Titanium alloy fatigue life prediction method based on microscopic scratches
A technology of fatigue life and prediction method, which is applied in the direction of measuring device, using repeated force/pulsation force to test material strength, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of simple method and convenient test
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment:
[0032] In the embodiment, the material is TC17 titanium alloy.
[0033] The method comprises the steps of:
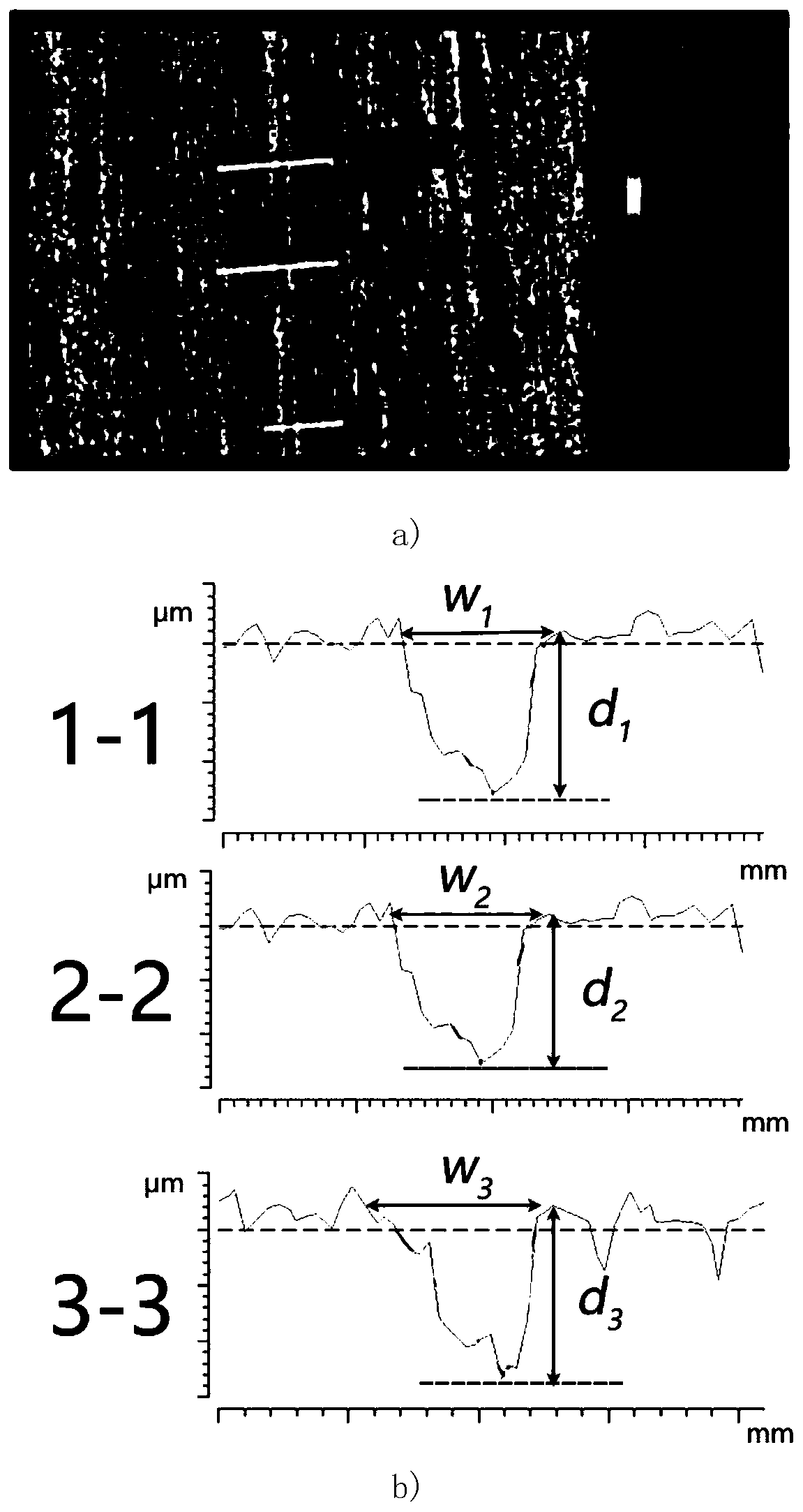
[0034] Step 1: Use the ZYGO three-dimensional interferometer to observe the microscopic scratches on the surface of the sample, such as figure 1 As shown in a), it is determined that there is a scratch in the observation area.
[0035] Step 2: Determine the width W and depth D of the scratch.
[0036] Select three scratch sections with larger dimensions as measurement targets, namely section 1-1, 2-2, 3-3, see figure 1 a); Measure the width and depth data of the three sections respectively to obtain w 1 ,w 2 ,w 3 and d 1 , d 2 , d 3 ,See figure 1 b); then the width W and depth D of the scratch can be calculated by formula (1).
[0037] The Murakami theory defines the surface defect damage parameter as the square root of the area obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com