Visual localization in images using weakly supervised neural network
A visual positioning and network technology, applied in the field of visual recognition systems, can solve problems such as time-consuming and non-scalable changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
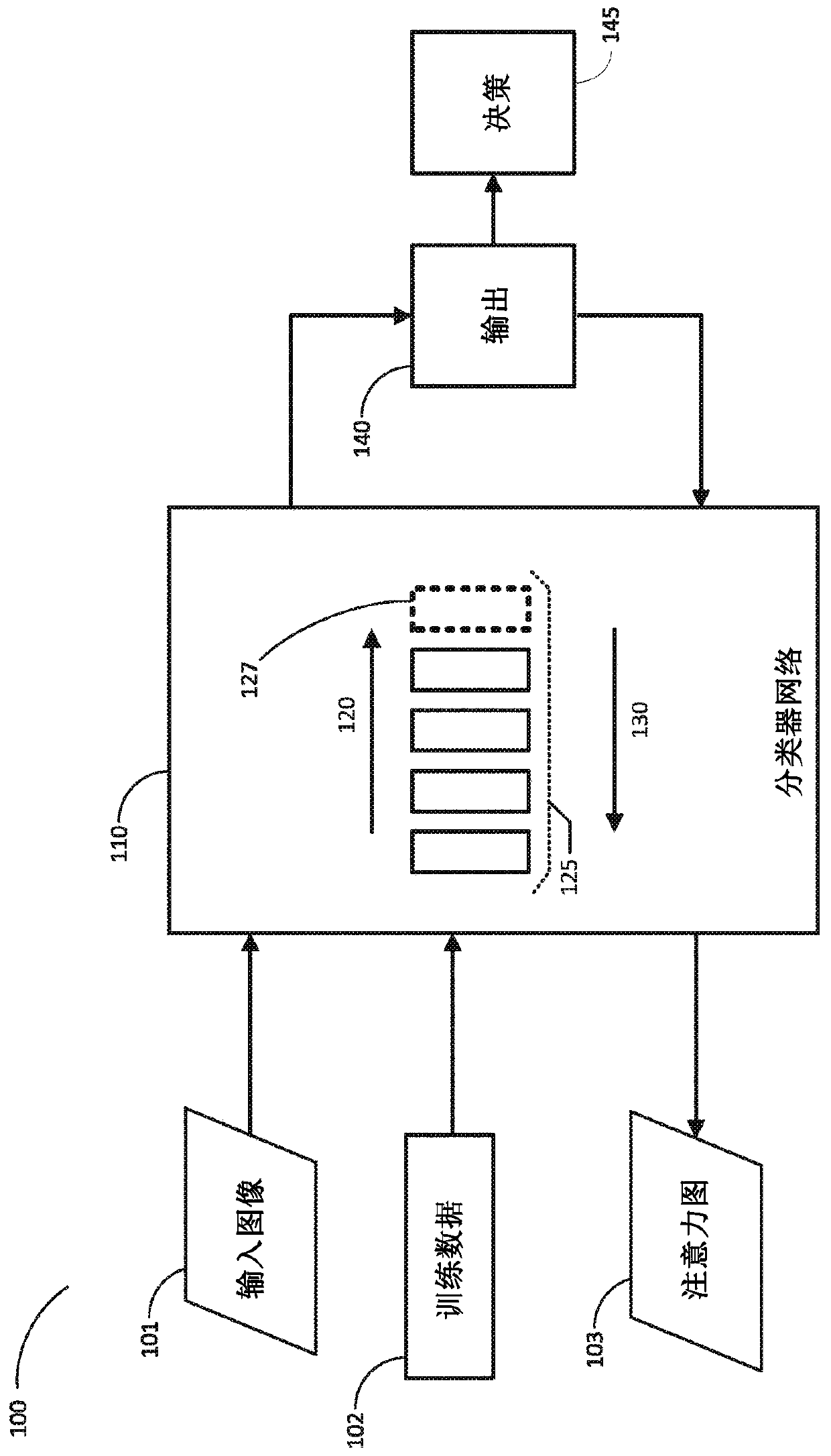
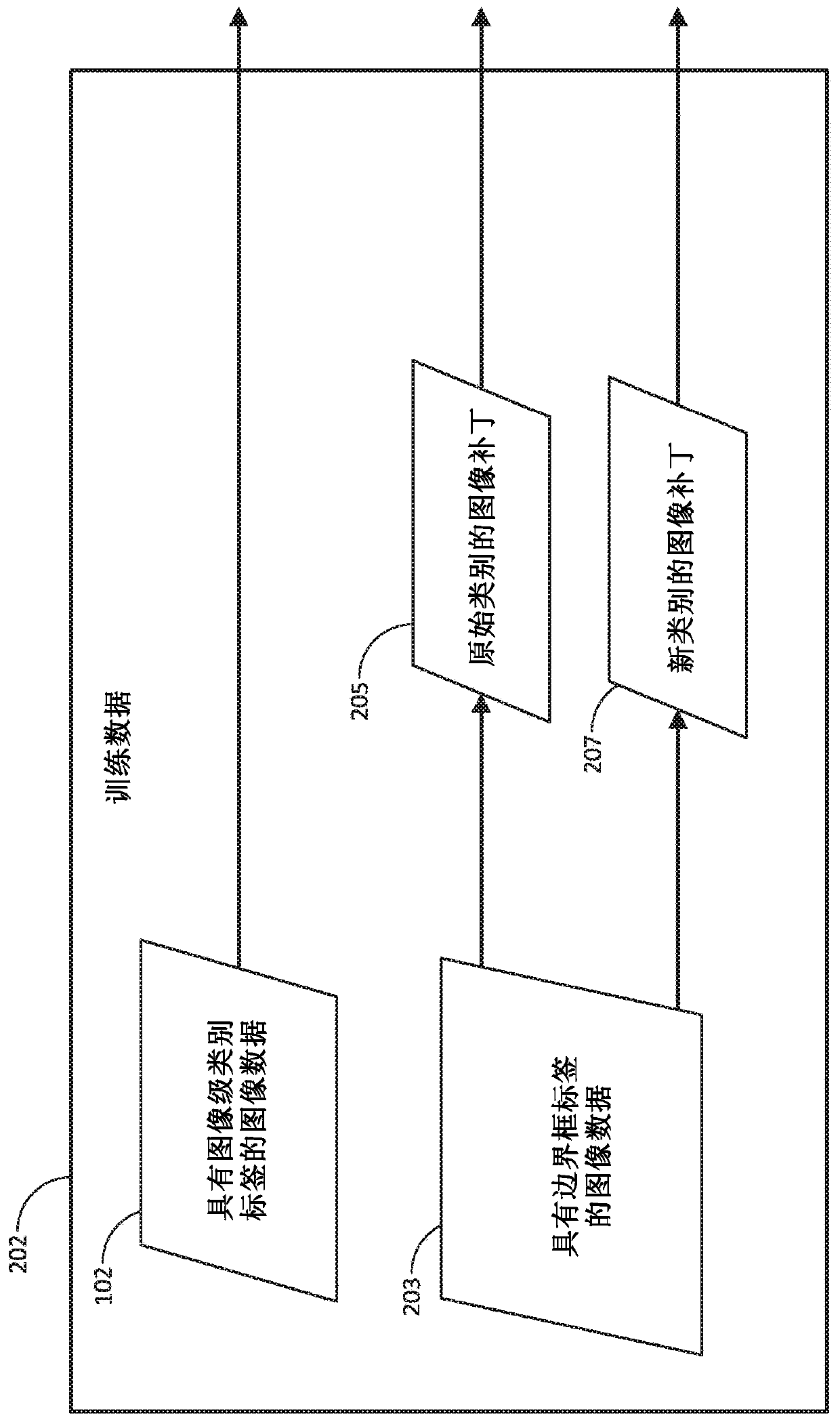
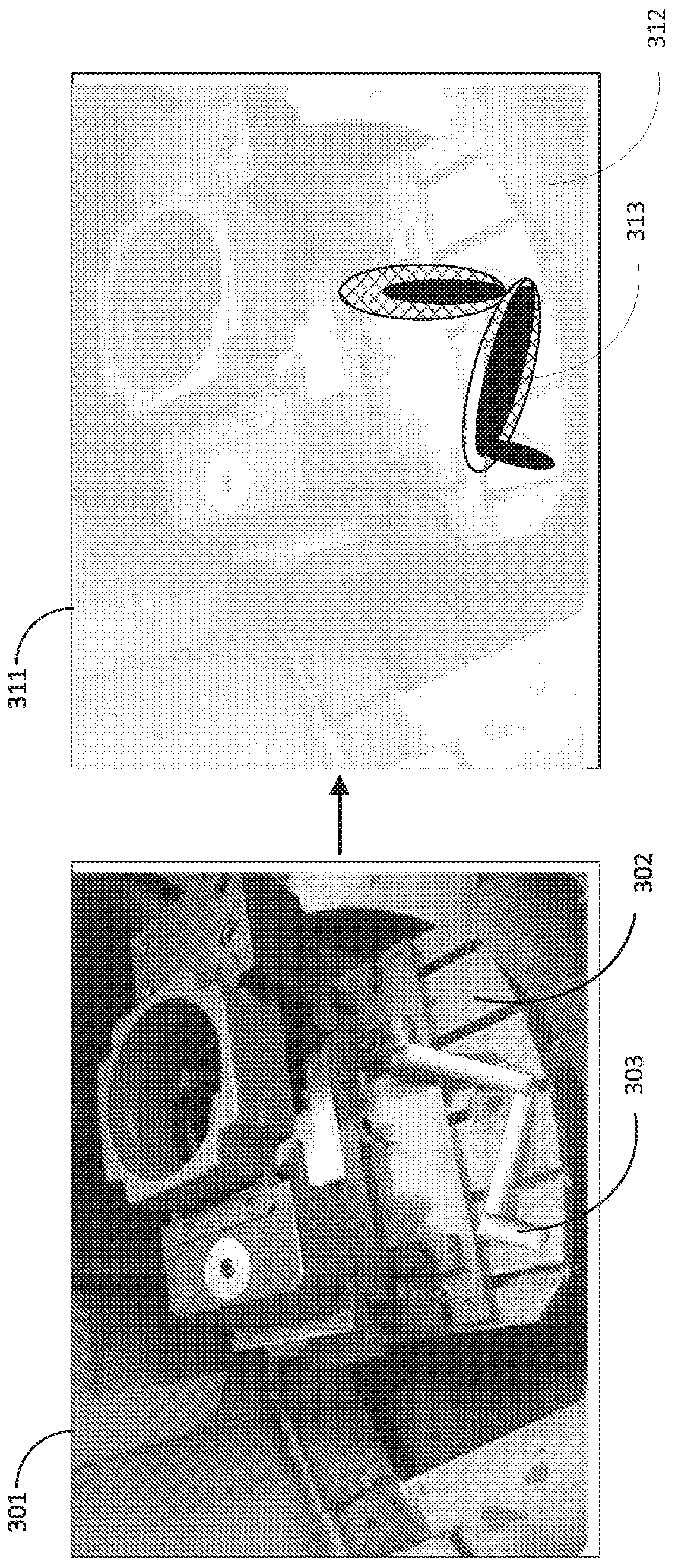
[0013] Aspects of embodiments of the present disclosure include a method of detecting localized regions in an image of one or more objects using a weakly supervised network. A classifier network, such as a convolutional neural network (CNN), can be trained to classify images as including features that classify objects or have conceptual classes. The captured images may be processed by a network of classifiers to classify the content of the images according to one or more categories. For example, classification can be applied to identify the presence of any anomalies in an image relative to the normal state for which it was trained. Anomalies may correspond to defects in objects depicted in the image, or to anomalies detected within normal settings. Without a priori knowledge (what shape or form the anomaly takes in the image), gradient-based inversion or backpropagation of the classifier network can be applied to discover the intrinsic properties of normal and abnormal parts ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com