Method for calculating and displaying beam-Kriging information flow through multi-scale sliding window
An information flow, multi-scale technology, applied in the field of data analysis, can solve problems such as difficult evaluation, long time series, and difficult verification of preconditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments.
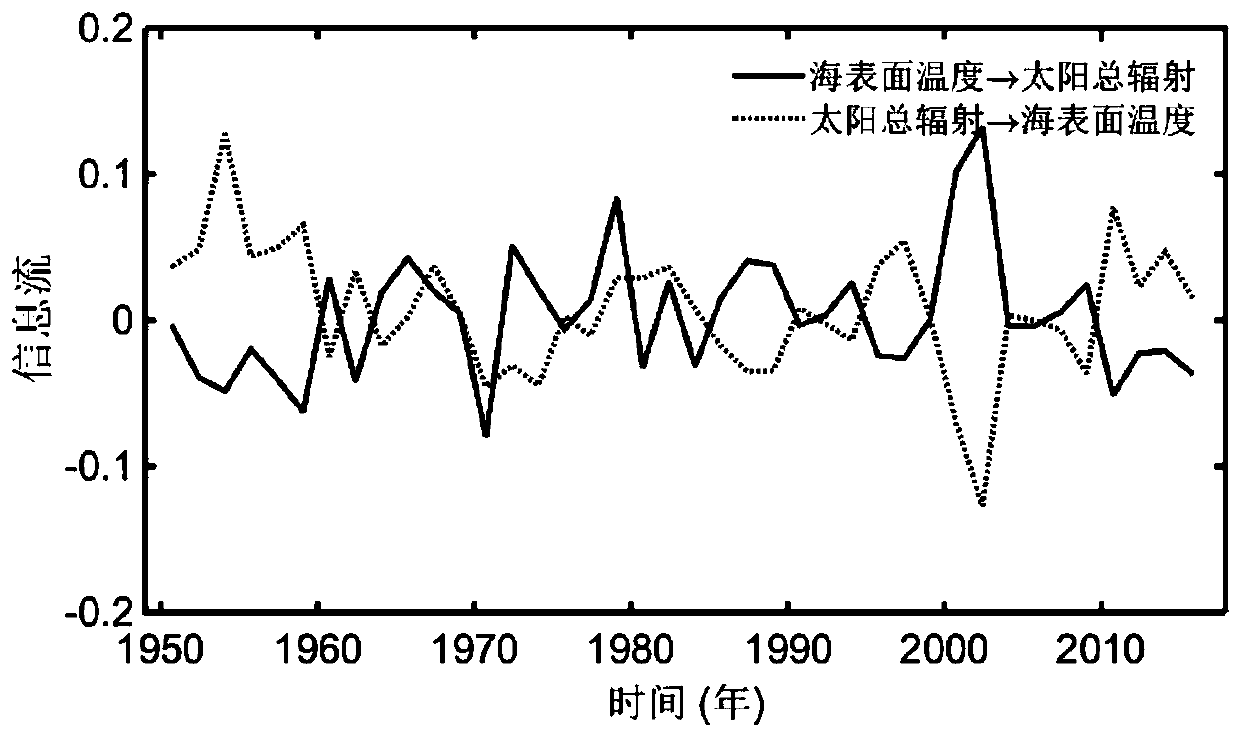
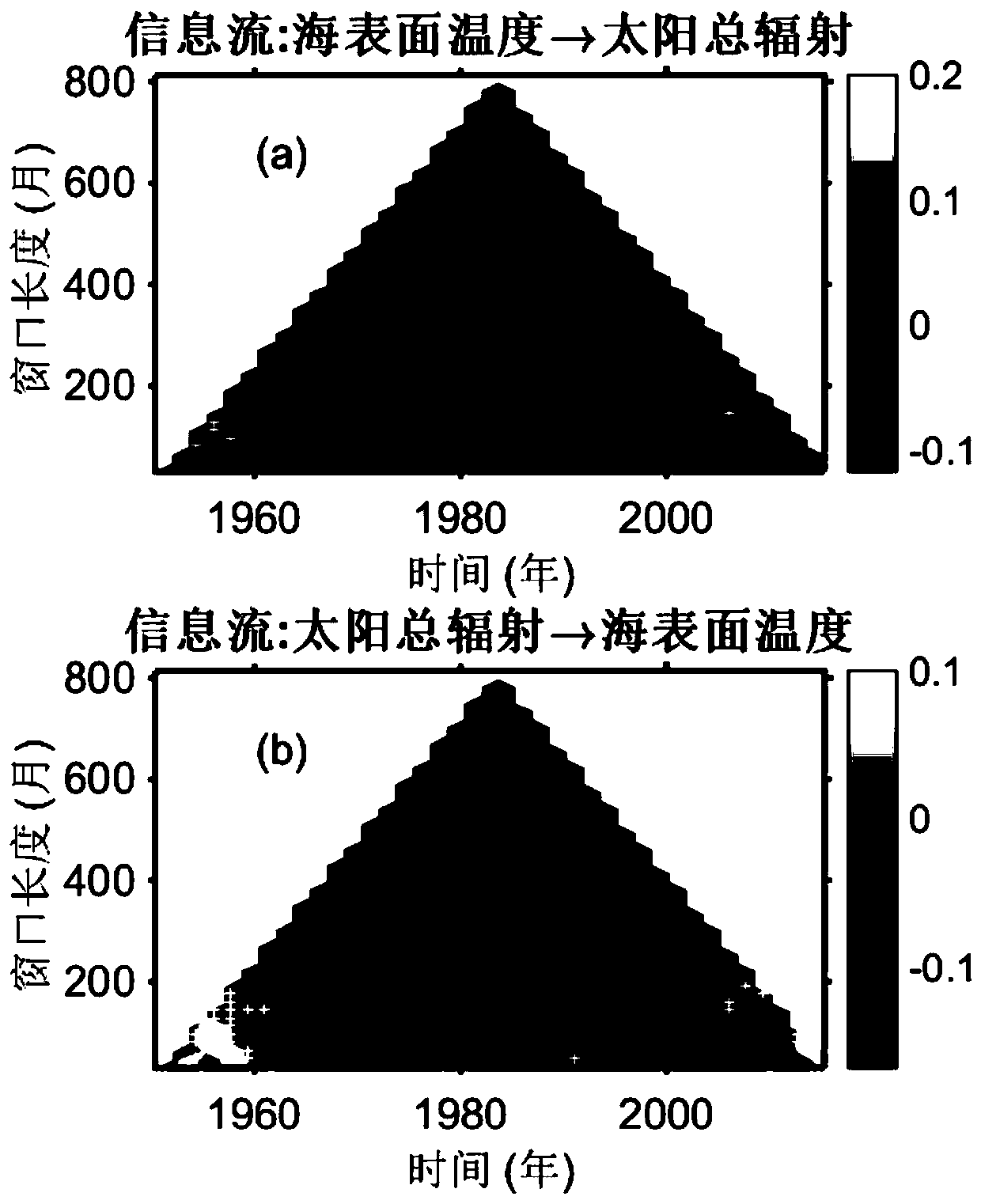
[0021] Step 1: Select the minimum window length, slide the window, and calculate the Liang-Kleeman information flow.
