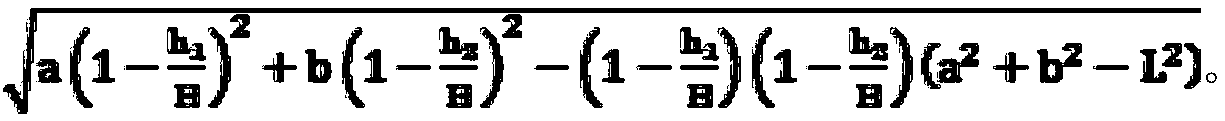Method for measuring distance between objects by using projections of objects in video
A technology for objects and objects in video, applied in the field of distance measurement, can solve problems such as difficulty in determining the focal plane, system error, and complicated calculation process, and achieve the effect of eliminating calculation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The present invention will be described in detail below by means of the accompanying drawings.
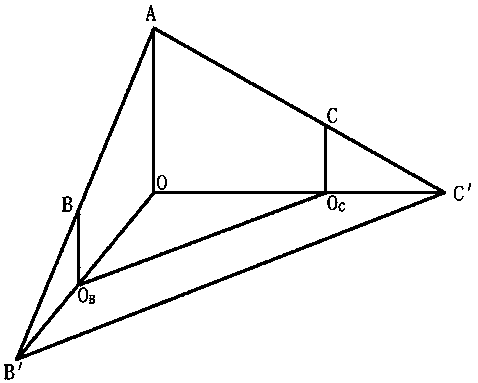
[0014] The method provided by the present invention uses the ground projection point, the relationship between the point to be measured and the three-point line of the camera to construct a tetrahedral model with two faces that are right-angled triangles, such as figure 1 As shown, point A is the vertex of the camera, O is the intersection point of the camera with a bottom surface, B and C are the two measured objects, and the projections of B and C to the ground are O B , O C , Point B' is the projection of point B in the video screen and the ground, point C' is the projection of point C in the video screen and the ground, connect point A to point O with a straight line, and connect point A, point B, point B 'points are connected with a straight line, point A, point C, and point C' are connected with a straight line, and points O, O B Point and B’ are connected by a strai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com