Energy-efficient and obstacle-avoiding underwater routing method
An energy-efficient, obstacle-avoiding technology, applied in the direction of reducing energy consumption, advanced technology, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as decision-making affecting the normal communication routing path of underwater nodes, difficulty in replacing batteries and charging, and limiting the life cycle of communication networks. , to improve the packet delivery rate, prolong the network life cycle, and avoid conflicts.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
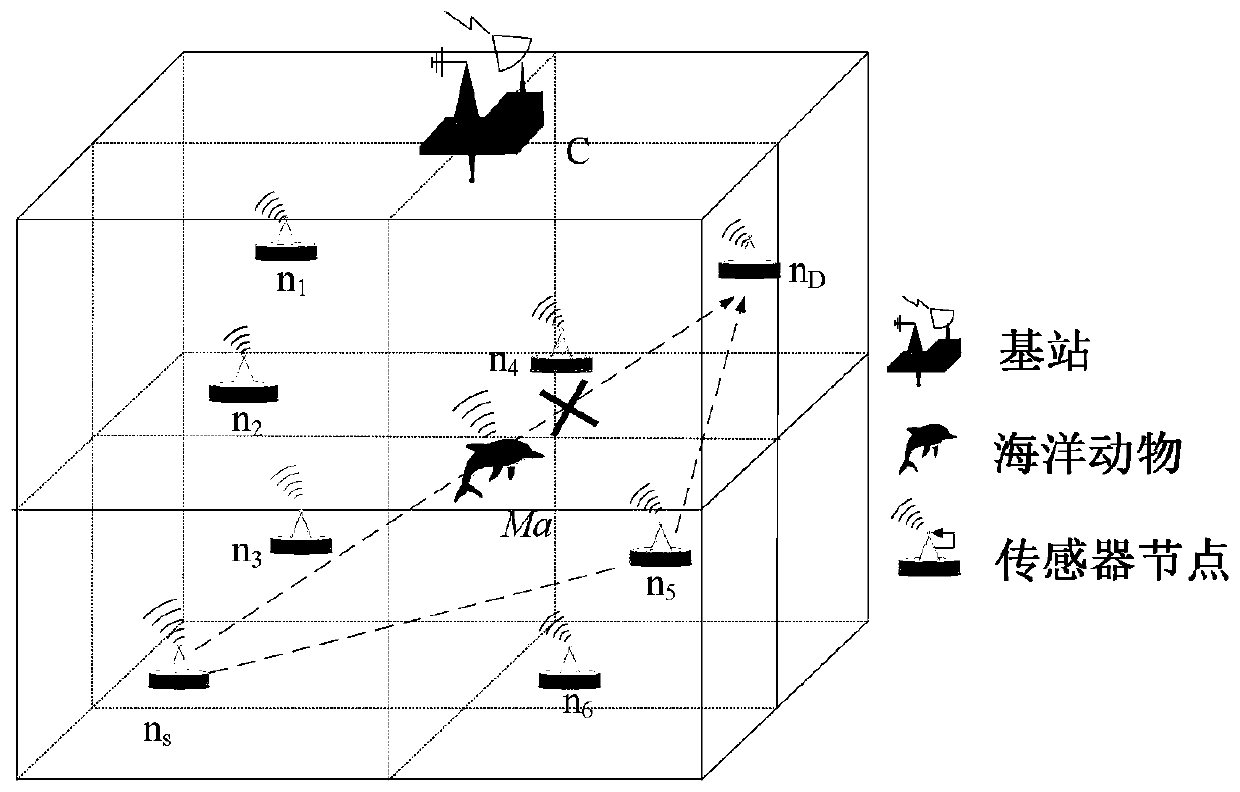
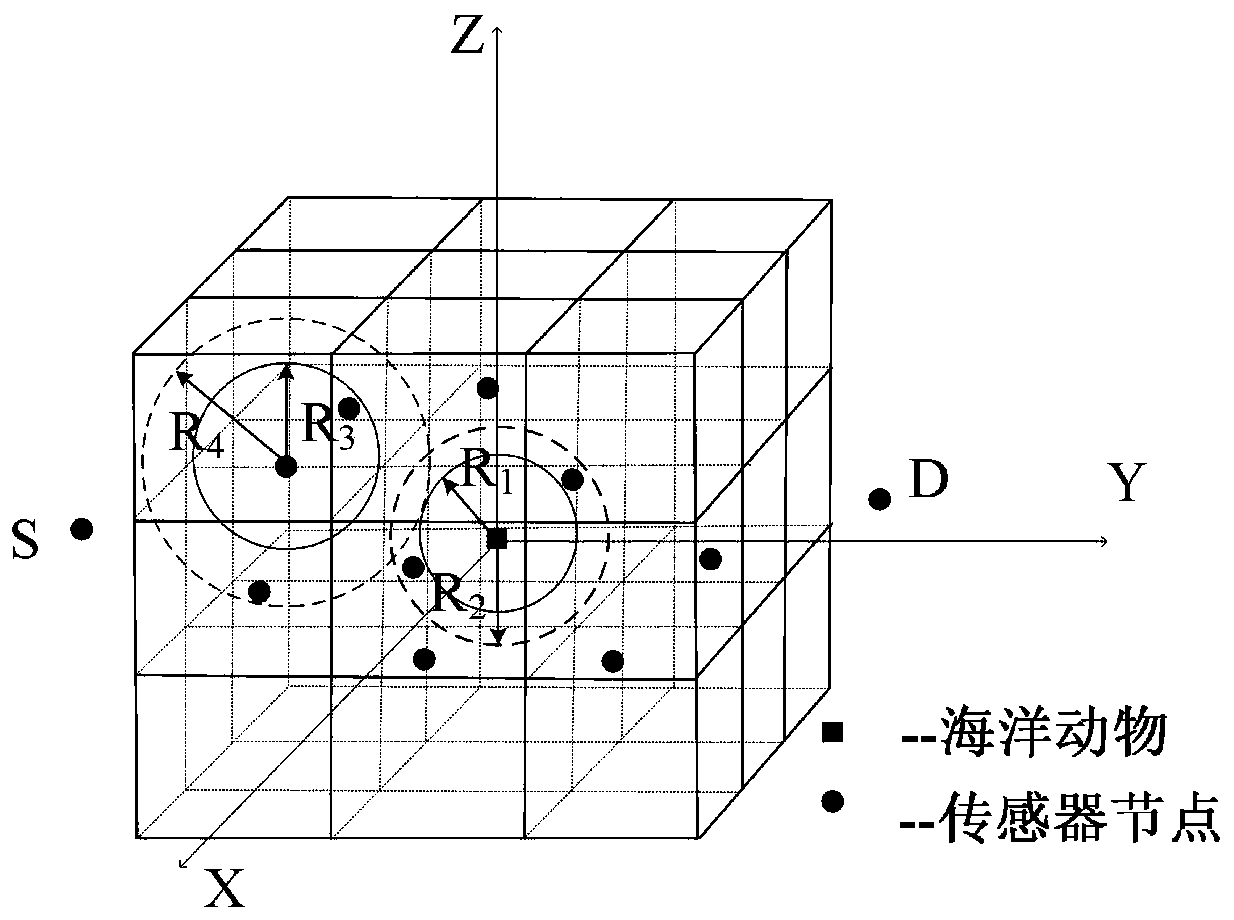
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention divides the entire underwater network structure into small network blocks of 