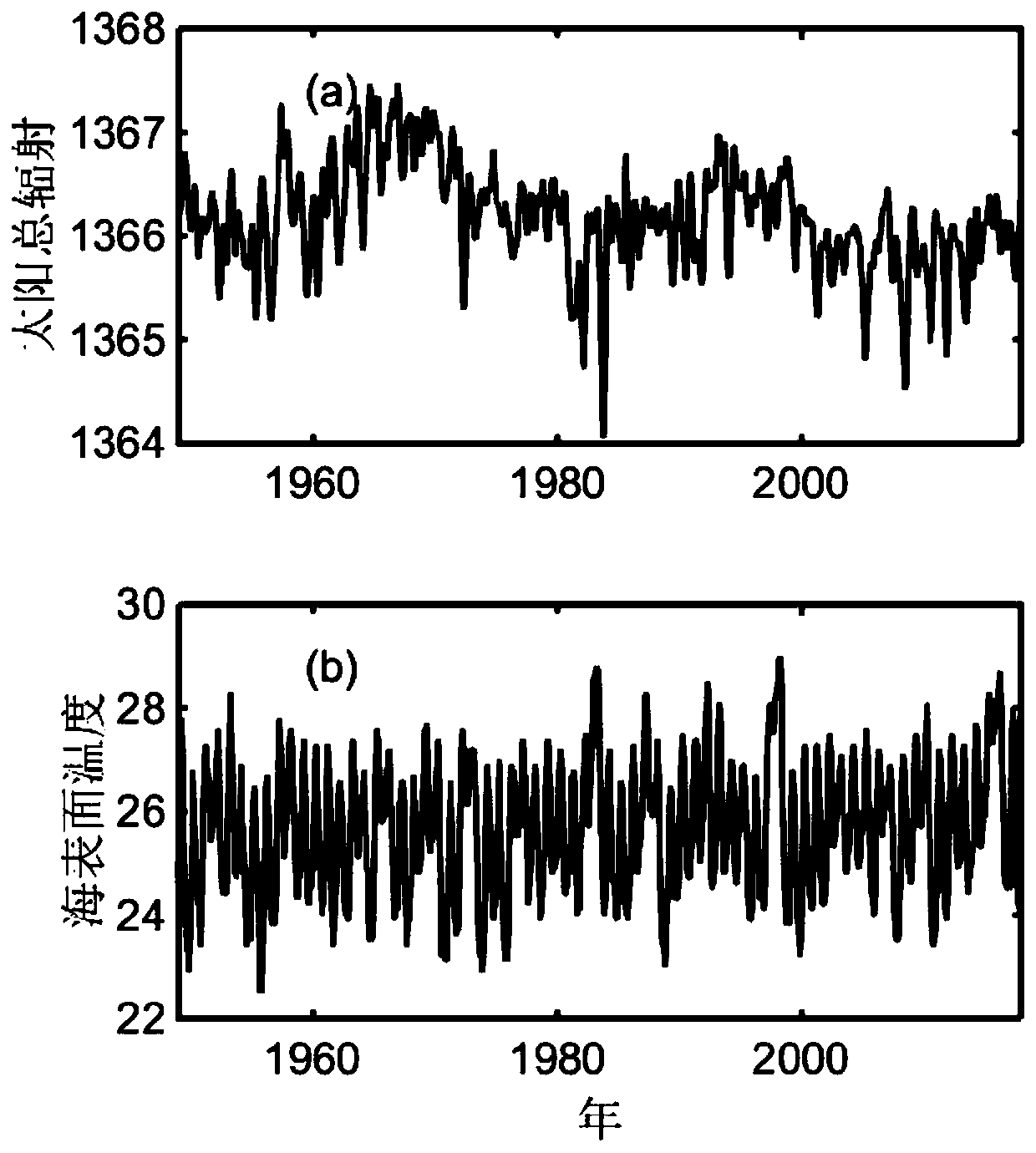
[0022] The smallest window is the smallest timescale we want to consider. If the window length is too small, the change of the time series in this time scale will be relatively small, lacking enough useful information. For this method, we need to calculate the correlation of two time series. If the amount of data is too small, it will also affect the confidence of the correlation coefficient. Therefore, the minimum window size should contain more than 30 sampling points.
[0023] Note that the two time series are X 1 and x 2 , then from X 2 Flow X 1 information flow T 2->1 Can be expressed as:
[0024]
[0025] where C=(C ij ) represents the sequence X 1 and x 2 The covariance matrix of C i,dj for sequence X i and x j The covariance matri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com