Method and device for reducing signal peak-to-average ratio based on frequency domain processing
A technology of signal peak-to-average ratio and frequency domain signal, which is applied in the field of wireless communication to improve the spread of signal spectrum, improve the rise of noise floor, and weaken the effect of PAPR rebound
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
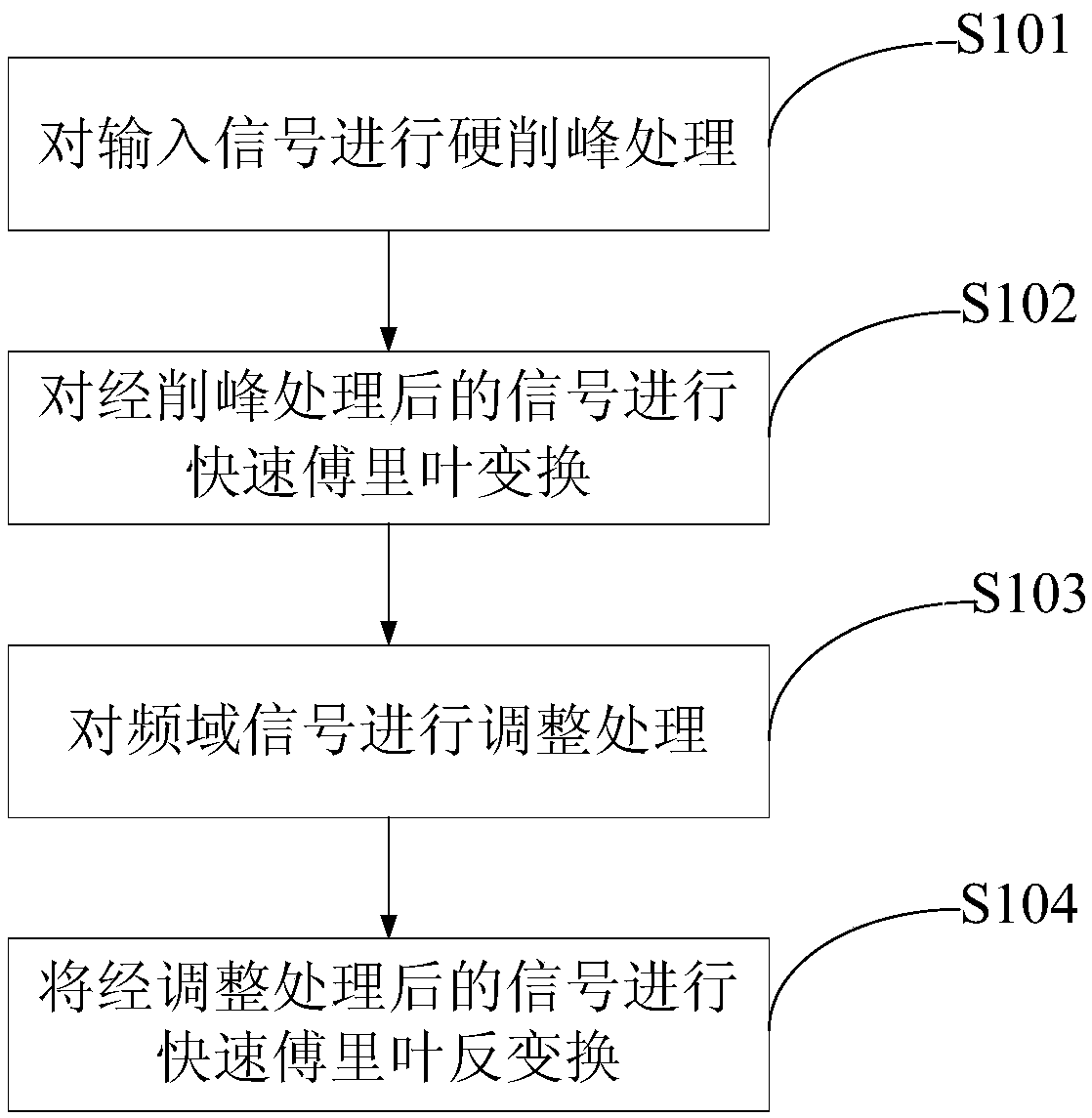
[0046] This embodiment provides a method for reducing the signal peak-to-average ratio based on frequency domain processing, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0047] S101. Perform hard clipping processing HC (Hard Clipping) on the input signal data_in, and the output signal after peak clipping processing is data_clip;
[0048] S102. Perform fast Fourier transform on the output signal data_clip, and output frequency domain signal data_freq; perform fast Fourier transform on the input signal data_in, and output frequency domain signal data_in_freq;
[0049] S103. Calculate the error vector magnitude EVM (Error Vector Magnitude) after peak clipping, and the described EVM calculation formula is: Among them, S max Indicates the maximum constellation amplitude, L indicates the length of the in-band signal; I indicates the range of the start and end points of the in-band signal; E(k) indicates the frequency domain difference of the signal before and after process...
