Permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with bilateral asymmetric V-shaped magnetic poles
A permanent magnet synchronous linear and asymmetric technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., to achieve the effects of positioning force and thrust fluctuation suppression, easy batch and automated production, and good thrust characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
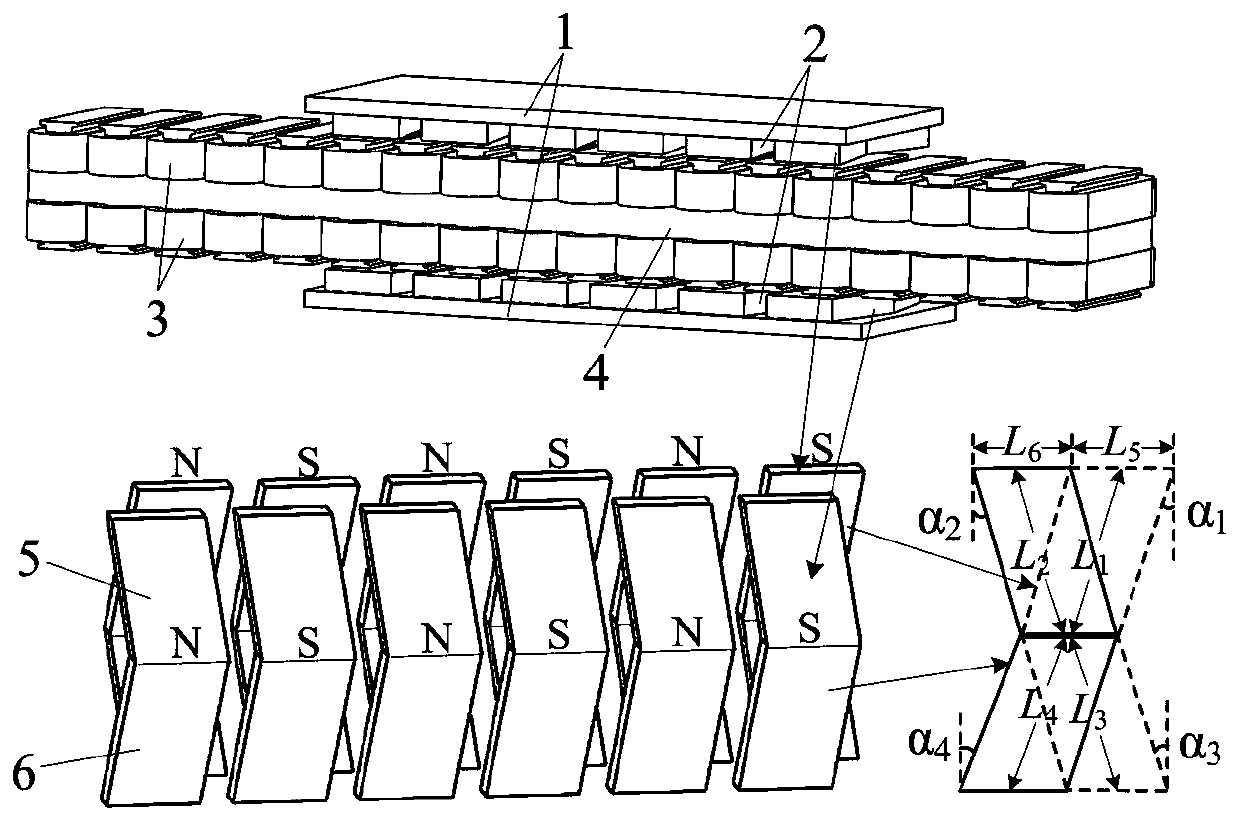
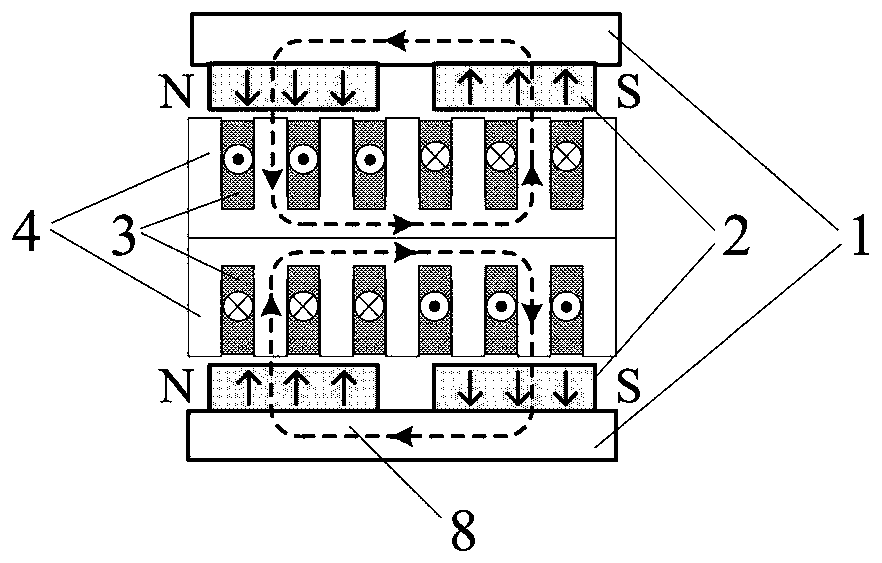
[0029] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with bilateral asymmetric V-shaped magnetic poles is composed of a secondary, a primary armature, and an air gap between the primary armature and the secondary; the bilateral secondary is located on both sides, and the primary motor pivot in the middle;
[0030] The setting secondary is composed of a flat yoke plate 1 and bilateral magnetic poles 2 arranged in parallel, and the polarity of each side of the bilateral magnetic poles 2 is N and S arranged alternately. Each side of the double-sided magnetic pole 2 is composed of multiple permanent magnets to form a V-shaped structure, and the magnetization direction of each permanent magnet of each side of the V-shaped magnetic pole is the same, and is perpendicular to the plane of the flat yoke plate.
[0031] The two-sided magnetic pole 2 is set to be mirror-symmetrical in spatial position, and the inclination directions of the permanent mag...
