A decoupling gas burner and its use method
A gas burner and decoupling technology, which is applied in the combustion method, combustion using multiple fuels, combustion using block fuel and gaseous fuel, etc., can solve the problems of poor mass transfer, non-flammability, and reduced combustion efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
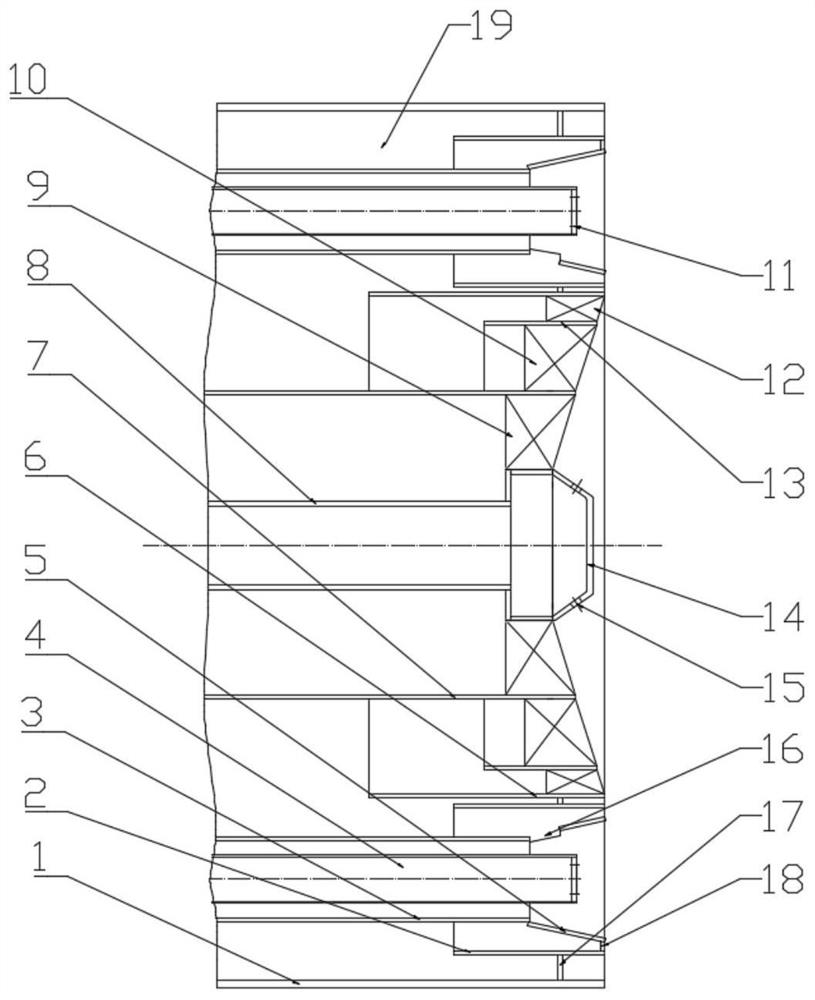
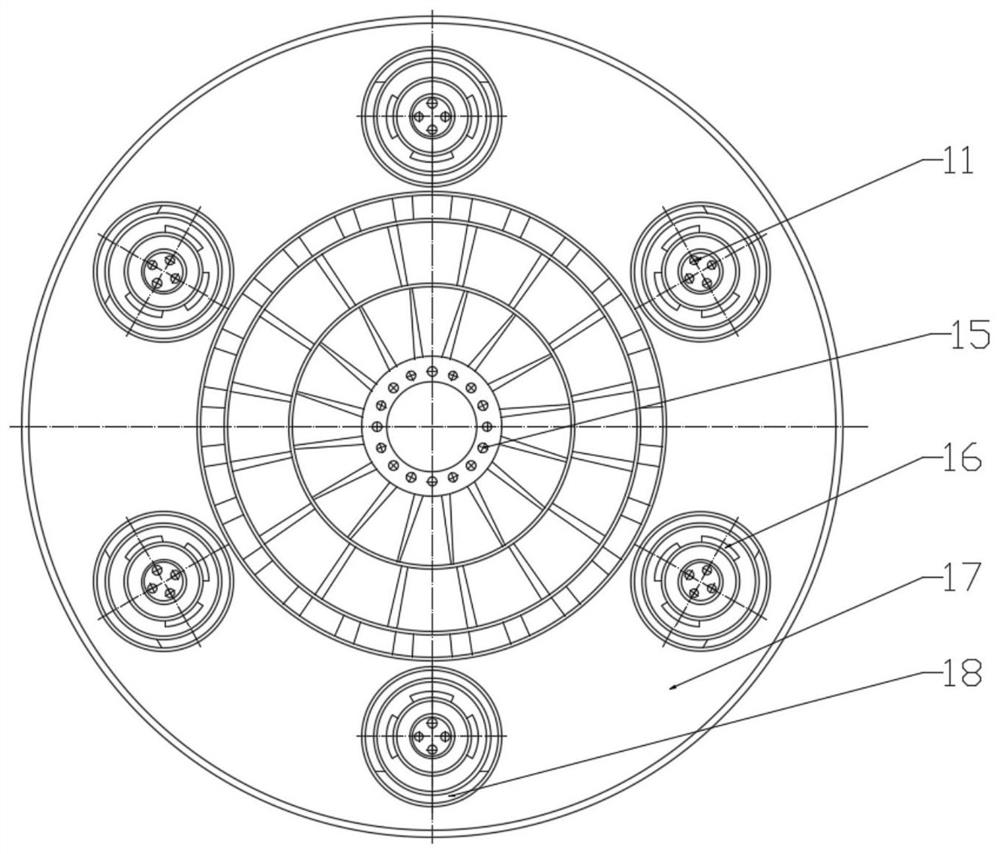
[0097] This embodiment provides a method for using a decoupled gas burner. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0098] (I) The central gas is sprayed into the furnace through the central gas pipe 8, and the primary air introduced by the primary air channel enters the furnace through the primary wind swirl blade 9, and the central gas and the primary air are mixed and initially burned in the furnace;
[0099] The central gas accounts for 20% of the total gas volume of the decoupled gas burner. The first-level wind includes central outer circulation flue gas and central air. The volume ratio of the central outer circulation flue gas to the total air volume of the decoupled gas burner is 1% under standard conditions, and the central air volume accounts for 1% of the total air volume of the decoupled gas burner. 5% of the total air volume.
[0100] (II) The gas in the air chamber 19 enters the secondary air channel to form the secondary air, and the secondary a...
Embodiment 2
[0105] This embodiment provides a method for using a decoupled gas burner. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0106] (I) The central gas is sprayed into the furnace through the central gas pipe 8, and the primary air introduced by the primary air channel enters the furnace through the primary wind swirl blade 9, and the central gas and the primary air are mixed and initially burned in the furnace;
[0107] Center gas accounts for 32% of the total gas volume of the decoupled gas burners. The first-level wind includes central outer circulation flue gas and central air. The volume ratio of the central outer circulation flue gas to the total air volume of the decoupled gas burner is 3% under standard conditions, and the central air volume accounts for 3% of the decoupled gas burner. 10% of the total air volume.
[0108] (II) The gas in the air chamber 19 enters the secondary air channel to form the secondary air, and the secondary air is divided into two stre...
Embodiment 3
[0113] This embodiment provides a method for using a decoupled gas burner. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0114] (I) The central gas is sprayed into the furnace through the central gas pipe 8, and the primary air introduced by the primary air channel enters the furnace through the primary wind swirl blade 9, and the central gas and the primary air are mixed and initially burned in the furnace;
[0115] Center gas accounts for 44% of the total gas volume of decoupled gas burners. The first-level wind includes the flue gas outside the center and the central air. The volume ratio of the flue gas outside the center to the total air volume of the decoupled gas burner is 5% under standard conditions, and the central air accounts for 5% of the total air volume of the decoupled gas burner. 15% of the total air volume.
[0116] (II) The gas in the air chamber 19 enters the secondary air channel to form the secondary air, and the secondary air is divided into t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com