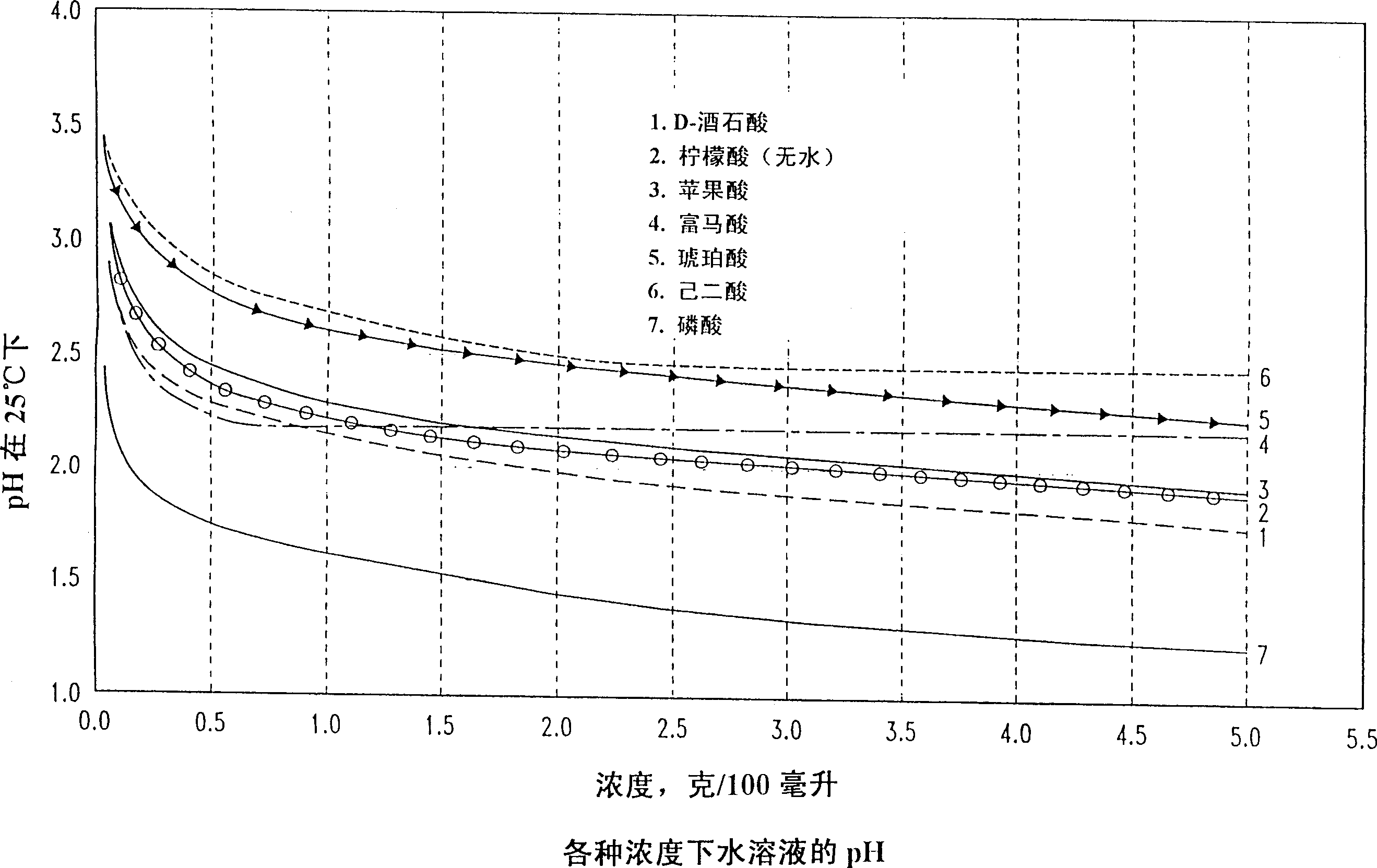
Method for optimizing the efficacy of chlorous acid disinfecting sprays for poultry and other meats
A technology of metal chlorite and lactic acid, applied in the preservation of meat/fish, preservation of meat/fish with acid, preservation of meat/fish with liquid, etc., can solve the problem of low disinfection degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This example illustrates the effect of spraying poultry carcasses with a solution of sodium chlorite activated with citric acid, at a concentration of 0.12%, in comparison with non-sprayed carcasses, wherein the content of citric acid was optimized by following the teachings of the present invention To produce enhanced antimicrobial activity, the antimicrobial activity is determined by measuring the content of (1) total aerobic microorganisms, (2) Escherichia coli and (3) total Escherichia coli (except Escherichia coli).
[0034] Experiments were carried out with a group of 10 commercially available chickens of mixed sex, 1.5-2.0 kg, with an average age of 35 days. It was processed in a small slaughter unit and sprayed with 3 oz. acidified chlorite solution for 30 seconds after the evisceration water wash. The spray is then left on the carcass for 30 seconds before the water is removed during further processing.
[0035] A spray solution contains the amount of citric a...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Phosphoric acid-chlorite
[0040] This example illustrates the difference in the ability to destroy the pathogenic bacteria Escherichia coli 0157:H7 between two 0.121% sodium chlorite spray compositions, both acidified with phosphoric acid. The threshold CAMR for both solutions was 2.60 (2.15×1.21). One solution had a phosphoric acid content that provided a CAMR of 0.661 and the other a CAMR of 2.69. A variety of representative cuts of cattle freshly slaughtered and trimmed according to commercial processes at a university slaughterhouse were selected and treated with a rifampicin-resistant Escherichia coli 0157:H7 strain mixed into a cow feces base This culture coats the surface of the meat cut. After contamination, the cuts were washed with low and high pressure water jets and divided into a control group and one or two test groups. Two minutes after washing, the test group was again sprayed with phosphoric acid-activated chlorite solution for 10 seconds. ...
Embodiment 4
[0045] This example illustrates the use of citric acid as the acidulant for a 0.121% sodium chlorite spray solution following the procedure of Example 3, wherein the citric acid level is selected to slightly exceed the CAMR required for the combination of acid and chlorite.
[0046] Pollutants
[0047] These results demonstrate that spraying meat with a citric acid activated sodium chlorite solution, where the concentration of citric acid exceeds the level required by the CAMR threshold, results in a very significant reduction in surface bacterial pathogen levels.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com