1000m×1000m×1000m. In shallow seas, each network block contains a normal sensor node. sensor node N j ={n 1 ,n 2 ,...n j} are deployed in these small network blocks according to a deployment strategy that can increase network connectivity and network coverage. Multiple marine animals are regarded as one obstacle, such as figure 1Ma in. Sensor nodes that are required to communicate with each other can sense, receive and forward data packets with consistent transmission range and energy consumption. Also, if the sensor node is not working, it is in a dormant state. The specific routing steps are as follows:
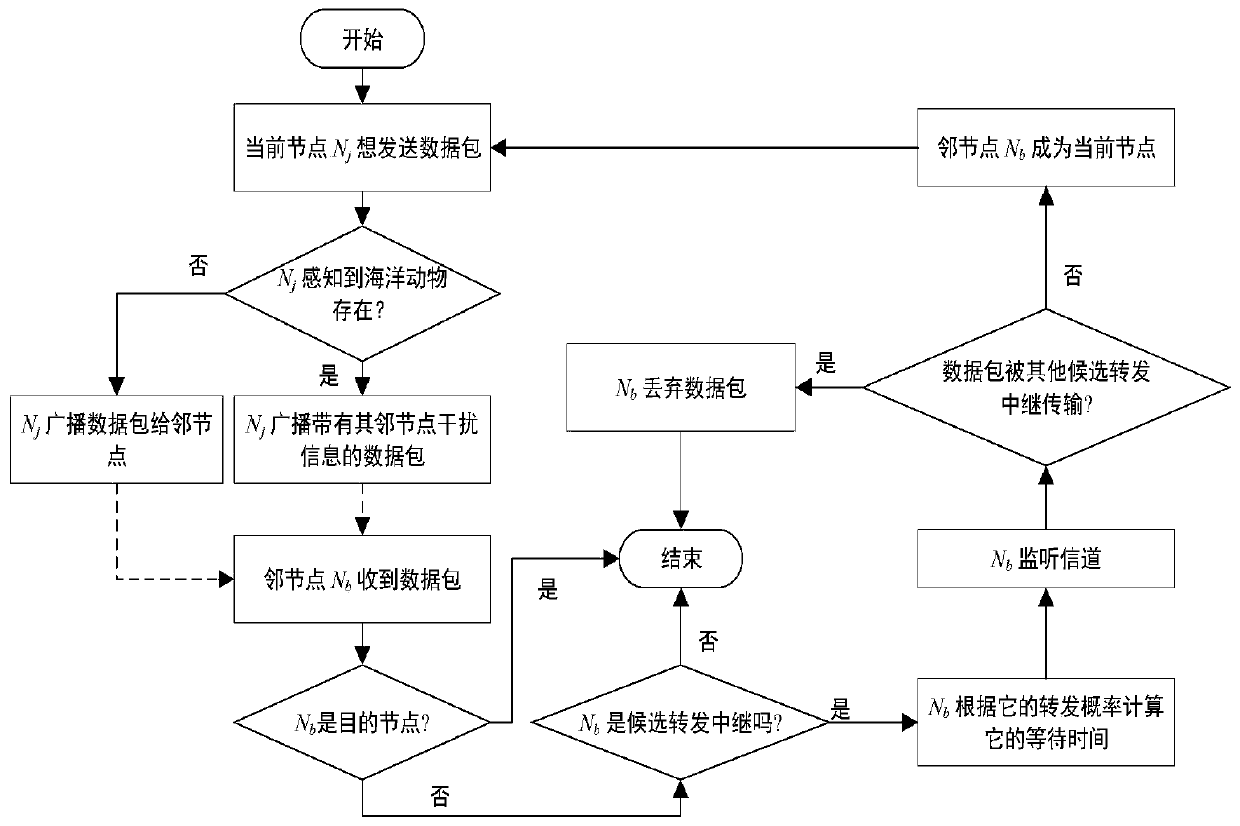
[0037] 1) When a sensor node (current node) wants to send a data packet and the current node perceives th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com