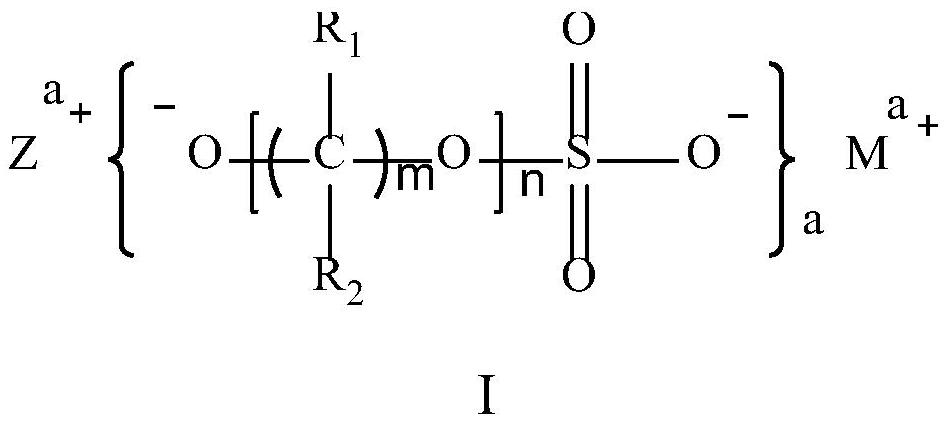Application of Compounds, Non-aqueous Electrolyte and Li-ion Secondary Batteries
A non-aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery technology, applied in secondary batteries, secondary battery repair/maintenance, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient wide temperature performance of lithium-ion batteries and unsatisfactory research results on battery stability , There is no problem such as research on long-term cycle characteristics of batteries, and the effects of excellent discharge load characteristics, low internal resistance, and suppression of gas generation are achieved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] This embodiment provides a lithium-ion secondary battery, the preparation process of which is as follows:
[0079] (1) Preparation of positive electrode sheet of lithium secondary battery
[0080] The positive electrode active material lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (LiNi 0.6 co 0.2 mn 0.2 o 2 ), the conductive agent Super-P, and the binder PVDF are dissolved in the solvent N-methylpyrrolidone at a mass ratio of 96:2.0:2.0 and mixed evenly to make a positive electrode slurry, and then the positive electrode slurry is evenly coated on the current collector aluminum foil , coating amount is 0.018g / cm 2 , followed by drying at 85°C, cold pressing, trimming, cutting, and stripping, and then drying at 85°C for 4 hours under vacuum conditions, welding the tabs, and making a positive electrode sheet of a lithium secondary battery that meets the requirements.
[0081] (2) Preparation of the negative electrode sheet of the lithium secondary battery
[0082] Negative...
Embodiment 2~4
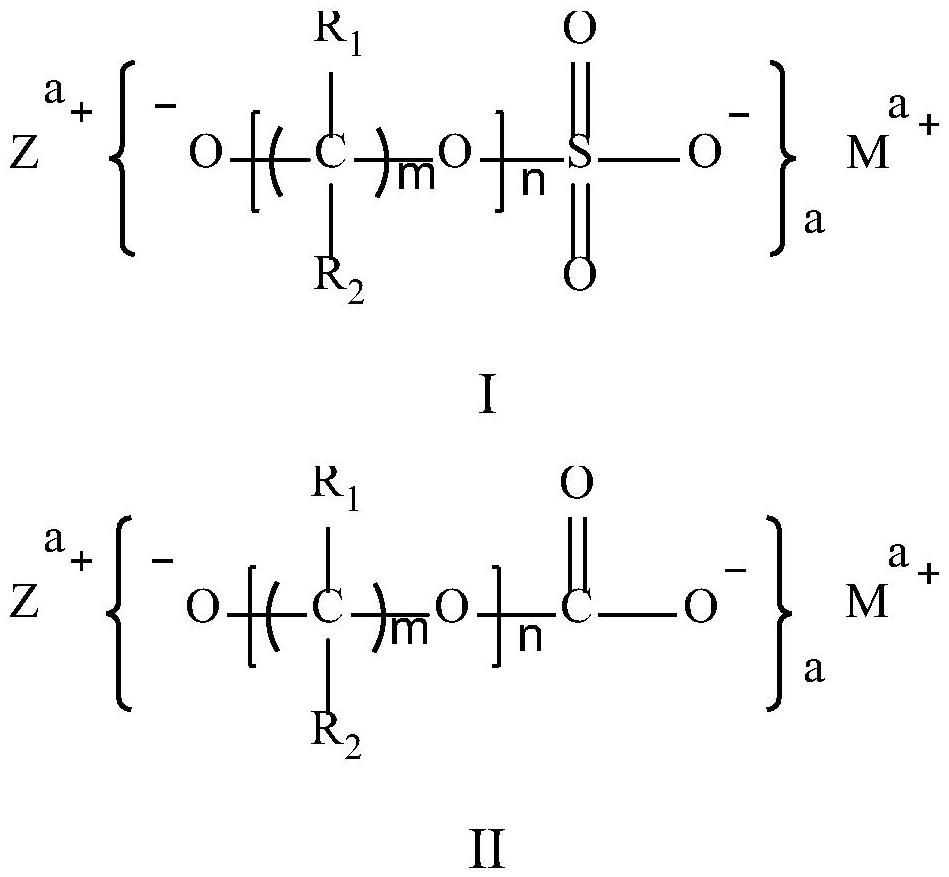
[0089] Embodiments 2 to 4 provide a lithium-ion secondary battery. The preparation method of the positive and negative plates of the lithium-ion secondary battery and the lithium-ion battery is the same as that of Example 1, and the preparation method of the electrolyte is also the same as that of Example 1, except that The difference is that in the electrolyte, the mass of lithium sulfate (I-1) containing hydroxyl lithium has different percentages in the total mass of the electrolyte.
[0090] In Example 2, the mass of lithium sulfate (I-1) containing hydroxyl lithium accounts for 0.1% of the total mass of the electrolyte.
[0091] In Example 3, the mass of lithium sulfate (I-1) containing hydroxyl lithium accounts for 0.3% of the total mass of the electrolyte.
[0092] In Example 4, the mass of lithium sulfate (I-1) containing hydroxyl lithium accounts for 1% of the total mass of the electrolyte.
Embodiment 5
[0094] Embodiment 5 provides a kind of lithium ion secondary battery, the difference with the preparation method of the lithium ion secondary battery of embodiment 1 is that the solvent is cyclic fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) and ethylene carbonate (EC) Mix with dimethyl carbonate (DMC) in mass ratio FEC:EC:DMC=3:1:2, and the rest of the steps and raw materials are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com