Embodiment 2
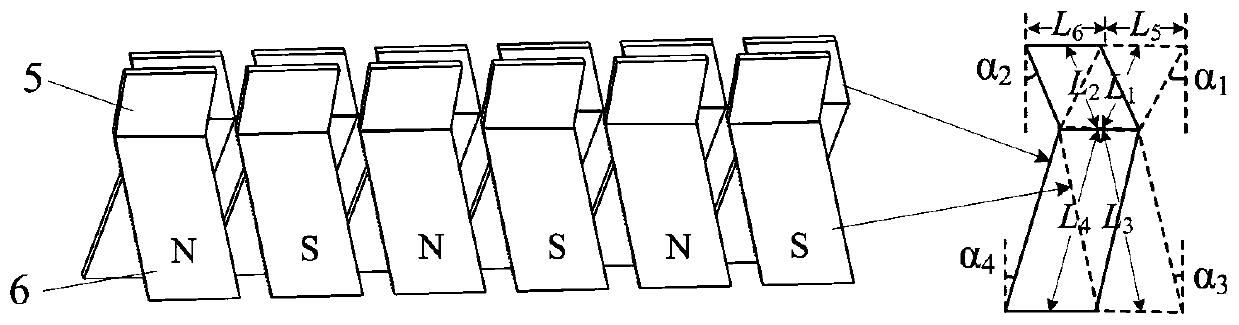
[0038] Embodiment 2: as image 3 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that in each V-shaped magnetic pole, the inclination angles of the first segment of the parallelogram permanent magnet 5 and the second segment of the permanent magnet 6 are not equal, α 1 ≠α 3 , α 2 ≠α 4 , the value range of each angle is the same as Embodiment 1; the length of the hypotenuse of the first segment permanent magnet 5 and the second segment permanent magnet 6 of the V-shaped magnetic pole is unequal L 1 ≠ L 3 , L 2 ≠ L 4 , the side length in the width direction still satisfies L 5 = L 6 .
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: as Figure 4As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that each V-shaped magnetic pole is composed of three permanent magnets, and the magnetization direction of each permanent magnet is the same, but the inclination angle is different. The permanent magnet 7 in the middle section has no inclination angle, and the inclination angles of the first permanent magnet 5 and the second permanent magnet 6 need to satisfy: α 1 = α 3 = α 2 = α 4 . The side lengths of the first permanent magnet 5 and the second permanent magnet 6 satisfy L 1 = L 2 = L 3 = L 4 , L 6 = L 7 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com