Embodiment 2
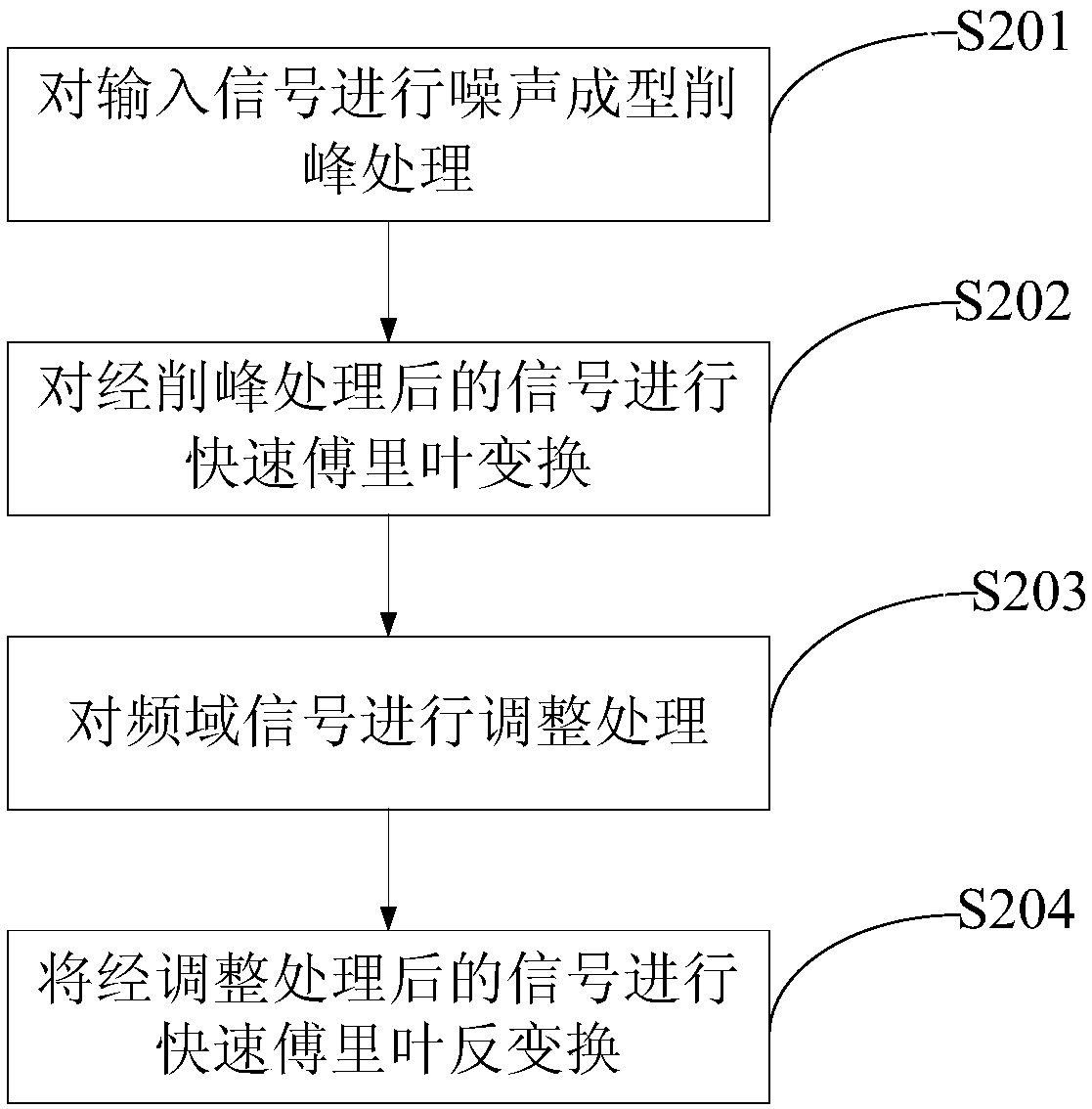
[0066] This embodiment provides a method for reducing the signal peak-to-average ratio based on frequency domain processing, such as figure 2 As shown, the method includes:
[0067] S201. Perform noise shaping peak clipping NS-CLIP (Noise Shape Clip) on the input signal data_in, and the output signal after peak clipping processing is data_clip;
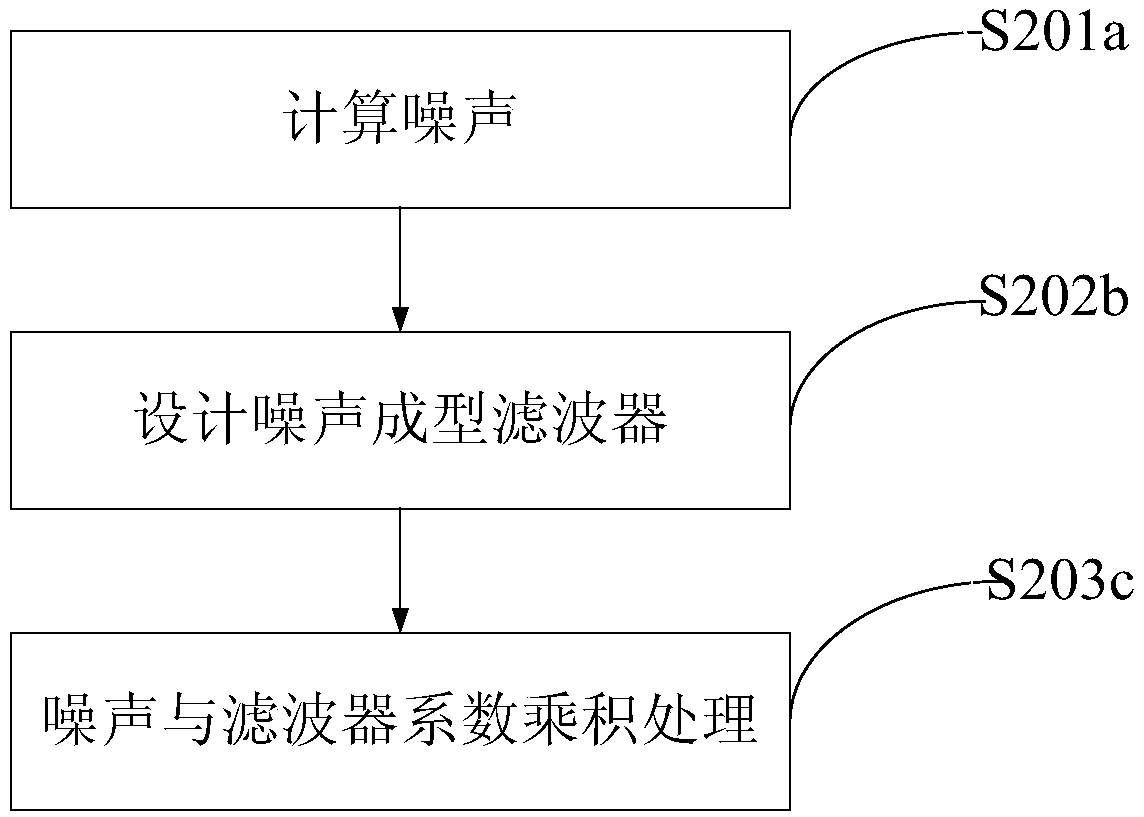
[0068] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, noise shaping peak clipping NS-CLIP (Noise Shape Clip) is used to perform peak clipping processing on the input signal data_in, such as Figure 2a as shown in:
[0069] S201a. Calculate noise information. Different from the hard clipping that directly cuts the peak, the noise shaping clipping first detects the peak information and retains the peak information, and then obtains the noise information. Wherein, the noise information can be obtained through the peak information and the crest factor CF (Crest Factor), specifically, noise = peak value - clipping thresho...
Embodiment 3
[0097] This embodiment provides a device for reducing the signal peak-to-average ratio based on frequency domain processing, such as Figure 4 As shown, the peak clipping module in this implementation is a hard peak clipping module, see Figure 5 , the device includes:
[0098] The hard peak clipping module 301 is used to perform hard peak clipping processing on the input signal data_in, and output the signal data_clip;
[0099] The first operation module 302 is configured to perform fast Fourier transform on the output signal data_clip to output a frequency domain signal data_freq; perform fast Fourier transform on the input signal data_in to output a frequency domain signal data_in_freq;
[0100] The calculation module 303 is configured to calculate the error vector magnitude EVM after peak clipping before adjusting the frequency domain signal data_freq.
[0101] The EVM calculation formula is: Among them, S max Indicates the maximum constellation amplitude, L indicates...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com