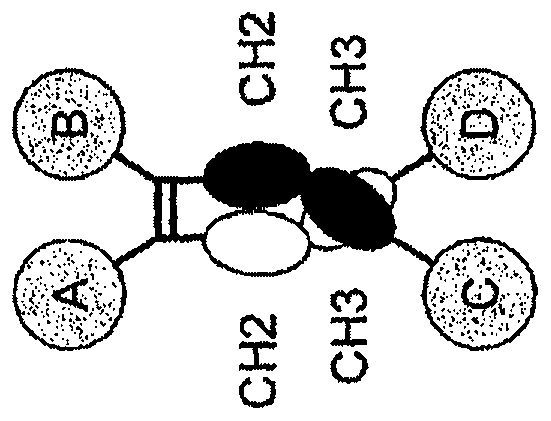
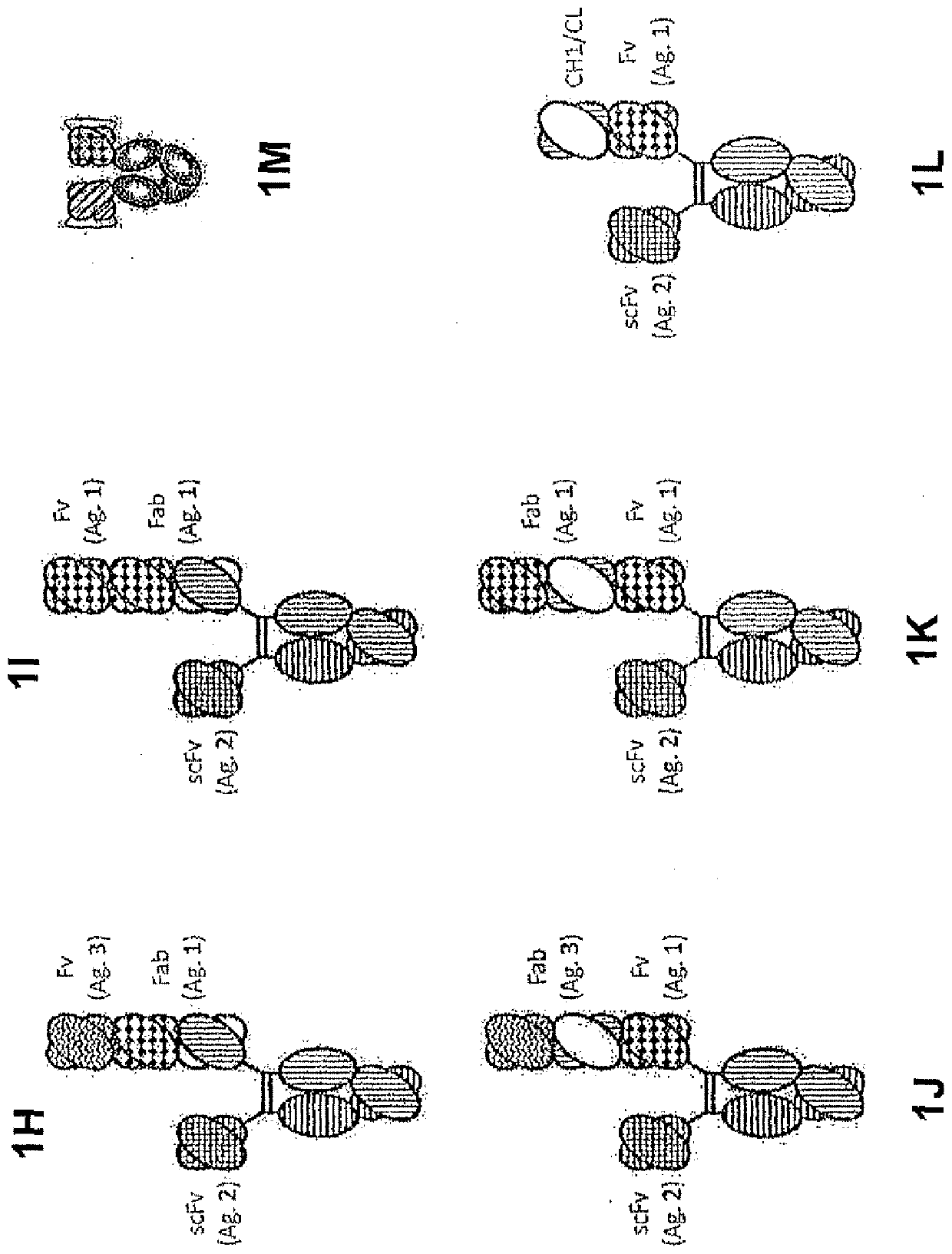
Heterodimeric proteins
A heterodimer and antibody technology, applied in the direction of immunoglobulin, hybrid immunoglobulin, antibody, etc., can solve the problems of non-specific activation and toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0380] Example 1. Design of unnatural charge displacements to reduce pI
[0381] The antibody constant chain is modified with a lower pi by engineered substitutions in the constant domain. A reduced pi can be engineered by substituting a basic amino acid (K or R) for an acidic amino acid (D or E), which results in a maximal decrease in pi. Mutations from basic to neutral amino acids and from neutral to acidic amino acids will also result in a decrease in pi. A list of amino acid pK values can be found in Table 1 of Bjellqvist et al., 1994, Electrophoresis 15:529-539.
[0382] We chose to develop substitutions in the CH1 (Cγ1) and CL (Ckappa or CK) regions of the antibody (sequences shown in Figure 13 middle) because, unlike the Fc region, they do not interact with natural ligands that affect the pharmacological properties of the antibody. In deciding which position to mutate, consideration is given to the surrounding environment and the number of contact points of the WT...
Embodiment 2
[0388] Embodiment 2. Transformation method of constant region pI transformation
[0389] Reduction of the pi of a protein or antibody can be performed in a number of ways. At the highest basic level, residues with high pKa (lysine, arginine and to some extent histidine) are replaced by neutral or negatively charged residues, and / or neutral residues are replaced by low pKa residues (aspartic acid and glutamic acid) were replaced. The particular substitution may depend on many factors, including position in structure, position in function, and immunogenicity.
[0390] Because immunogenicity is an issue, some effort can be made to minimize the risk that pI-lowering substitutions will cause immunogenicity. One way to reduce risk is to minimize the mutational load of the variant, ie, reduce the pi with the smallest number of mutations. Charge exchange mutations, in which K, R, or H are replaced by D or E, have the greatest effect on reducing pi, so these substitutions are prefer...
Embodiment 3
[0394] Example 3. Isotype light chain constant region variants
[0395] The homology between CK and Cλ is not as high as that between IgG subclasses, however the sequence and structural homology that exists is still used to guide substitutions to form the isotype low-pi light chain constant region. exist Figure 56 In , positions with residues contributing to higher pi (K, R and H) or lower pi (D and E) are highlighted in bold. Gray indicates lysine, arginine and histidine that can be replaced, preferably with aspartic acid or glutamic acid, to lower the isoelectric point. These variants, alone or in combination, can be combined independently and optionally with all other heavy chain variants in the backbone having at least one light chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com