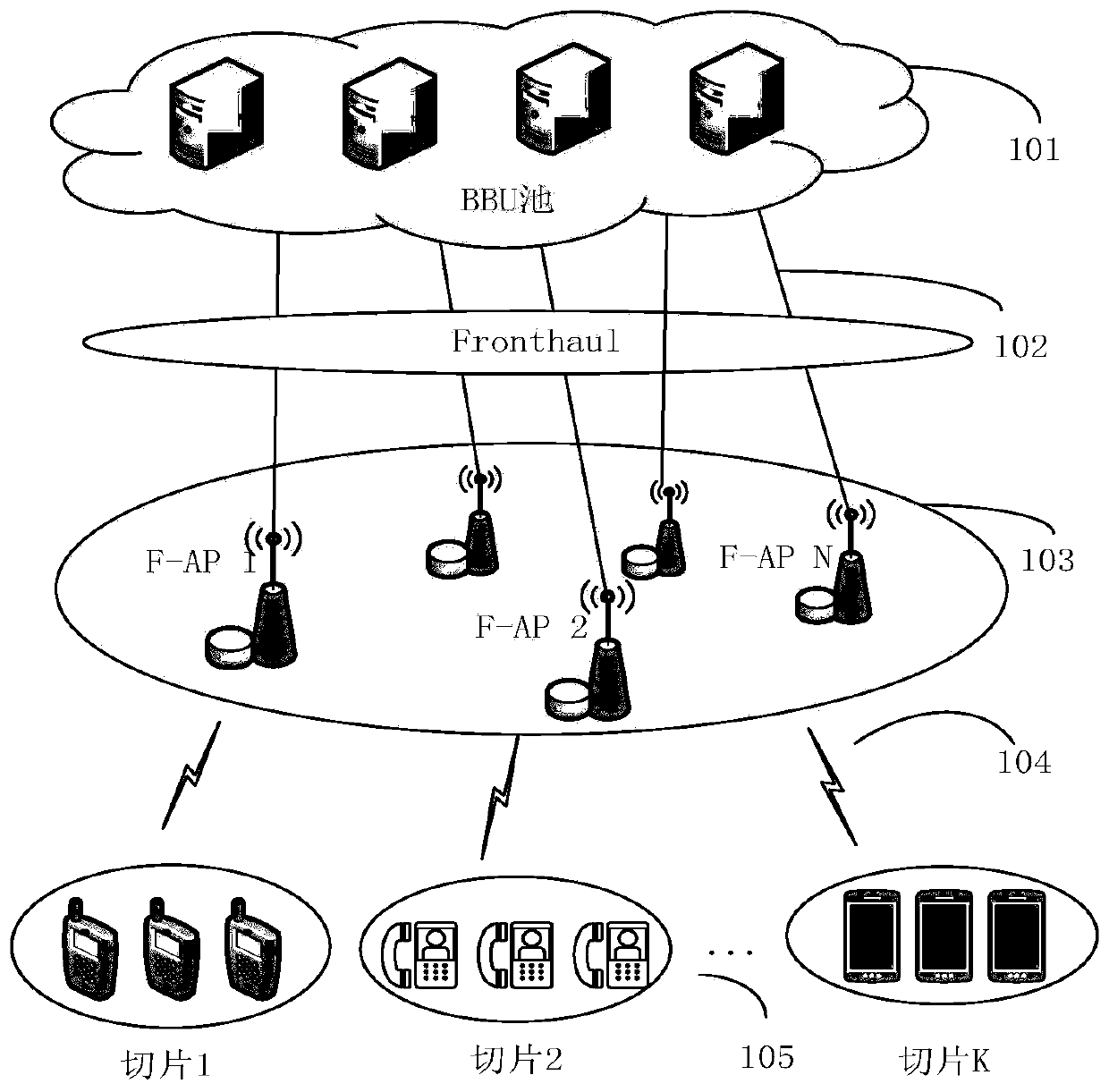
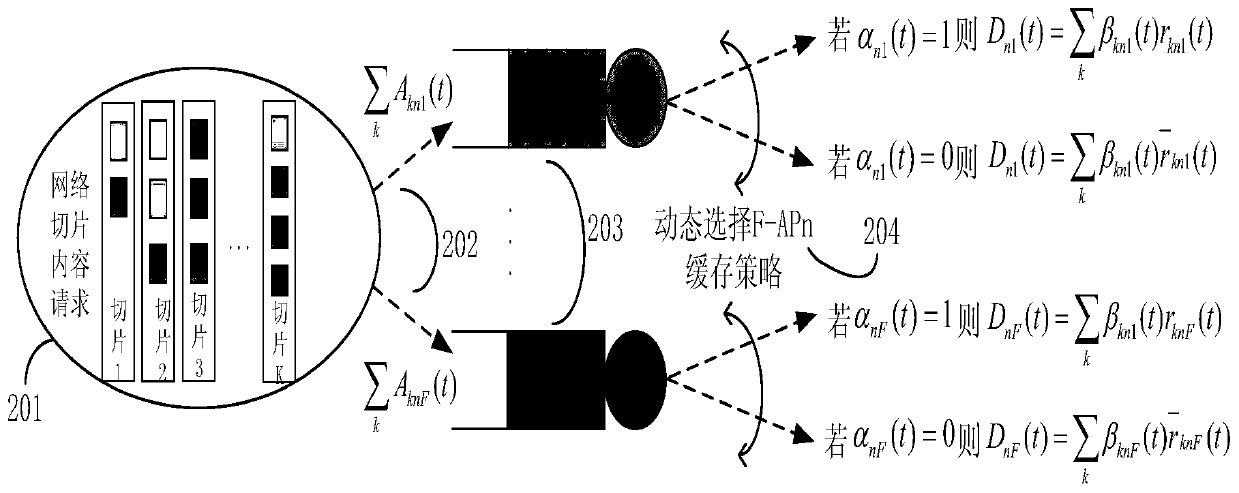
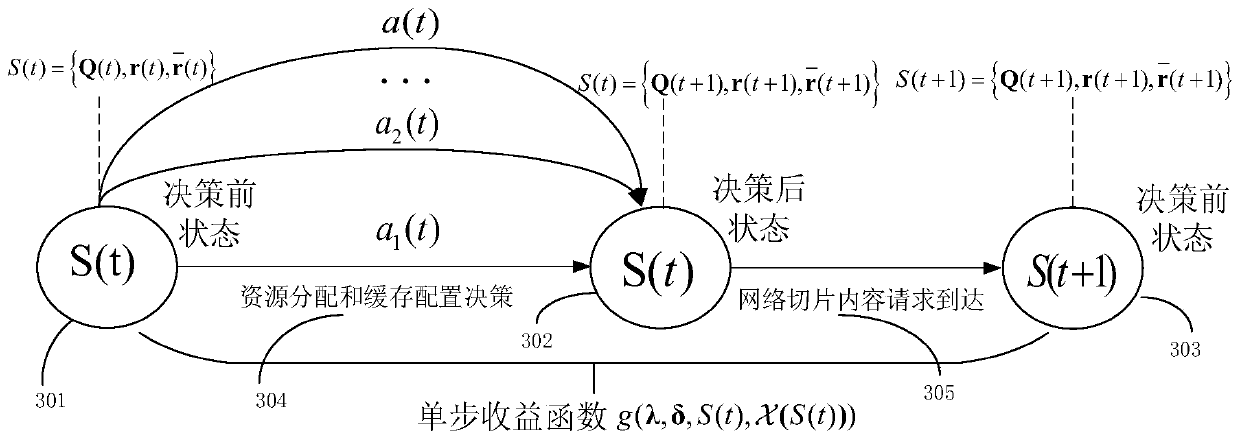
[0040] see figure 1 as shown, figure 1It is an F-RAN scene diagram, which includes five parts: BBU pool 101, which is used to process baseband signals; fronthaul fronthaul link 102, which is a wired transmission link, connecting BBU and edge fog node 103; edge fog node 103 has computing, Edge network devices with caching and communication capabilities; wireless access link 104, a communication link for wireless connection between users in the network slice and the edge fog node 103; content requests dynamically arriving from the network slice 105 are queued at the edge fog node 103. The edge fog node 103 determines resource allocation and content based on information such as the length of the virtual queue established for the content, the data rate of the content transmitted by the fronthaul link and the wireless access link, and comprehen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com